Volume 16 - Special Issue on Cognitive Sciences
BCN 2025, 16 - Special Issue on Cognitive Sciences: 159-178 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Najafi-Dehjalali R, Dadashi M, Hassani Abharian P, Farahani H, Faridi A R. Bibliometric Analysis of Craving in Drug and Behavioral Addiction During the Last Decade. BCN 2025; 16 (S1) :159-178
URL: http://bcn.iums.ac.ir/article-1-2769-en.html
URL: http://bcn.iums.ac.ir/article-1-2769-en.html
Roghayeh Najafi-Dehjalali1 

 , Mohsen Dadashi2
, Mohsen Dadashi2 

 , Peyman Hassani Abharian *3
, Peyman Hassani Abharian *3 

 , Hojjatullah Farahani4
, Hojjatullah Farahani4 

 , Ali Reza Faridi1
, Ali Reza Faridi1 




 , Mohsen Dadashi2
, Mohsen Dadashi2 

 , Peyman Hassani Abharian *3
, Peyman Hassani Abharian *3 

 , Hojjatullah Farahani4
, Hojjatullah Farahani4 

 , Ali Reza Faridi1
, Ali Reza Faridi1 


1- Department of Addiction Studies, School of Medicine, Zanjan University of Medical Sciences, Zanjan, Iran.
2- Department of Clinical Psychology, Faculty of Medicine, Zanjan University of Medical Sciences, Zanjan, Iran.
3- Department of Cognitive Psychology and Rehabilitation, Institute for Cognitive Science Studies (IRICSS), Tehran, Iran.
4- Department of Psychology, Faculty of Humanities, Tarbit Modares University, Tehran, Iran.
2- Department of Clinical Psychology, Faculty of Medicine, Zanjan University of Medical Sciences, Zanjan, Iran.
3- Department of Cognitive Psychology and Rehabilitation, Institute for Cognitive Science Studies (IRICSS), Tehran, Iran.
4- Department of Psychology, Faculty of Humanities, Tarbit Modares University, Tehran, Iran.
Full-Text [PDF 4011 kb]
| Abstract (HTML)
Full-Text:
1. Introduction
Addiction is a chronic relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking, loss of control, and developing a negative emotional state (such as negative affect, anxiety, and irritability) when the substance is unavailable (Gay et al., 2022). Drug addiction and addictive behaviors pose global health challenges, cognitive functions, emotional responses, and cravings (Perrotta & Perri, 2022). Over the past two decades, many problematic or extreme behaviors have increasingly been categorized as addictions due to their resemblance to traditional psychoactive drug addiction (Gomez et al., 2022). During the 18th and 19th centuries, at the onset of the scientific revolution, psychiatrists such as Pinel, Rush, Kripplin, Bleuler, and Freud presented clinical observations suggesting that biological factors also contribute to the addiction process (Nathan et al., 2016). Following World War II, both diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM)-I and DSM-II, influenced by psychodynamic theories, emphasized these theories to explain the process of addiction. However, it was with the development of DSM-III that a clear theoretical stance on addiction was explicitly taken. Subsequent editions, such as DSM-IV and DSM-V, have adopted a biological perspective on the addiction process. DSM-V, in particular, references a growing body of empirical research that implicates specific brain mechanisms in addiction and provides a clear framework in this context (Nathan et al., 2016). The most recent iteration, DSM-V, defines "non-substance-related disorders" as addictive disorders that do not involve the use of psychoactive substances (Gay et al., 2022). It also places substance use disorder on a continuum ranging from mild to severe (Perry & Cornish, 2022b). A prominent characteristic of substance use disorder is relapse, often triggered by craving—an intensely subjective experience of the desire to consume (Venniro et al., 2021).
Craving represents a common symptom in individuals with drug use disorders and is observed in cases of dependence on substances such as alcohol, nicotine, cannabis, cocaine, and other psychoactive substances (Zheng et al., 2021). In the DSM-V, craving is recognized as a dynamic phenomenon (Venniro et al., 2021), and it occupies a central role in both addiction research and treatment. This concept, which has historical mentions dating back to ancient times, possesses a lengthy and somewhat intricate history (Ekendahl & Karlsson, 2022). Over the past four decades, around 10000 articles have been dedicated to exploring this subject (Sayette et al., 2000). However, akin to other addiction-related concepts, craving lacks a standard, universally accepted definition, and the definition of this construct has faced many challenges (Ekendahl & Karlsson, 2022). Furthermore, controversies abound regarding the definition, measurement, function, neural underpinnings, and practical utility of craving in understanding the processes underlying addiction (Sayette et al., 2000). Notably, craving stands out as a significant risk factor for relapse and represents a crucial target for treatment interventions (Lambert et al., 2022).
Craving is defined as an "intensive desire" or "urge" to consume a substance or engage in a particular behavior. In the context of drug addiction, craving serves as a predictive factor for substance-seeking behavior and relapse following a period of abstinence (Song et al., 2019). The act of returning to drug consumption, commonly referred to as relapse, represents a substantial obstacle to effective treatment. Relapse is frequently triggered by various factors, including re-exposure to substances, the recurrence of symptoms associated with prior substance use, or exposure to stressors (Perry & Cornish, 2022a).
According to the elaborated intrusion theory of desire, craving is an intense desire for "cognitive events laden with affection, in which a pleasurable or relaxing object or activity becomes the focal point of attention." This model suggests five categories of stimuli that can trigger craving, encompassing external cues (such as an advertisement), the anticipation of a response (e.g. stress), associated thoughts (for instance, thinking about someone with whom one frequently engages in gambling or drinking), negative affection (including depressed mood), and physiological symptoms (like withdrawal symptoms) (Cornil et al., 2021). In a study by Limbrick-Oldfield et al. (2017), it was demonstrated that craving exhibits a negative correlation with the duration of the abstinence period. As the length of abstinence increases, the craving induced by gambling symptoms decreases (Limbrick-Oldfield et al., 2017). Recent neuroimaging research has revealed the significant role of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, among other brain regions, in craving. The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex is implicated in reward processing, motivation, and decision-making. Its circuits provide the foundation for integrating pertinent cognitive and motivational information and exercising inhibitory control over tempting options that promise immediate reward (Rezvanian et al., 2022). In cognitive neuroscience, the predominant approach to investigating the neural responses related to craving is examining the response pattern to the cues (de Lara & Perales, 2020).
In contrast to paradigms for studying addictive behavior, the primary advantage of the cue-based response approach is its solid grounding in general behavioral theories, which has been widely studied (Drummond, 2000). The craving field has witnessed numerous studies exploring existing theories and methodologies, some of which employ systematic review methods while others utilize alternative review approaches. In a review study, the response to cues and relapse were identified as pivotal constructs that have been integrated into various theoretical models of behavioral addictions. This article comprehensively reviews theoretical assumptions and experimental investigations emphasizing the relationship between cue responses and craving at multiple levels, including the cognitive, physiological, environmental, and neurological dimensions, to comprehend and sustain specific behavioral addictions (Wegmann & Brand, 2018).
Another review study underscored the substantial body of literature implicating the influence of negative affect and cravings in the recurrence of addictive disorders. Nearly 90% of the studies analyzed in this systematic review demonstrated a positive correlation between negative affections and cravings. This meta-analysis, along with the reported studies, underscores the significance of negative affection as a critical component of craving, albeit with individual variations in response (to craving) (Cyr et al., 2022).
Various review studies have delved into the subject of drug addiction and its impact on individuals with addiction disorders. Classic review studies, through their comprehensive examination of the existing literature, have played a crucial role in identifying research gaps and providing a comprehensive overview of this field. The body of knowledge in this domain continues to expand (Figure 1).
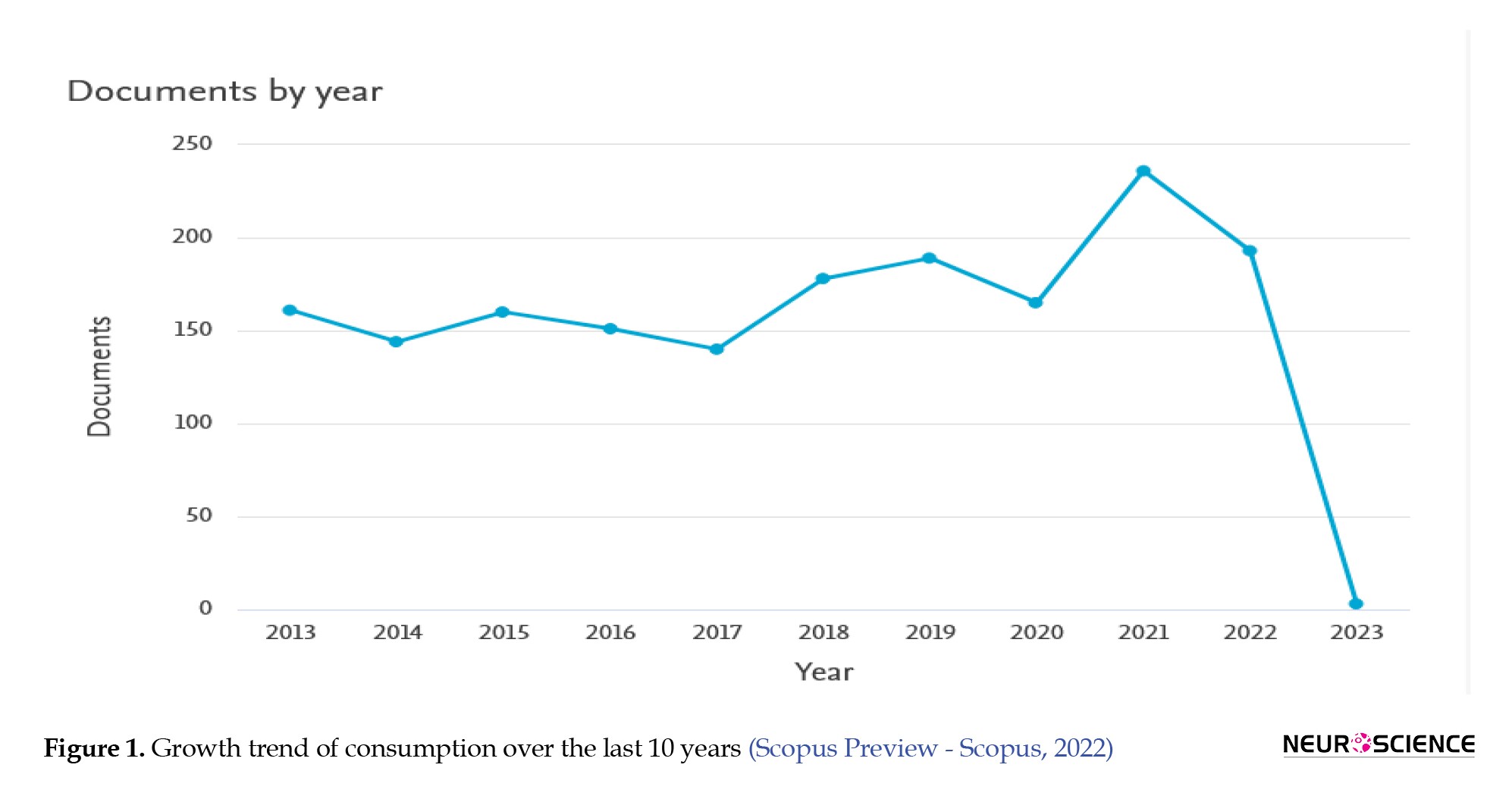
Consequently, bibliometric research is one of the essential study types required to keep pace with this growing body of knowledge. Although in its early stages, bibliometrics grapples with functional analysis, document network analysis, content analysis of publications, and scientific documents available within citation databases across various knowledge domains (Moradi & Miralmasi, 2022). With the burgeoning and widespread knowledge related to carving across various scientific disciplines (Figure 2), many traditional review techniques struggle to summarize literature due to their descriptive nature. As understanding of craving accumulates and knowledge growth in this area remains upward, researchers increasingly turn to bibliographic reviews to map the landscape of existing studies.
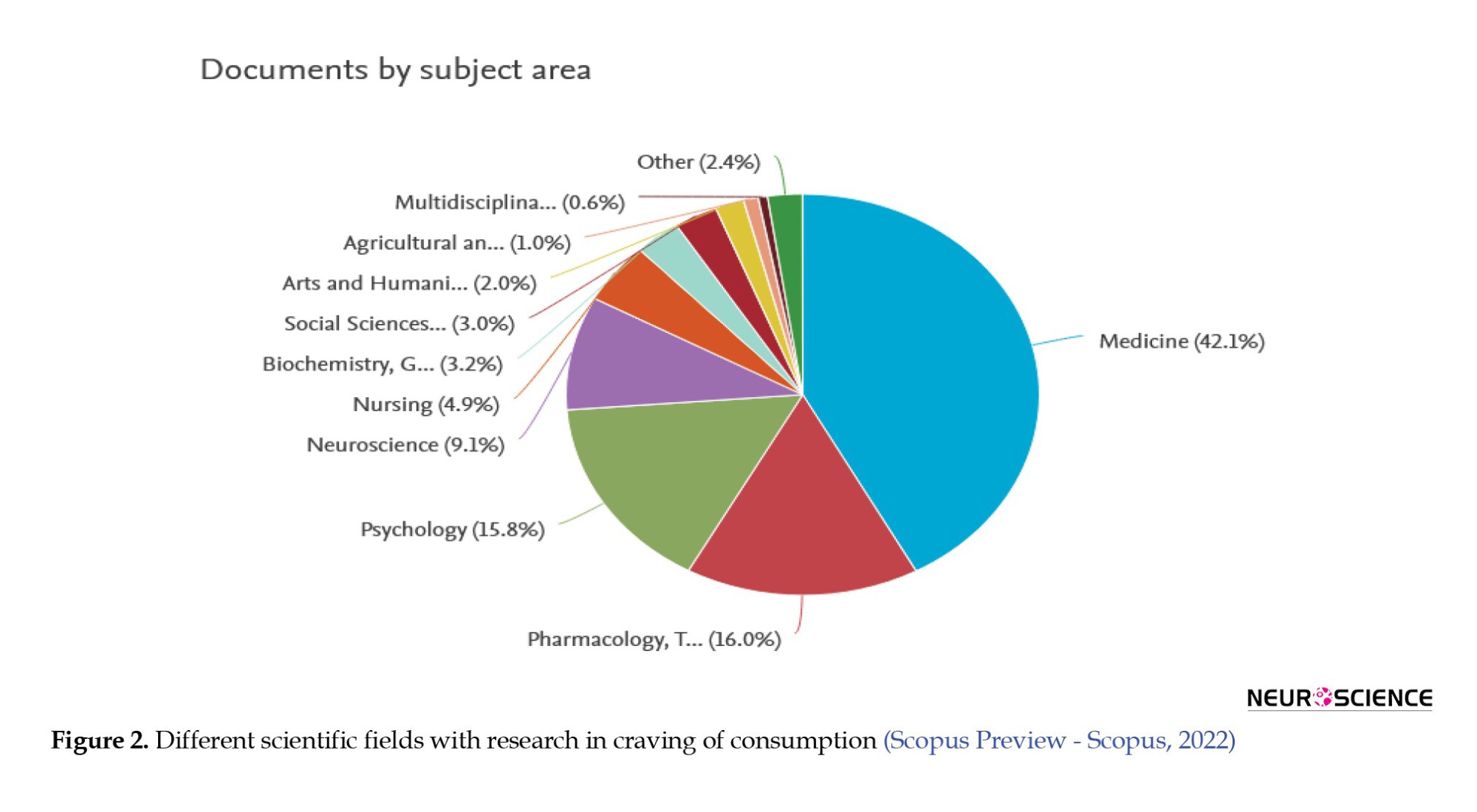
They intend to shed light on the factors driving this growth and the areas where further research is needed. Given the critical role of craving in the processes of relapse and the treatment of addictive disorders, this study seeks to address the following objectives:
1. Examining and visually representing the structure of keywords prevalent in published articles within this field,
2. Analyzing the co-authorship network of researchers involved in published articles focused on craving,
3. Identifying authors who influence the co-authorship network based on citation network analysis indicators, and
4. Determining the authors, countries, or institutions that have contributed the most research documents in this field or have had the most substantial impact.
Furthermore, no comprehensive study centered around this keyword has ever been conducted. Given the significance of scientific indices associated with this keyword, the findings of this research are expected to offer valuable insights for addiction research, addiction treatment strategies, understanding the factors influencing relapse, and efforts to prevent relapse and reinitiate substance consumption.
2. Research Methodology
A review is a research methodology designed to systematically and methodically investigate the background of a research topic. Its purpose is to discover, describe, integrate, explain, or critique patterns, relationships, and trends within a body of knowledge that may not be readily discerned through primary studies and first-rate sources (Shahsavari & Alamolhoda, 2019). The increasing accessibility to digital data within scientific inputs and outputs has opened unprecedented opportunities to explore the structure and evolution of science (Uzzi et al., 2018). Scientometrics, situated at the intersection of science and data analysis, offers a systematic approach to unraveling scientific fields' past, present, and future directions. It has always been central to the research community because it empowers researchers with a deeper understanding of their specialized fields and identities. Scientometrics studies play a pivotal role in raising awareness, informing, and educating both internal and external stakeholders about emerging disciplines while suggesting potential corrective actions to steer research in the desired direction (Serenko, 2021). The scientific literature spans various disciplines, primarily neuroscience, psychiatry, and addiction journals. interestingly, few publications account for most citations (Zurián et al., 2021). However, previous research findings have indicated that most publications in the Social Sciences, including addiction research, tend to appear in the Scopus database after being indexed by the Google Scholar search engine (Martín-Martín et al., 2021). Given the research problem and nature of the literature review, researchers need to employ a common language that resonates with their peers. This common language aligns with the philosophical underpinnings of scientific research and guides how research is conducted (Park et al., 2020). Paradigms, in essence, encapsulate researchers' beliefs and values about the world. Consequently, paradigms have far-reaching implications for every decision made throughout the research process (Kamal, 2019).
In broad terms, paradigms encompass two primary research approaches: Quantitative and qualitative. Quantitative research involves measuring variables applied to a specific phenomenon and is often employed to test existing theories. In this study, the researcher has adopted a quantitative paradigm consistent with this approach (Park et al., 2020). In line with this paradigm, the researcher must employ specific research strategies, commencing with a search strategy that aids in organizing thoughts before searching. This search strategy, rooted in the comparative perspective of the quantitative approach, involves formulating a bibliographic research plan or strategy that consists of six core steps (Figure 3).

The first phase involves selecting the scope of the problem and research inquiry. Drawing from the literature covered in Section 1, collected by searching "publish or perish" (Harzing, 2010), it becomes evident that the escalating number of articles in the field of addiction necessitates validation. This validation effort extends to understanding the factors that fuel and sustain this proliferation, notably the intricate structure of craving. As a result, the researcher embarks on a mission to distill this knowledge's essence and forecast future research trends.
In the second step and following Snyder (2019), the researcher devises research objectives that fall into functional objectives and creating a scientific roadmap (Moradi & Miralmasi, 2020). These objectives are as follows:
1. Identifying the most influential author within the field of craving.
2. Identifying the most influential publication within the field of craving.
3. Identifying the most influential institute or university contributing to research on craving.
4. Identifying the most influential country with a substantial impact on the field of craving.
5. Identifying the most influential article within the domain of craving research
In addition, the objectives of citation network analysis are as follows:
1. Identifying the most impactful co-citation patterns within the realm of craving research.
2. Identifying the most impactful co-authorship patterns evident in craving research.
3. Identifying the most impactful co-lexical patterns within the field of craving.
4. Identifying the most impactful concurrent patterns prevalent in craving research
In the third step, the research aims to access valid citation data about cravings from top-tier citation databases and search engines. Although various studies have explored the coverage and accuracy of these databases (Martín-Martín et al., 2021), the significance of bibliographic databases has grown substantially in recent times. They serve as primary sources for publication metadata and universally accepted bibliometric indicators used in research evaluation (Pranckutė, 2021).
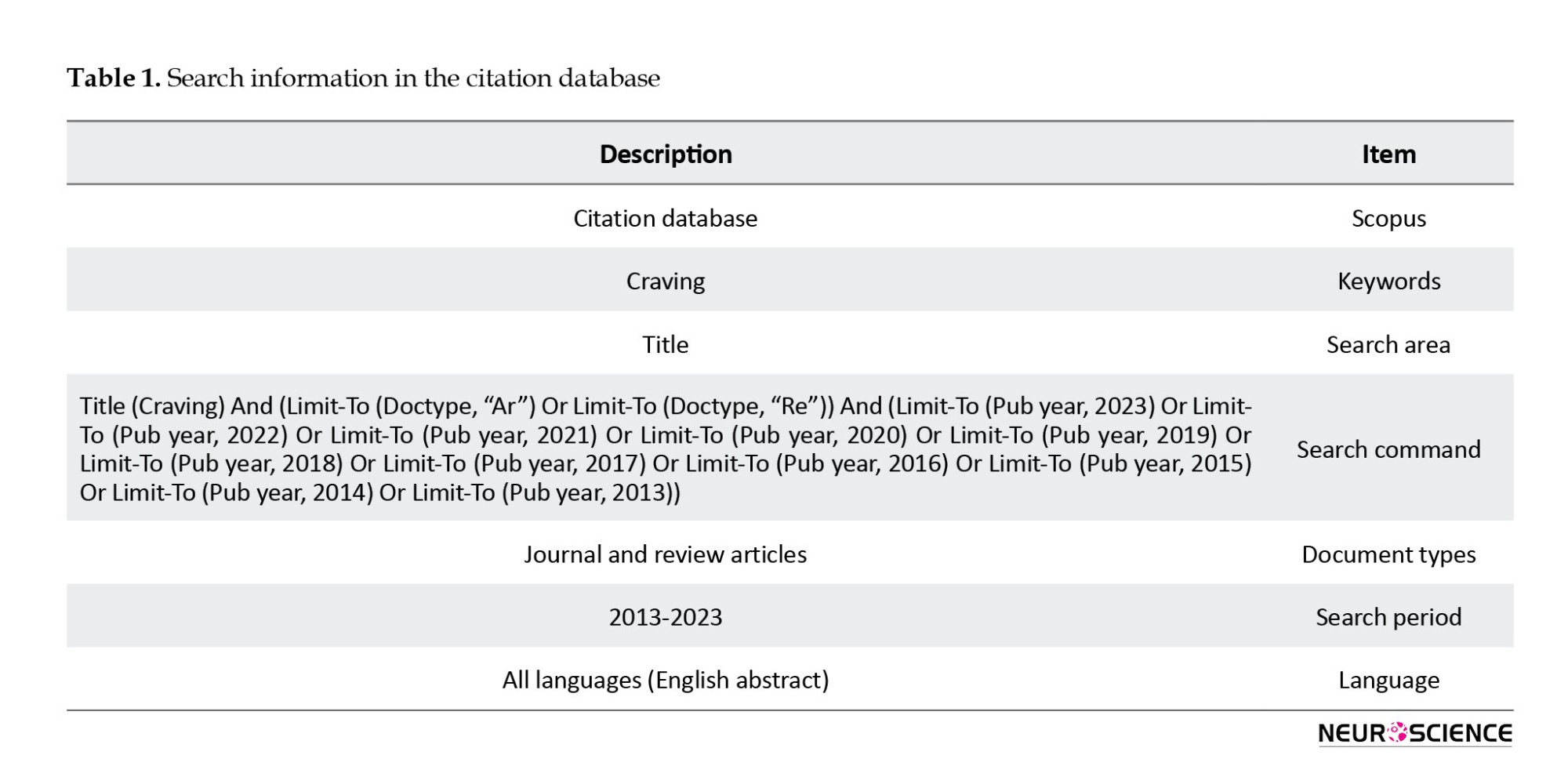
Scientometric research heavily relies on large-scale citation databases and journal articles (Thelwall & Sud, 2022). Within the Scopus database, the number of distinct journals has increased exponentially, underlining the importance of highly cited articles for researchers and editors (Yaminfirooz & Ardali, 2018). Considering the prevalence of humanities studies within the Scopus citation database and its precision and accuracy in citation data, the researchers selected the Scopus reference database. A well-defined policy and strategy were established to achieve a comprehensive repository of documentary information. Management organization tools like Mendeley and its extensions were employed to identify and establish concepts related to this research structure. Subsequently, a systematic search process was carried out involving synonyms, binary operators, and quotation marks. The data extracted from this search were inputted into the Mendeley data management software. A rigorous pre-processing step was conducted, eliminating low-value and extraneous data. Data lacking English abstracts, author names, or other essential citation attributes were excluded from the analysis. Moreover, materials such as books, letters to the editor, web pages, and seminar articles are disregarded. The remaining results are then summarized and subjected to detailed analysis. The instructions for this search are outlined in Table 1.
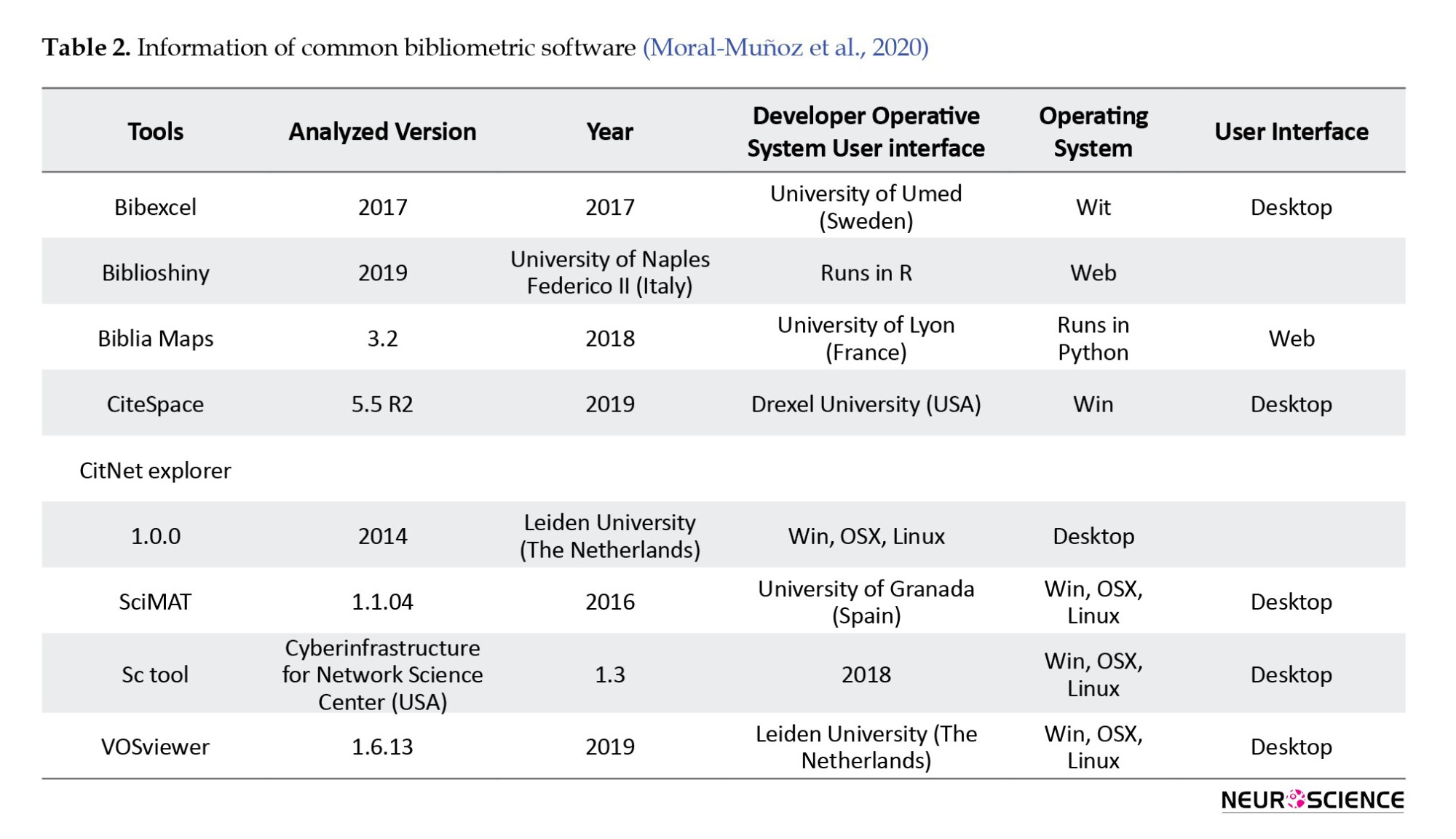
The fourth step is to choose the right software for bibliometric data analysis. The researcher has selected and acquired proficiency in the following software tools for conducting the specified operations. This decision was influenced by recent technological advancements and the emergence of various websites and software applications that offer diverse approaches to fulfilling descriptive objectives and conducting citation network analysis. It is worth noting that these tools have gained recognition and endorsement from reputable academic organizations and institutions (Table 2).
The software applications in this field are as follows:
Publish, or Perish software, which was created by Professor Harzing in 2008 to gather citation data from search engines. The current version is version 8, compatible with Windows 64-bit (Harzing, 2010).
Mendeley software organizes and manages research resources. The version currently used is 1.98, designed for 64-bit Windows (Scipous, 2022).
To adhere to preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) protocol criteria, tasks such as identifying duplicate research are performed using Microsoft Excel for data analysis and visualization.
VOSviewer software was developed by Leiden University in the Netherlands. It offers researchers exceptionally high-quality network analysis and visualization capabilities. This research used version 1.6.18 of the software on a 64-bit Windows system (Van Eck & Waltman, 2010).
In this research, the initial step involved the installation of R Software, version 4.2. Subsequently, R Studio macros from the free, non-commercial version of 2022 were added to R. Finally, an HTML-based bibliometric software package was installed to facilitate comprehensive functional information and network analysis. This software package was developed by the RStudio Team based in Boston, MA, USA (RStudio Team, 2022).
The fifth step comprises collecting information, screening, and extracting the information. Based on the research, it was found that there were 14615 documents related to the keyword craving in the Scopus citation database. Due to the high frequency of this phrase in the keywords and abstracts of scientific documents, the researcher limited the review to studies that exclusively included the keyword "craving" in their titles. Consequently, 3407 scientific documents remained for analysis. Two stages of data screening and cleaning were conducted. The first stage occurred in citation databases, where the researcher filtered and removed irrelevant data. In the second stage, involving the remaining 3407 studies from the previous phase, the researcher re-screened the data using a standard screening protocol such as PRISMA (Page et al., 2021), updated in 2020.
3. Results
The researcher conducted descriptive and network analysis in the sixth step of the research methodology (Moradi & Miralmasi, 2020).
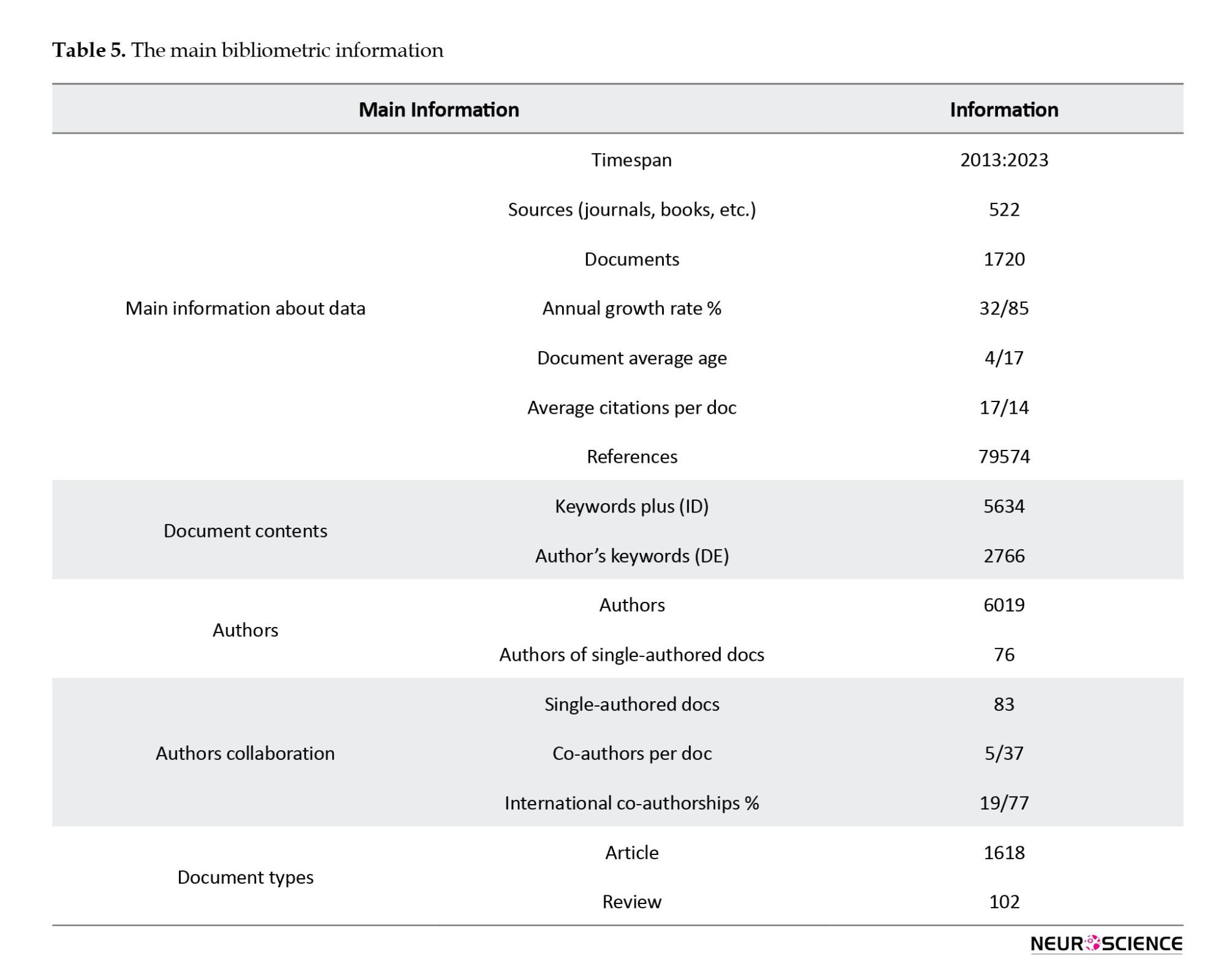
In this research, 1720 scientific documents, comprising both primary research articles and review articles, were examined. These articles were authored by 6019 authors and published through 522 sources.
Functional analysis of documents and authors
The definition of authorship in scientific articles and documents is a necessary and intricate procedure largely reliant on informal arrangements. An author of a scientific document or a group of co-authors consists of individuals who have contributed substantially to the study (Albarracín et al., 2020). Citing an author aims to alert researchers to previously published works related to the topic. Nonetheless, research indicates that articles with multiple authors receive more citations than single-authored articles (Yaminfirooz & Ardali, 2018).
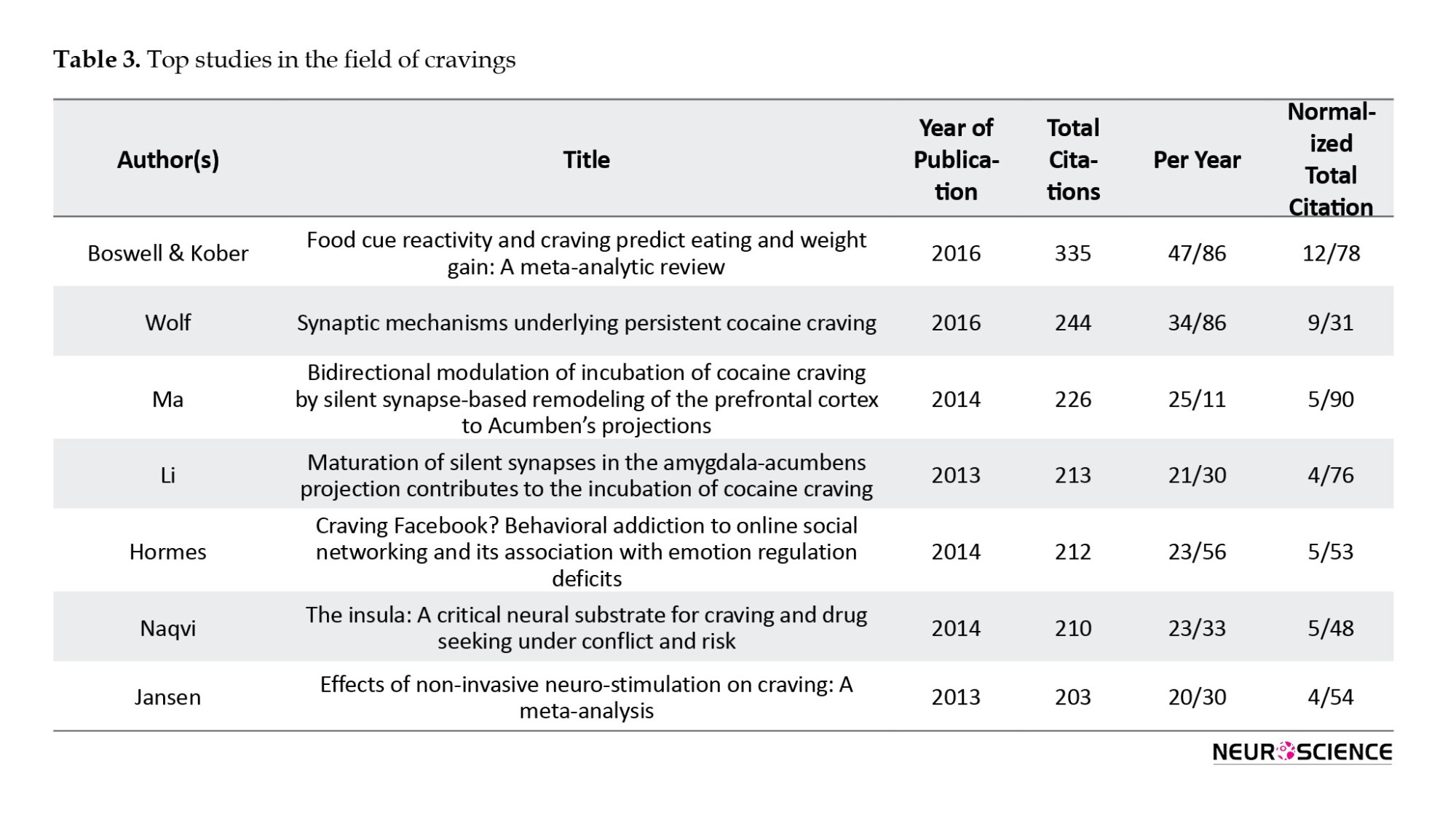
As evident in Table 3, Boswell's (2016) meta-analysis study, titled "predicting weight gain through response to food cues and food cravings," has garnered 355 citations (Boswell & Kober, 2016). Another study from 2016, titled "synaptic mechanisms underlying persistent cocaine craving," delves into the challenges faced by individuals with cocaine addiction in achieving abstinence. It emphasizes that the primary issue is not the initial use but the subsequent avoidance of cocaine. This animal study suggests that craving for cocaine during the abstinence period is attributable to neural plasticity in the reward circuitry, which sustains elevated levels of craving. Furthermore, this research highlights the potential of craving studies to identify new therapeutic targets and enhance our comprehension of experience-dependent neural plasticity in the brains of adults under normal conditions and in the context of addiction (Wolf, 2016).
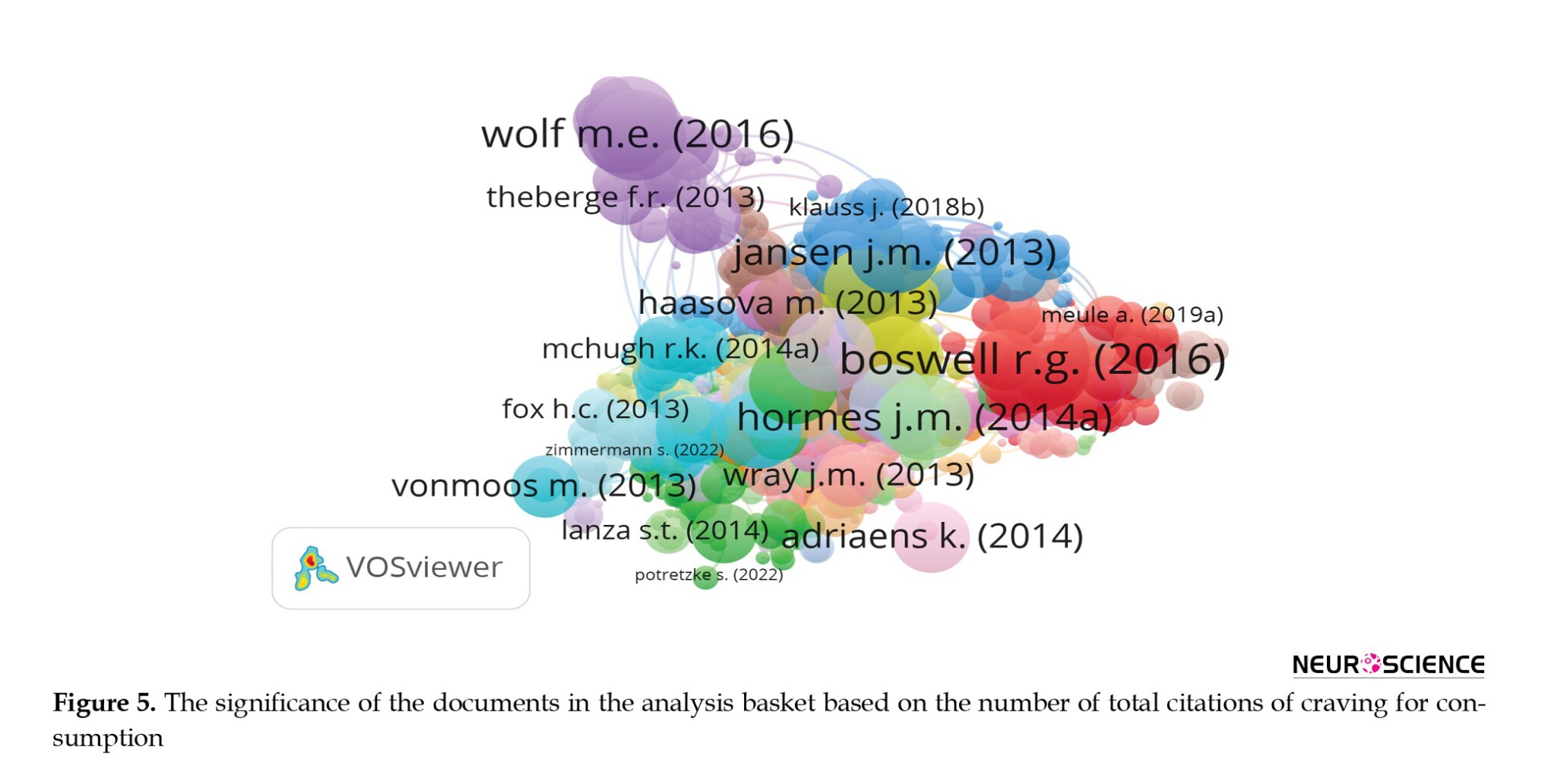
The information analysis in VOSviewer software assigns greater weight to authors in the field of craving who have received more citations. Consequently, the names of these highly cited authors are displayed in a larger font size. Based on this analysis, it is evident that Boswell (2016)” and “Wolf, (2016)” are the most prominent and influential authors in the field of craving, as they have garnered a significant number of citations and recognition within the research community.
As shown in Table 4, Li X stands out as the most prolific contributor in the field of desire, having authored 40 scientific documents in the last ten years. Following Li X, Sinhar and Shahami Harik ranked second with 25 scientific documents. However, it is noteworthy that none of these authors have produced highly cited or heavily referenced works. This outcome underscores that the quantity of scientific documents produced does not necessarily reflect their quality.

Functional analysis of publications, organizations
Effective research policies provide the essential framework for guiding research management within higher education institutions and study programs (De La Cruz Vargas, 2019). These strategies should encompass the promotion of research, enhancement of research infrastructure, financial support for research endeavors, and training researchers to produce high-quality work. Such knowledge dissemination not only enhances the reputation of institutions through their scientific output but also positions universities as leaders and generators of new knowledge. Consequently, they are recognized as dedicated contributors to research and innovation, ultimately fostering the development of their respective countries (Millones-Gómez et al., 2021). In light of the information presented in Table 5, which outlines the key bibliometric details, it is evident that 522 publications have contributed to disseminating the 1720 scientific documents in this study.
Also, Table 6 presents the journals with the highest scientific output in consumer participation.
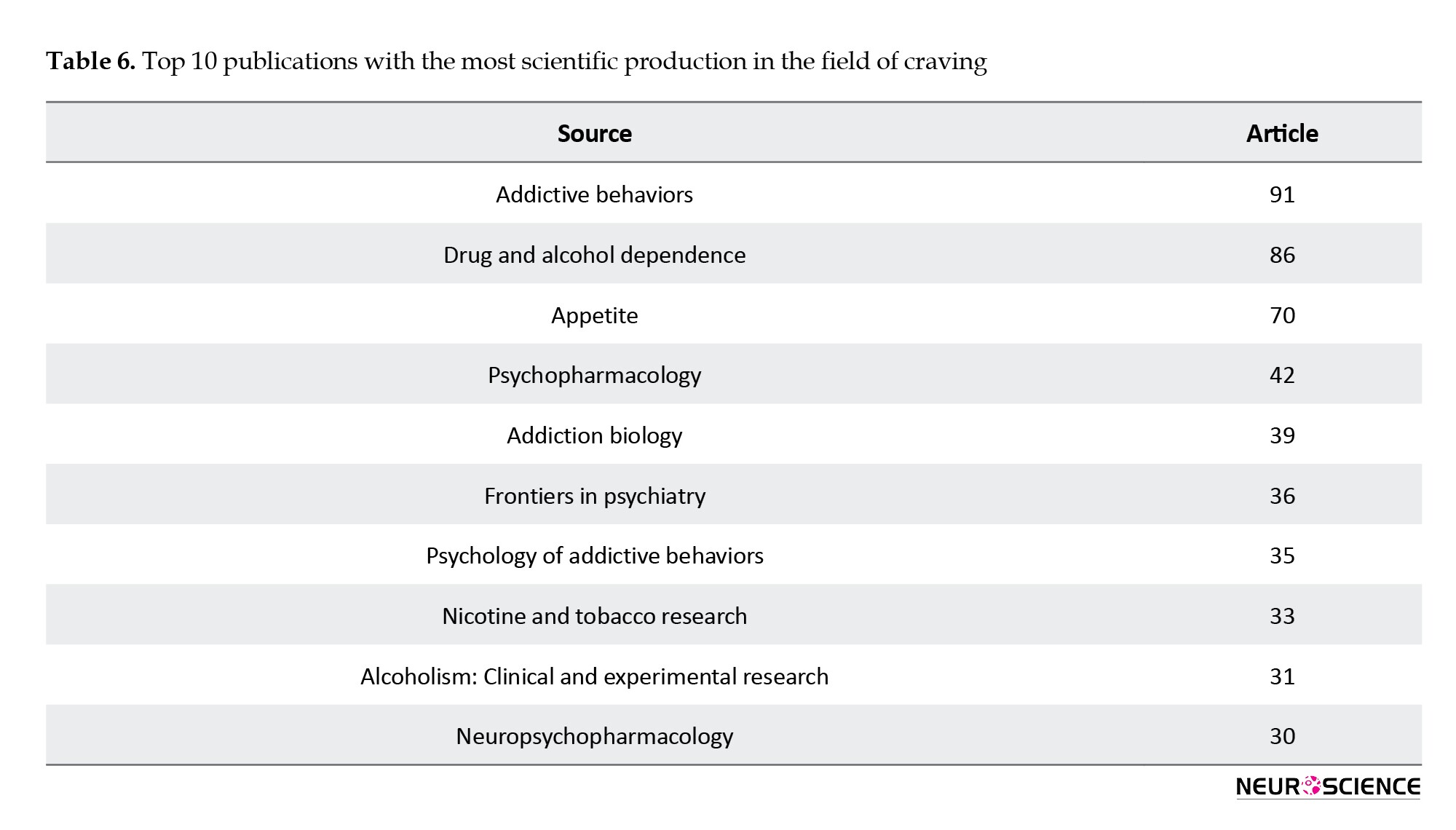
Journals often employ expert reviews to sift through and select the best articles for publication (Candel & Naccache, 2021). Addictive Behaviors is an international journal with a site score 6.7 and an impressive impact factor of 4.591.
Since its inception in 1975, this journal has been dedicated to publishing high-quality human research concerning addictive behaviors and disorders, as well as behavioral addictions, which encompass areas such as gambling and technology. Its primary focus lies in disseminating behavioral and psychosocial research. On the other hand, The journal of drug and alcohol dependence is an international journal that employs biomedical and psychological approaches. It holds a site score of 1.6 and an impact factor of 4.852. This journal serves as a platform for the publication of original research, scientific reviews, commentaries, and policy analyses, all within the domain of drug, alcohol, and tobacco consumption and addiction (Drug & Alcohol Dependence,1976).
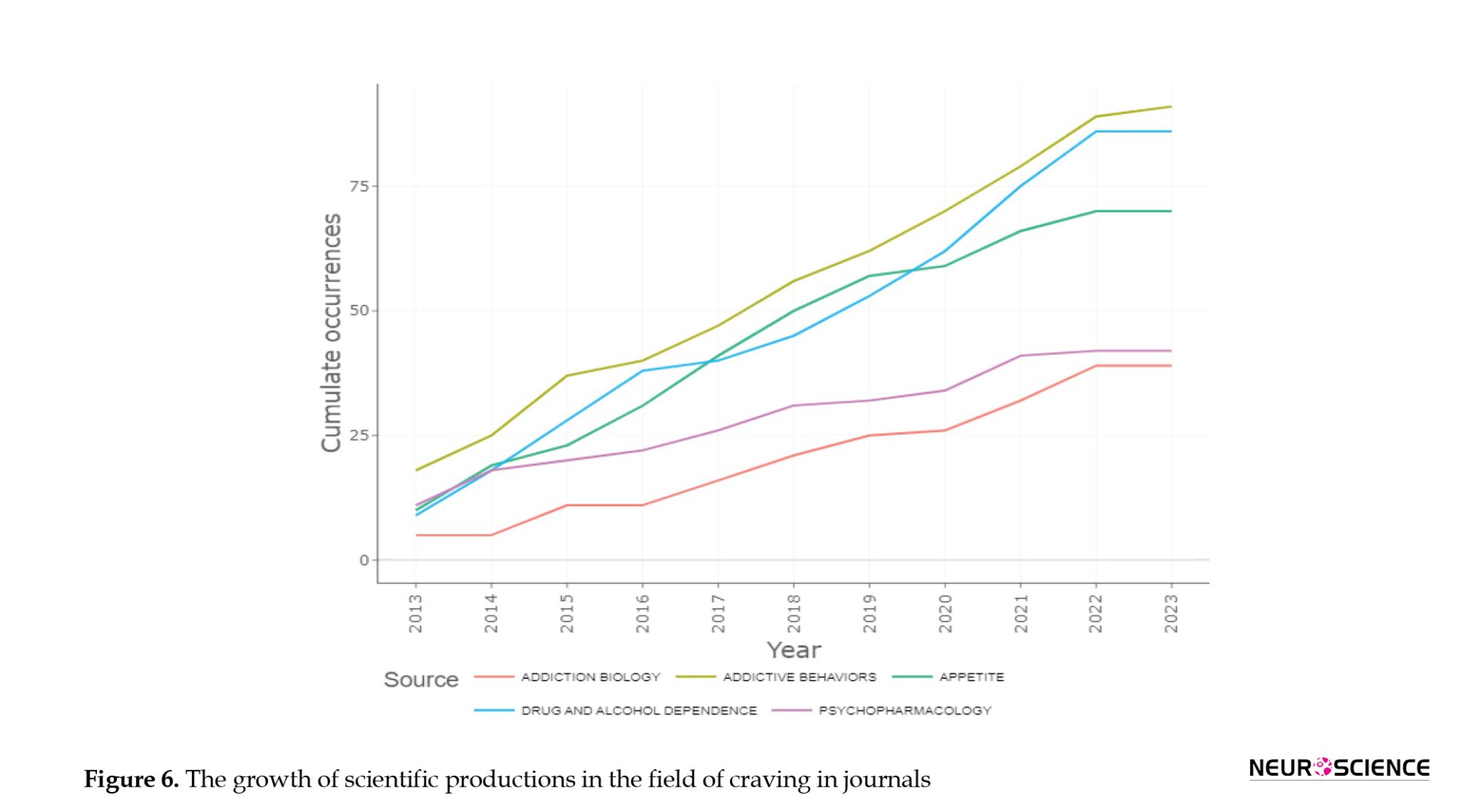
An analysis of publications from the top five journals in the field of drug consumption reveals a noticeable increase in the number of scientific documents being published in this area.
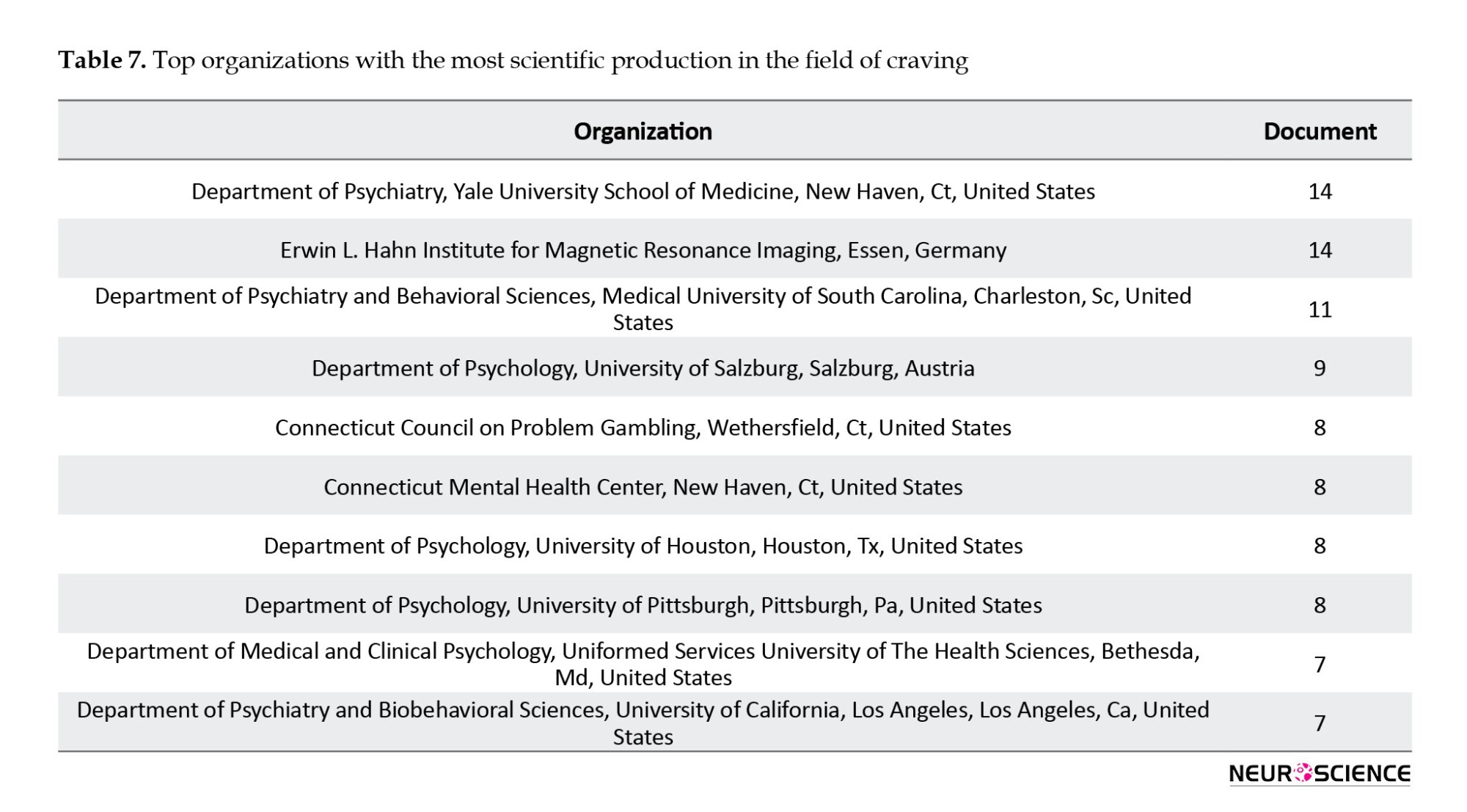
Table 7 and Figure 7 show that the Department of Psychiatry at Yale University School of Medicine in New Haven, CT, USA, has produced the highest number of scientific publications on addiction. Following closely is the Erwin L. Hahn Magnetic Resonance Imaging Institute in Essen, Germany. These two institutions, each having contributed 14 published scientific documents, collectively account for nearly 40% of the world’s scientific productions in craving.

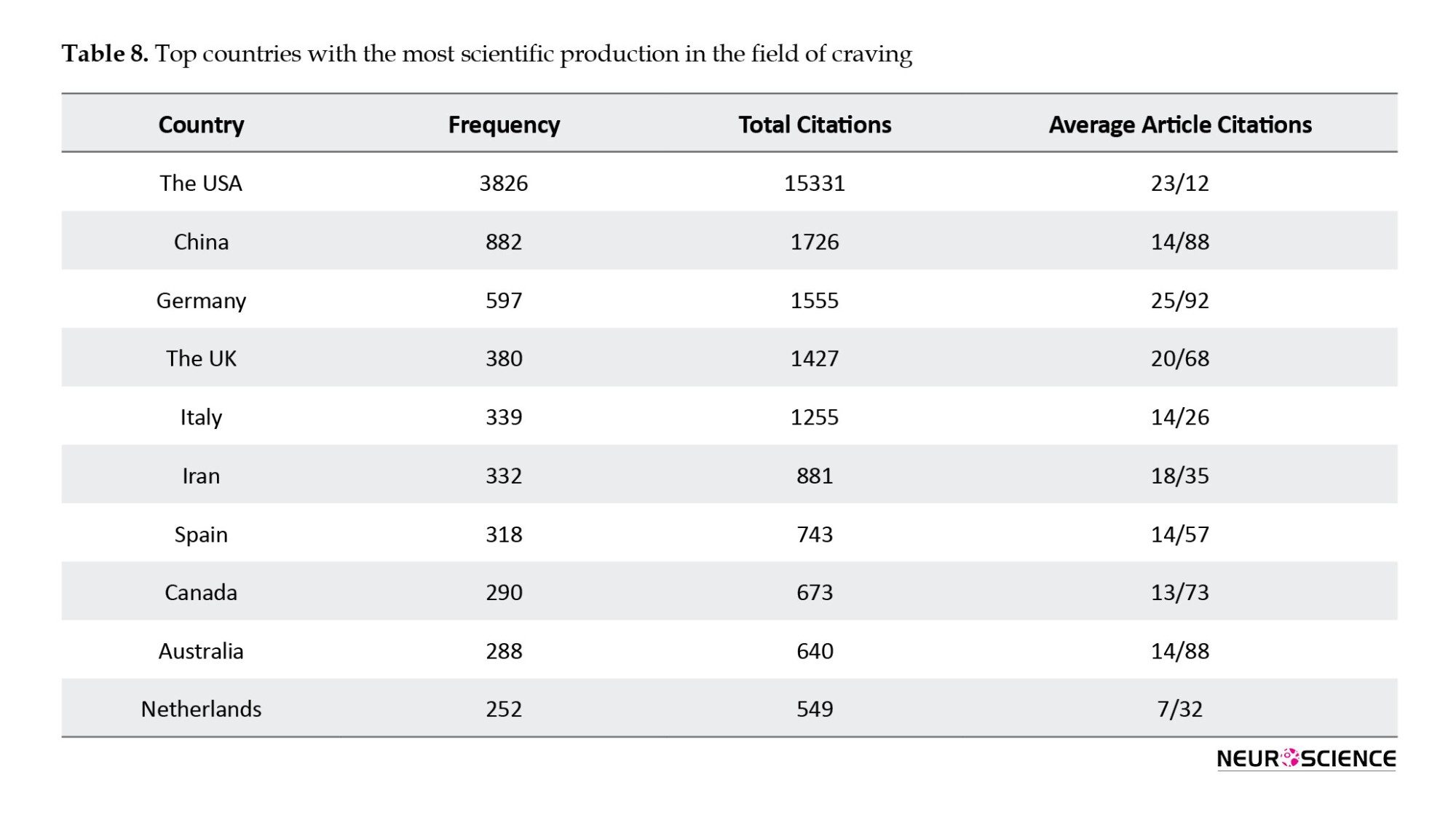
Functional analysis of countries
Among countries, the United States, China, Germany, Italy, and England emerged as the main contributors to scientific productions in the field of craving. The United States significantly outpaces other countries in terms of the quantity of scientific products and the number of references made to these scientific documents.
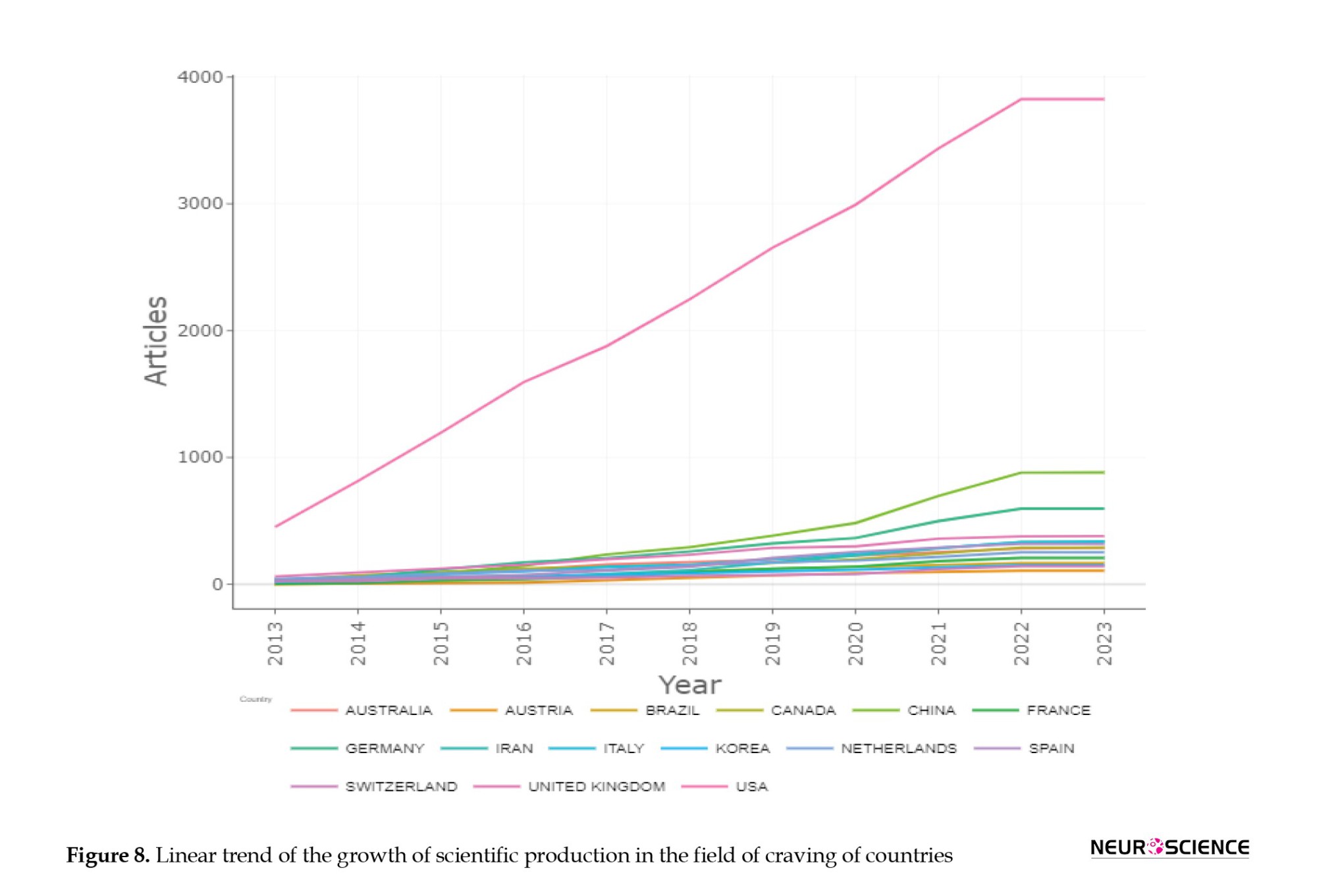
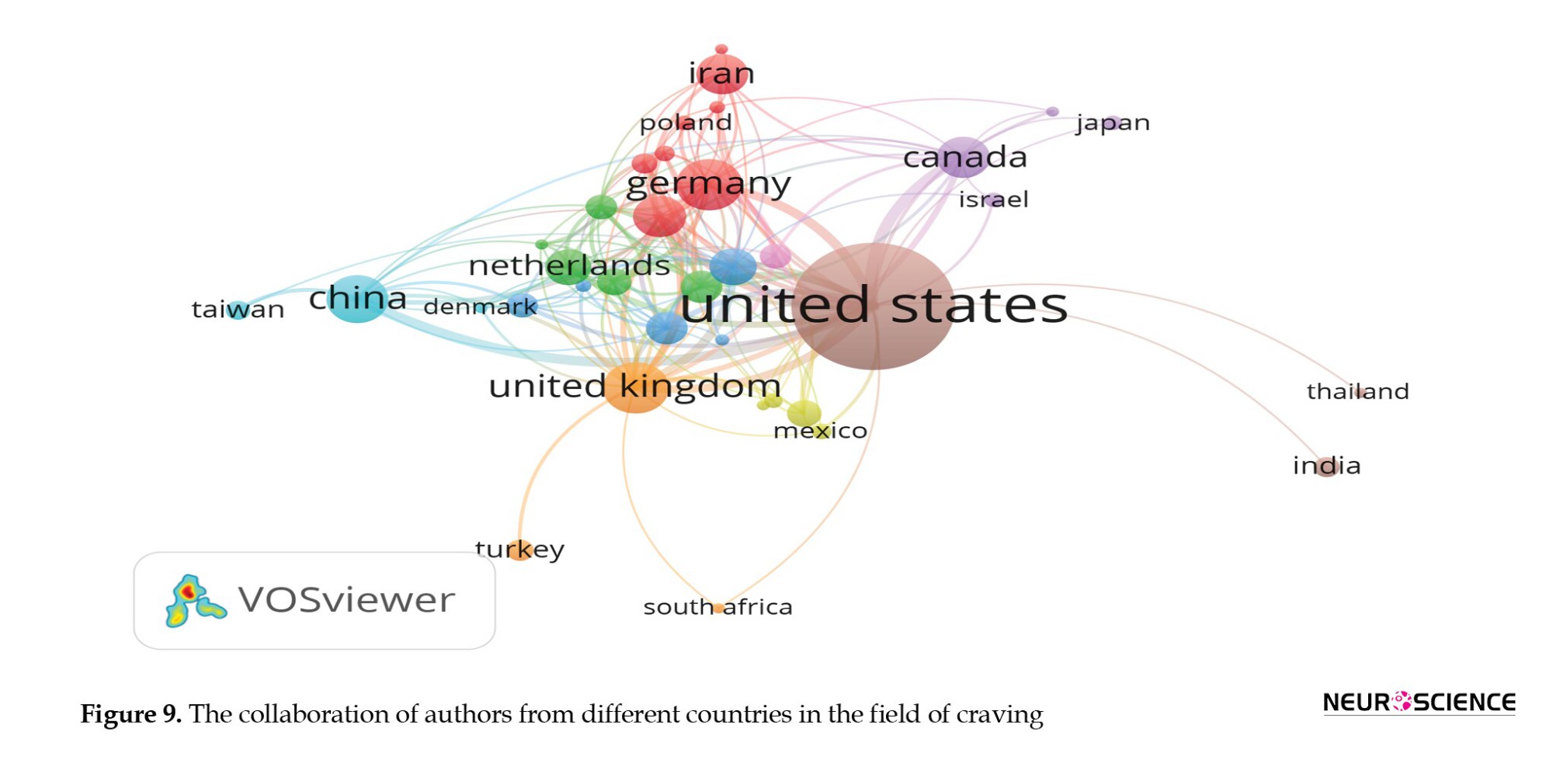
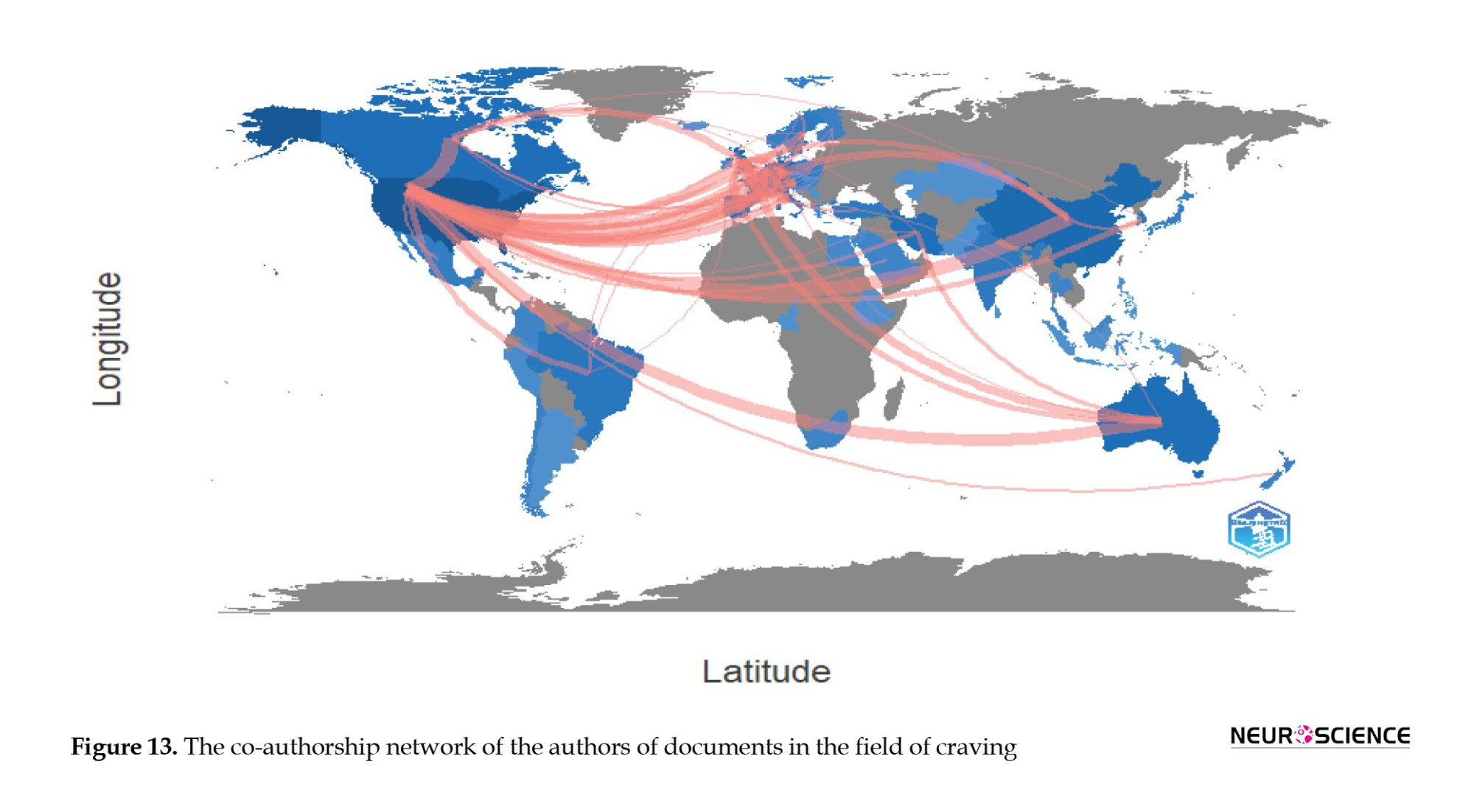
Figure 9 shows that researchers in the United States have collaborated significantly with their counterparts in several countries. Notable collaboration partners for researchers in the United States include China, Germany, the Netherlands, England, Canada, and Iran. This collaborative network highlights the international research dimension in craving and underscores the global nature of scientific inquiry and cooperation.
Vocabulary analysis
In the digital age, effectively harnessing knowledge necessitates information retrieval skills to navigate the extensive repository of scientific information available through web technology. Among these skills, proficiently searching the internet for specific terms is crucial for gaining accurate access to target information. A keyword, also referred to as an index term or descriptor, serves as a term that characterizes the subject matter of a document or search query (Babaii & Taase, 2013). Statistical analysis of keywords plays a pivotal role in identifying emerging fields and trends within science. It serves as a foundational tool for gauging these fields’ effectiveness in deepening our understanding and pushing the boundaries of scientific knowledge (Scandura & Williams, 2000).
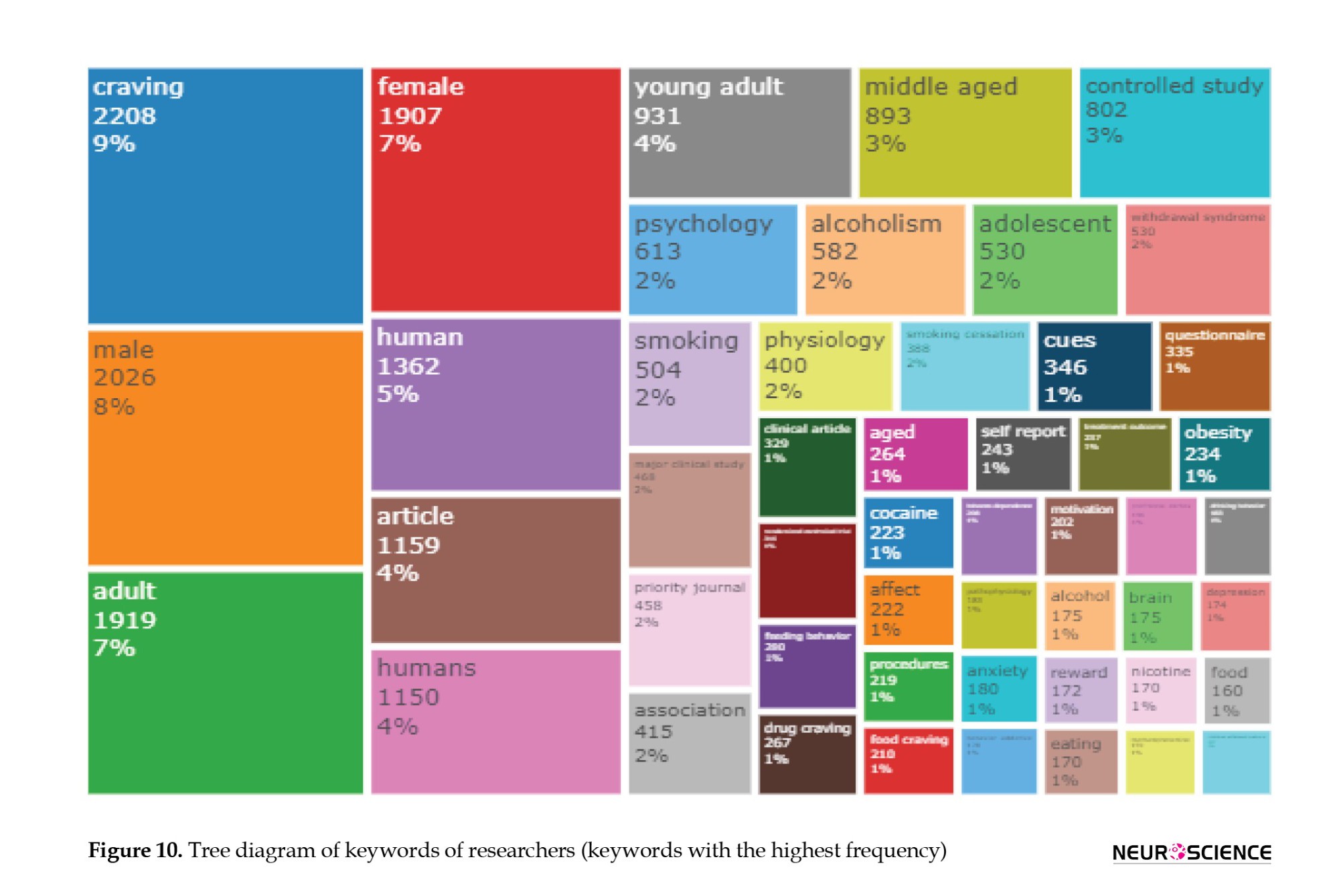
In this diagram, each rectangle represents a keyword, and its size indicates its importance and weight within the dataset of 1720 scientific documents. Notably, the term “desire” stands out with the highest frequency. However, it is interesting to observe that words like “man,” “adult,” and “women” also hold a high frequency within the dataset, suggesting their significance and prevalence in the context of the research or documents being analyzed. These keywords provide valuable insights into key themes and topics addressed in the corpus of scientific documents.
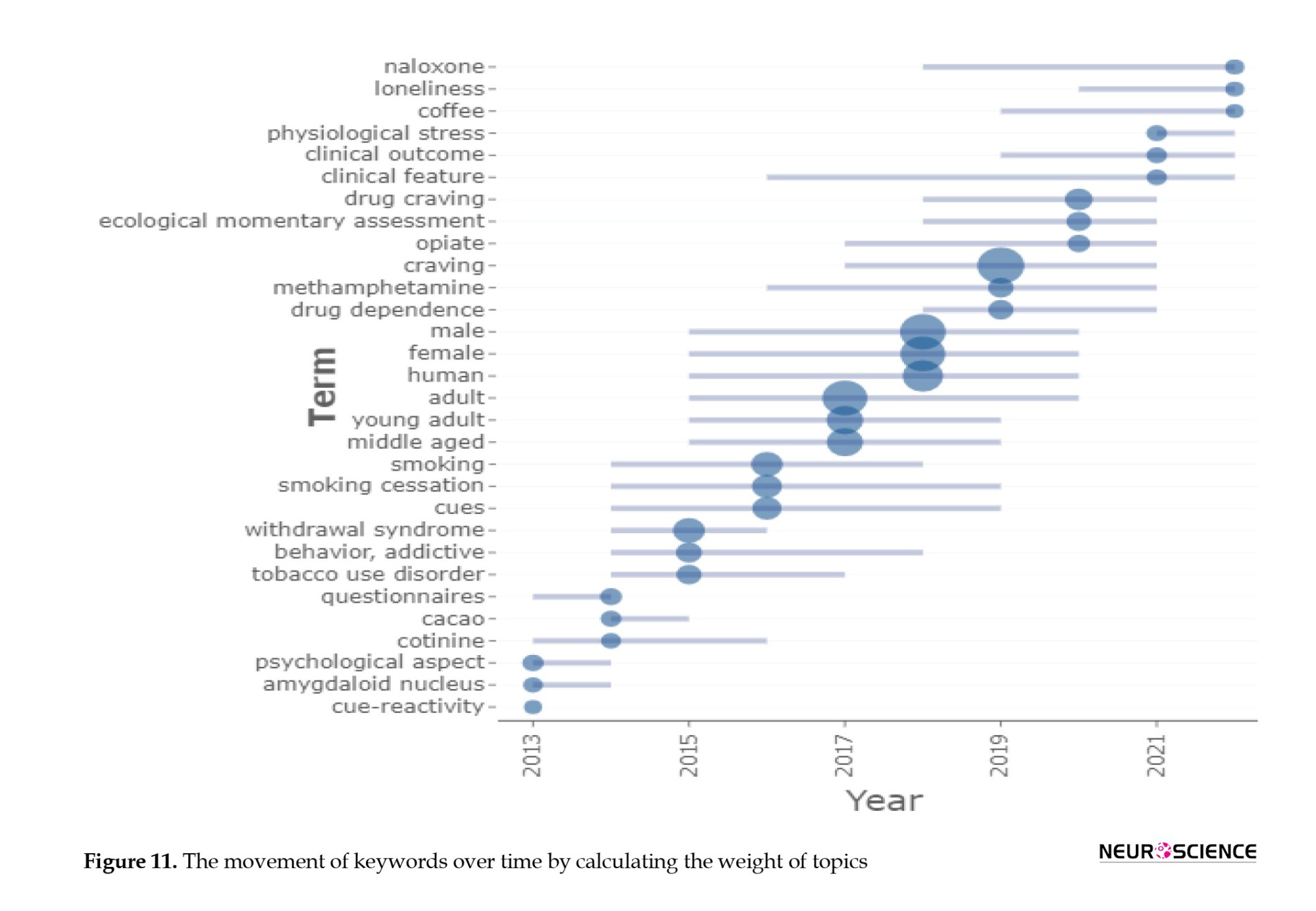
The evolution of keywords over the past decade in this field reflects a shift from words like “reaction to cues,” which are more concerned with theorizing and understanding the etiology of craving or behavior, towards terms such as “naloxone,” which are directly associated with addiction treatment and rehabilitation interventions and behaviors. This progression in keyword usage mirrors the evolving focus and research interests within the field, with the earlier emphasis on understanding the underlying processes and causes of craving and later emphasis on practical interventions and treatments.
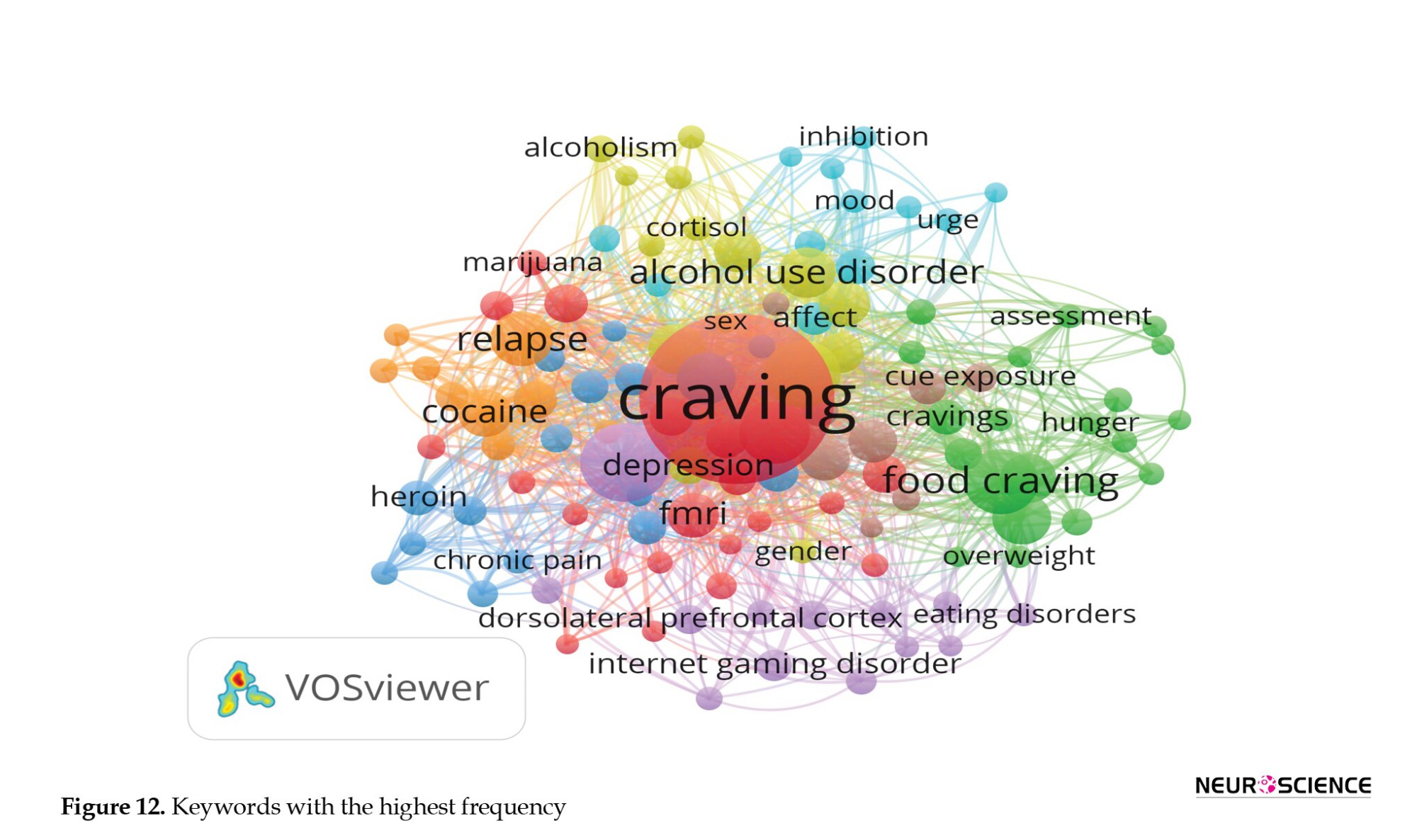
Network analysis and bibliometric scientific mapping
Scientific mapping or bibliometric cartography visually represents the relationships between disciplines, specialties, documents, or authors within a scientific field. It serves as a means of monitoring the development of a scientific field, identifying research boundaries, and revealing the cognitive structure and evolution of that field. Scientometric information mapping is closely linked to preparing forecasts for the development of science, improving the quality of existing collaborations, and fostering the emergence of new collaborative opportunities. It is a valuable tool for gaining insights into the dynamics and trends within a given area of research (Ashrafioun & Rosenberg, 2012a).
The network of co-authorship or collaboration among authors in the field reveals that the United States has been heavily engaged in collaborative efforts with researchers from other countries. Given the substantial number of scientific products from the United States in this field, it is not surprising that it is a key player in international collaborations. This finding demonstrates the global nature of scientific research and highlights the importance of international cooperation in advancing knowledge and addressing complex issues, such as those related to addiction and craving.
4. Discussion
Visual representation methods in scientometrics can be a foundation for formulating initial working hypotheses to analyze scientometrics data and for presenting the final results (Smyrnova-Trybulska et al., 2017). This study revealed that Boswell and Kober’s meta-analytic review (2016) explored food cue reactivity and its relationship to craving for predicting eating and weight gain. It received the highest number of citations, totaling 607 (Boswell & Kober, 2016). On the other hand, Li X, who has produced 40 scientific publications in the last decade, emerged as one of the most prolific researchers in the craving field. one of li’s most cited articles, titled “volitional reduction of anterior cingulate cortex activity produces decreased cue craving in smoking cessation: A preliminary real-time fMRI study,” received 199 citations (Li et al., 2013). This finding underscores Li X ’s significant influence in the field of craving.
These results highlight that the quantity of scientific publications by an author does not necessarily indicate the quality of those publications. Based on the outcomes of our analyses, The journal of addictive behaviors, with a site score of 6.7 and an impact factor of 4.591, published the highest number of articles related to craving. This journal, part of Elsevier Publications, has significantly contributed to the field. Moreover, the Department of Psychiatry at Yale University School of Medicine in New Haven, CT, USA, played a pivotal role by producing many articles.
The United States stands out prominently compared to other countries in terms of the volume of scientific productions and the number of references to these scientific documents. Most notably, collaborations among researchers were primarily seen among countries such as the United States, China, Germany, the Netherlands, England, Canada, and Iran.
In the pool of these studies, the term “craving” was the most frequently used keyword. However, words like “man,” “adult,” and “women” also demonstrated high-frequency usage. The shifting trends in keywords over the past decade indicate a transition from focusing on terms like “response to cues” to keywords such as “naloxone.”
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, studies related to drug addiction or addictive behaviors continue to be at the forefront of worldwide research on etiology and therapeutic interventions for addictive disorders. The enduring prominence of authors and publications dedicated to these topics remains noteworthy.
An examination of the top authors and publications in the field of craving reveals a shift in research trends from drug craving to cravings associated with behavioral addictions, such as food cravings. Additionally, an assessment of articles authored by leading researchers suggests a paradigm shift from experimental studies to the utilization of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), including real-time fMRI (rtfMRI), in the study of cravings. The changing patterns in keywords further indicate the evolution from examining and evaluating cravings to addressing the treatment of both drug addiction and behavioral addictions.
The scientometrics approach not only facilitates the analysis of traditional disciplines but also serves as a valuable tool for exploring the interaction and evolution of science across various fields and specialties. This approach, characterized by visualizing and mapping knowledge and information, ultimately constructs a scientific map encompassing a specific specialty, subject area, discipline, or group of disciplines.
The methods for visually representing scientometrics information can serve as a foundation for generating initial working hypotheses while analyzing scientometrics data and presenting the final results.
This research used statistical analyses to identify the most influential authors, publications, institutes, universities, and articles on craving and addictive behaviors. Furthermore, patterns of co-authorship, co-citation, co-word analysis, and coincidences in the realm of drug addiction and addictive behaviors were examined.
To this end, a comprehensive search was conducted in the Scopus reference database. Ultimately, our analysis encompassed 1720 research and review articles published within the last decade related to craving in the context of drug use or addictive behaviors. As demonstrated by the outcomes of our analyses, Boswell’s study (2016) received the most citations, totaling 355. However, Li X, which has produced 40 scientific documents, ranks among the top contributors in the field of craving over the past decade. This finding underscores the principle that the quantity of scientific publications by an author does not necessarily equate to the quality of those publications.
The journal of addictive behaviors, boasting a site score of 6.7 and an impact factor of 4.591, as part of Elsevier Publications, and the Department of Psychiatry at Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA, have emerged as the most prolific sources of articles in this field. Notably, the United States maintains a significantly higher scientific production and references to these scientific documents than other countries. Collaboration among researchers is particularly prevalent in the United States, China, Germany, the Netherlands, England, Canada, and Iran.
Among these studies, the term “craving” has been the most frequently used keyword, while words such as “men,” “adult,” and “women” have been highly prevalent. Notably, the evolution of keywords over the past decade demonstrates a shift from terms like “response to cues” to keywords such as “naloxone.” In conclusion, it can be inferred that research on drug addiction and addictive behaviors remains at the forefront of worldwide studies on etiology and therapeutic interventions for addictive disorders. The prominence of authors and publications in this field continues to be remarkable.
Study limitations
The present study may have potential limitations:
The search for bibliometric analysis did not allow for the reading and in-depth analysis of the selected articles due to their large number.
Only one database was utilized, which could potentially result in the omission of relevant information.
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
This study was conducted in compliance with all ethical principles and was approved by Zanjan University of Medical Sciences, Zanjan, Iran (Code: IR.ZUMS.REC.1399.449).
Funding
This study was funded by Zanjan University of Medical Sciences, Zanjan, Iran
Authors' contributions
Implementation, data collection, and writing the original draft: Roghayeh Najafi-Dehjalali; Supervison and project coordination: Mohsen Dadashi, and Peyman Hassani Abharian; Consultation, review and editing: Hojjatullah Farahani, and Ali Reza Faridi.
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mohsen Moradi and Aida Miralmas for their technical guidance throughout this project.
References
Addiction is a chronic relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking, loss of control, and developing a negative emotional state (such as negative affect, anxiety, and irritability) when the substance is unavailable (Gay et al., 2022). Drug addiction and addictive behaviors pose global health challenges, cognitive functions, emotional responses, and cravings (Perrotta & Perri, 2022). Over the past two decades, many problematic or extreme behaviors have increasingly been categorized as addictions due to their resemblance to traditional psychoactive drug addiction (Gomez et al., 2022). During the 18th and 19th centuries, at the onset of the scientific revolution, psychiatrists such as Pinel, Rush, Kripplin, Bleuler, and Freud presented clinical observations suggesting that biological factors also contribute to the addiction process (Nathan et al., 2016). Following World War II, both diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM)-I and DSM-II, influenced by psychodynamic theories, emphasized these theories to explain the process of addiction. However, it was with the development of DSM-III that a clear theoretical stance on addiction was explicitly taken. Subsequent editions, such as DSM-IV and DSM-V, have adopted a biological perspective on the addiction process. DSM-V, in particular, references a growing body of empirical research that implicates specific brain mechanisms in addiction and provides a clear framework in this context (Nathan et al., 2016). The most recent iteration, DSM-V, defines "non-substance-related disorders" as addictive disorders that do not involve the use of psychoactive substances (Gay et al., 2022). It also places substance use disorder on a continuum ranging from mild to severe (Perry & Cornish, 2022b). A prominent characteristic of substance use disorder is relapse, often triggered by craving—an intensely subjective experience of the desire to consume (Venniro et al., 2021).
Craving represents a common symptom in individuals with drug use disorders and is observed in cases of dependence on substances such as alcohol, nicotine, cannabis, cocaine, and other psychoactive substances (Zheng et al., 2021). In the DSM-V, craving is recognized as a dynamic phenomenon (Venniro et al., 2021), and it occupies a central role in both addiction research and treatment. This concept, which has historical mentions dating back to ancient times, possesses a lengthy and somewhat intricate history (Ekendahl & Karlsson, 2022). Over the past four decades, around 10000 articles have been dedicated to exploring this subject (Sayette et al., 2000). However, akin to other addiction-related concepts, craving lacks a standard, universally accepted definition, and the definition of this construct has faced many challenges (Ekendahl & Karlsson, 2022). Furthermore, controversies abound regarding the definition, measurement, function, neural underpinnings, and practical utility of craving in understanding the processes underlying addiction (Sayette et al., 2000). Notably, craving stands out as a significant risk factor for relapse and represents a crucial target for treatment interventions (Lambert et al., 2022).
Craving is defined as an "intensive desire" or "urge" to consume a substance or engage in a particular behavior. In the context of drug addiction, craving serves as a predictive factor for substance-seeking behavior and relapse following a period of abstinence (Song et al., 2019). The act of returning to drug consumption, commonly referred to as relapse, represents a substantial obstacle to effective treatment. Relapse is frequently triggered by various factors, including re-exposure to substances, the recurrence of symptoms associated with prior substance use, or exposure to stressors (Perry & Cornish, 2022a).
According to the elaborated intrusion theory of desire, craving is an intense desire for "cognitive events laden with affection, in which a pleasurable or relaxing object or activity becomes the focal point of attention." This model suggests five categories of stimuli that can trigger craving, encompassing external cues (such as an advertisement), the anticipation of a response (e.g. stress), associated thoughts (for instance, thinking about someone with whom one frequently engages in gambling or drinking), negative affection (including depressed mood), and physiological symptoms (like withdrawal symptoms) (Cornil et al., 2021). In a study by Limbrick-Oldfield et al. (2017), it was demonstrated that craving exhibits a negative correlation with the duration of the abstinence period. As the length of abstinence increases, the craving induced by gambling symptoms decreases (Limbrick-Oldfield et al., 2017). Recent neuroimaging research has revealed the significant role of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, among other brain regions, in craving. The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex is implicated in reward processing, motivation, and decision-making. Its circuits provide the foundation for integrating pertinent cognitive and motivational information and exercising inhibitory control over tempting options that promise immediate reward (Rezvanian et al., 2022). In cognitive neuroscience, the predominant approach to investigating the neural responses related to craving is examining the response pattern to the cues (de Lara & Perales, 2020).
In contrast to paradigms for studying addictive behavior, the primary advantage of the cue-based response approach is its solid grounding in general behavioral theories, which has been widely studied (Drummond, 2000). The craving field has witnessed numerous studies exploring existing theories and methodologies, some of which employ systematic review methods while others utilize alternative review approaches. In a review study, the response to cues and relapse were identified as pivotal constructs that have been integrated into various theoretical models of behavioral addictions. This article comprehensively reviews theoretical assumptions and experimental investigations emphasizing the relationship between cue responses and craving at multiple levels, including the cognitive, physiological, environmental, and neurological dimensions, to comprehend and sustain specific behavioral addictions (Wegmann & Brand, 2018).
Another review study underscored the substantial body of literature implicating the influence of negative affect and cravings in the recurrence of addictive disorders. Nearly 90% of the studies analyzed in this systematic review demonstrated a positive correlation between negative affections and cravings. This meta-analysis, along with the reported studies, underscores the significance of negative affection as a critical component of craving, albeit with individual variations in response (to craving) (Cyr et al., 2022).
Various review studies have delved into the subject of drug addiction and its impact on individuals with addiction disorders. Classic review studies, through their comprehensive examination of the existing literature, have played a crucial role in identifying research gaps and providing a comprehensive overview of this field. The body of knowledge in this domain continues to expand (Figure 1).

Consequently, bibliometric research is one of the essential study types required to keep pace with this growing body of knowledge. Although in its early stages, bibliometrics grapples with functional analysis, document network analysis, content analysis of publications, and scientific documents available within citation databases across various knowledge domains (Moradi & Miralmasi, 2022). With the burgeoning and widespread knowledge related to carving across various scientific disciplines (Figure 2), many traditional review techniques struggle to summarize literature due to their descriptive nature. As understanding of craving accumulates and knowledge growth in this area remains upward, researchers increasingly turn to bibliographic reviews to map the landscape of existing studies.

They intend to shed light on the factors driving this growth and the areas where further research is needed. Given the critical role of craving in the processes of relapse and the treatment of addictive disorders, this study seeks to address the following objectives:
1. Examining and visually representing the structure of keywords prevalent in published articles within this field,
2. Analyzing the co-authorship network of researchers involved in published articles focused on craving,
3. Identifying authors who influence the co-authorship network based on citation network analysis indicators, and
4. Determining the authors, countries, or institutions that have contributed the most research documents in this field or have had the most substantial impact.
Furthermore, no comprehensive study centered around this keyword has ever been conducted. Given the significance of scientific indices associated with this keyword, the findings of this research are expected to offer valuable insights for addiction research, addiction treatment strategies, understanding the factors influencing relapse, and efforts to prevent relapse and reinitiate substance consumption.
2. Research Methodology
A review is a research methodology designed to systematically and methodically investigate the background of a research topic. Its purpose is to discover, describe, integrate, explain, or critique patterns, relationships, and trends within a body of knowledge that may not be readily discerned through primary studies and first-rate sources (Shahsavari & Alamolhoda, 2019). The increasing accessibility to digital data within scientific inputs and outputs has opened unprecedented opportunities to explore the structure and evolution of science (Uzzi et al., 2018). Scientometrics, situated at the intersection of science and data analysis, offers a systematic approach to unraveling scientific fields' past, present, and future directions. It has always been central to the research community because it empowers researchers with a deeper understanding of their specialized fields and identities. Scientometrics studies play a pivotal role in raising awareness, informing, and educating both internal and external stakeholders about emerging disciplines while suggesting potential corrective actions to steer research in the desired direction (Serenko, 2021). The scientific literature spans various disciplines, primarily neuroscience, psychiatry, and addiction journals. interestingly, few publications account for most citations (Zurián et al., 2021). However, previous research findings have indicated that most publications in the Social Sciences, including addiction research, tend to appear in the Scopus database after being indexed by the Google Scholar search engine (Martín-Martín et al., 2021). Given the research problem and nature of the literature review, researchers need to employ a common language that resonates with their peers. This common language aligns with the philosophical underpinnings of scientific research and guides how research is conducted (Park et al., 2020). Paradigms, in essence, encapsulate researchers' beliefs and values about the world. Consequently, paradigms have far-reaching implications for every decision made throughout the research process (Kamal, 2019).
In broad terms, paradigms encompass two primary research approaches: Quantitative and qualitative. Quantitative research involves measuring variables applied to a specific phenomenon and is often employed to test existing theories. In this study, the researcher has adopted a quantitative paradigm consistent with this approach (Park et al., 2020). In line with this paradigm, the researcher must employ specific research strategies, commencing with a search strategy that aids in organizing thoughts before searching. This search strategy, rooted in the comparative perspective of the quantitative approach, involves formulating a bibliographic research plan or strategy that consists of six core steps (Figure 3).

The first phase involves selecting the scope of the problem and research inquiry. Drawing from the literature covered in Section 1, collected by searching "publish or perish" (Harzing, 2010), it becomes evident that the escalating number of articles in the field of addiction necessitates validation. This validation effort extends to understanding the factors that fuel and sustain this proliferation, notably the intricate structure of craving. As a result, the researcher embarks on a mission to distill this knowledge's essence and forecast future research trends.
In the second step and following Snyder (2019), the researcher devises research objectives that fall into functional objectives and creating a scientific roadmap (Moradi & Miralmasi, 2020). These objectives are as follows:
1. Identifying the most influential author within the field of craving.
2. Identifying the most influential publication within the field of craving.
3. Identifying the most influential institute or university contributing to research on craving.
4. Identifying the most influential country with a substantial impact on the field of craving.
5. Identifying the most influential article within the domain of craving research
In addition, the objectives of citation network analysis are as follows:
1. Identifying the most impactful co-citation patterns within the realm of craving research.
2. Identifying the most impactful co-authorship patterns evident in craving research.
3. Identifying the most impactful co-lexical patterns within the field of craving.
4. Identifying the most impactful concurrent patterns prevalent in craving research
In the third step, the research aims to access valid citation data about cravings from top-tier citation databases and search engines. Although various studies have explored the coverage and accuracy of these databases (Martín-Martín et al., 2021), the significance of bibliographic databases has grown substantially in recent times. They serve as primary sources for publication metadata and universally accepted bibliometric indicators used in research evaluation (Pranckutė, 2021).
Scientometric research heavily relies on large-scale citation databases and journal articles (Thelwall & Sud, 2022). Within the Scopus database, the number of distinct journals has increased exponentially, underlining the importance of highly cited articles for researchers and editors (Yaminfirooz & Ardali, 2018). Considering the prevalence of humanities studies within the Scopus citation database and its precision and accuracy in citation data, the researchers selected the Scopus reference database. A well-defined policy and strategy were established to achieve a comprehensive repository of documentary information. Management organization tools like Mendeley and its extensions were employed to identify and establish concepts related to this research structure. Subsequently, a systematic search process was carried out involving synonyms, binary operators, and quotation marks. The data extracted from this search were inputted into the Mendeley data management software. A rigorous pre-processing step was conducted, eliminating low-value and extraneous data. Data lacking English abstracts, author names, or other essential citation attributes were excluded from the analysis. Moreover, materials such as books, letters to the editor, web pages, and seminar articles are disregarded. The remaining results are then summarized and subjected to detailed analysis. The instructions for this search are outlined in Table 1.

The fourth step is to choose the right software for bibliometric data analysis. The researcher has selected and acquired proficiency in the following software tools for conducting the specified operations. This decision was influenced by recent technological advancements and the emergence of various websites and software applications that offer diverse approaches to fulfilling descriptive objectives and conducting citation network analysis. It is worth noting that these tools have gained recognition and endorsement from reputable academic organizations and institutions (Table 2).

The software applications in this field are as follows:
Publish, or Perish software, which was created by Professor Harzing in 2008 to gather citation data from search engines. The current version is version 8, compatible with Windows 64-bit (Harzing, 2010).
Mendeley software organizes and manages research resources. The version currently used is 1.98, designed for 64-bit Windows (Scipous, 2022).
To adhere to preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) protocol criteria, tasks such as identifying duplicate research are performed using Microsoft Excel for data analysis and visualization.
VOSviewer software was developed by Leiden University in the Netherlands. It offers researchers exceptionally high-quality network analysis and visualization capabilities. This research used version 1.6.18 of the software on a 64-bit Windows system (Van Eck & Waltman, 2010).
In this research, the initial step involved the installation of R Software, version 4.2. Subsequently, R Studio macros from the free, non-commercial version of 2022 were added to R. Finally, an HTML-based bibliometric software package was installed to facilitate comprehensive functional information and network analysis. This software package was developed by the RStudio Team based in Boston, MA, USA (RStudio Team, 2022).
The fifth step comprises collecting information, screening, and extracting the information. Based on the research, it was found that there were 14615 documents related to the keyword craving in the Scopus citation database. Due to the high frequency of this phrase in the keywords and abstracts of scientific documents, the researcher limited the review to studies that exclusively included the keyword "craving" in their titles. Consequently, 3407 scientific documents remained for analysis. Two stages of data screening and cleaning were conducted. The first stage occurred in citation databases, where the researcher filtered and removed irrelevant data. In the second stage, involving the remaining 3407 studies from the previous phase, the researcher re-screened the data using a standard screening protocol such as PRISMA (Page et al., 2021), updated in 2020.
3. Results
The researcher conducted descriptive and network analysis in the sixth step of the research methodology (Moradi & Miralmasi, 2020).
In this research, 1720 scientific documents, comprising both primary research articles and review articles, were examined. These articles were authored by 6019 authors and published through 522 sources.
Functional analysis of documents and authors
The definition of authorship in scientific articles and documents is a necessary and intricate procedure largely reliant on informal arrangements. An author of a scientific document or a group of co-authors consists of individuals who have contributed substantially to the study (Albarracín et al., 2020). Citing an author aims to alert researchers to previously published works related to the topic. Nonetheless, research indicates that articles with multiple authors receive more citations than single-authored articles (Yaminfirooz & Ardali, 2018).
As evident in Table 3, Boswell's (2016) meta-analysis study, titled "predicting weight gain through response to food cues and food cravings," has garnered 355 citations (Boswell & Kober, 2016). Another study from 2016, titled "synaptic mechanisms underlying persistent cocaine craving," delves into the challenges faced by individuals with cocaine addiction in achieving abstinence. It emphasizes that the primary issue is not the initial use but the subsequent avoidance of cocaine. This animal study suggests that craving for cocaine during the abstinence period is attributable to neural plasticity in the reward circuitry, which sustains elevated levels of craving. Furthermore, this research highlights the potential of craving studies to identify new therapeutic targets and enhance our comprehension of experience-dependent neural plasticity in the brains of adults under normal conditions and in the context of addiction (Wolf, 2016).

The information analysis in VOSviewer software assigns greater weight to authors in the field of craving who have received more citations. Consequently, the names of these highly cited authors are displayed in a larger font size. Based on this analysis, it is evident that Boswell (2016)” and “Wolf, (2016)” are the most prominent and influential authors in the field of craving, as they have garnered a significant number of citations and recognition within the research community.
As shown in Table 4, Li X stands out as the most prolific contributor in the field of desire, having authored 40 scientific documents in the last ten years. Following Li X, Sinhar and Shahami Harik ranked second with 25 scientific documents. However, it is noteworthy that none of these authors have produced highly cited or heavily referenced works. This outcome underscores that the quantity of scientific documents produced does not necessarily reflect their quality.

Functional analysis of publications, organizations
Effective research policies provide the essential framework for guiding research management within higher education institutions and study programs (De La Cruz Vargas, 2019). These strategies should encompass the promotion of research, enhancement of research infrastructure, financial support for research endeavors, and training researchers to produce high-quality work. Such knowledge dissemination not only enhances the reputation of institutions through their scientific output but also positions universities as leaders and generators of new knowledge. Consequently, they are recognized as dedicated contributors to research and innovation, ultimately fostering the development of their respective countries (Millones-Gómez et al., 2021). In light of the information presented in Table 5, which outlines the key bibliometric details, it is evident that 522 publications have contributed to disseminating the 1720 scientific documents in this study.

Also, Table 6 presents the journals with the highest scientific output in consumer participation.

Journals often employ expert reviews to sift through and select the best articles for publication (Candel & Naccache, 2021). Addictive Behaviors is an international journal with a site score 6.7 and an impressive impact factor of 4.591.

Since its inception in 1975, this journal has been dedicated to publishing high-quality human research concerning addictive behaviors and disorders, as well as behavioral addictions, which encompass areas such as gambling and technology. Its primary focus lies in disseminating behavioral and psychosocial research. On the other hand, The journal of drug and alcohol dependence is an international journal that employs biomedical and psychological approaches. It holds a site score of 1.6 and an impact factor of 4.852. This journal serves as a platform for the publication of original research, scientific reviews, commentaries, and policy analyses, all within the domain of drug, alcohol, and tobacco consumption and addiction (Drug & Alcohol Dependence,1976).

An analysis of publications from the top five journals in the field of drug consumption reveals a noticeable increase in the number of scientific documents being published in this area.
Table 7 and Figure 7 show that the Department of Psychiatry at Yale University School of Medicine in New Haven, CT, USA, has produced the highest number of scientific publications on addiction. Following closely is the Erwin L. Hahn Magnetic Resonance Imaging Institute in Essen, Germany. These two institutions, each having contributed 14 published scientific documents, collectively account for nearly 40% of the world’s scientific productions in craving.


Functional analysis of countries
Among countries, the United States, China, Germany, Italy, and England emerged as the main contributors to scientific productions in the field of craving. The United States significantly outpaces other countries in terms of the quantity of scientific products and the number of references made to these scientific documents.

Figure 9 shows that researchers in the United States have collaborated significantly with their counterparts in several countries. Notable collaboration partners for researchers in the United States include China, Germany, the Netherlands, England, Canada, and Iran. This collaborative network highlights the international research dimension in craving and underscores the global nature of scientific inquiry and cooperation.

Vocabulary analysis
In the digital age, effectively harnessing knowledge necessitates information retrieval skills to navigate the extensive repository of scientific information available through web technology. Among these skills, proficiently searching the internet for specific terms is crucial for gaining accurate access to target information. A keyword, also referred to as an index term or descriptor, serves as a term that characterizes the subject matter of a document or search query (Babaii & Taase, 2013). Statistical analysis of keywords plays a pivotal role in identifying emerging fields and trends within science. It serves as a foundational tool for gauging these fields’ effectiveness in deepening our understanding and pushing the boundaries of scientific knowledge (Scandura & Williams, 2000).

In this diagram, each rectangle represents a keyword, and its size indicates its importance and weight within the dataset of 1720 scientific documents. Notably, the term “desire” stands out with the highest frequency. However, it is interesting to observe that words like “man,” “adult,” and “women” also hold a high frequency within the dataset, suggesting their significance and prevalence in the context of the research or documents being analyzed. These keywords provide valuable insights into key themes and topics addressed in the corpus of scientific documents.
The evolution of keywords over the past decade in this field reflects a shift from words like “reaction to cues,” which are more concerned with theorizing and understanding the etiology of craving or behavior, towards terms such as “naloxone,” which are directly associated with addiction treatment and rehabilitation interventions and behaviors. This progression in keyword usage mirrors the evolving focus and research interests within the field, with the earlier emphasis on understanding the underlying processes and causes of craving and later emphasis on practical interventions and treatments.

Network analysis and bibliometric scientific mapping
Scientific mapping or bibliometric cartography visually represents the relationships between disciplines, specialties, documents, or authors within a scientific field. It serves as a means of monitoring the development of a scientific field, identifying research boundaries, and revealing the cognitive structure and evolution of that field. Scientometric information mapping is closely linked to preparing forecasts for the development of science, improving the quality of existing collaborations, and fostering the emergence of new collaborative opportunities. It is a valuable tool for gaining insights into the dynamics and trends within a given area of research (Ashrafioun & Rosenberg, 2012a).

The network of co-authorship or collaboration among authors in the field reveals that the United States has been heavily engaged in collaborative efforts with researchers from other countries. Given the substantial number of scientific products from the United States in this field, it is not surprising that it is a key player in international collaborations. This finding demonstrates the global nature of scientific research and highlights the importance of international cooperation in advancing knowledge and addressing complex issues, such as those related to addiction and craving.


4. Discussion
Visual representation methods in scientometrics can be a foundation for formulating initial working hypotheses to analyze scientometrics data and for presenting the final results (Smyrnova-Trybulska et al., 2017). This study revealed that Boswell and Kober’s meta-analytic review (2016) explored food cue reactivity and its relationship to craving for predicting eating and weight gain. It received the highest number of citations, totaling 607 (Boswell & Kober, 2016). On the other hand, Li X, who has produced 40 scientific publications in the last decade, emerged as one of the most prolific researchers in the craving field. one of li’s most cited articles, titled “volitional reduction of anterior cingulate cortex activity produces decreased cue craving in smoking cessation: A preliminary real-time fMRI study,” received 199 citations (Li et al., 2013). This finding underscores Li X ’s significant influence in the field of craving.
These results highlight that the quantity of scientific publications by an author does not necessarily indicate the quality of those publications. Based on the outcomes of our analyses, The journal of addictive behaviors, with a site score of 6.7 and an impact factor of 4.591, published the highest number of articles related to craving. This journal, part of Elsevier Publications, has significantly contributed to the field. Moreover, the Department of Psychiatry at Yale University School of Medicine in New Haven, CT, USA, played a pivotal role by producing many articles.
The United States stands out prominently compared to other countries in terms of the volume of scientific productions and the number of references to these scientific documents. Most notably, collaborations among researchers were primarily seen among countries such as the United States, China, Germany, the Netherlands, England, Canada, and Iran.
In the pool of these studies, the term “craving” was the most frequently used keyword. However, words like “man,” “adult,” and “women” also demonstrated high-frequency usage. The shifting trends in keywords over the past decade indicate a transition from focusing on terms like “response to cues” to keywords such as “naloxone.”
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, studies related to drug addiction or addictive behaviors continue to be at the forefront of worldwide research on etiology and therapeutic interventions for addictive disorders. The enduring prominence of authors and publications dedicated to these topics remains noteworthy.
An examination of the top authors and publications in the field of craving reveals a shift in research trends from drug craving to cravings associated with behavioral addictions, such as food cravings. Additionally, an assessment of articles authored by leading researchers suggests a paradigm shift from experimental studies to the utilization of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), including real-time fMRI (rtfMRI), in the study of cravings. The changing patterns in keywords further indicate the evolution from examining and evaluating cravings to addressing the treatment of both drug addiction and behavioral addictions.
The scientometrics approach not only facilitates the analysis of traditional disciplines but also serves as a valuable tool for exploring the interaction and evolution of science across various fields and specialties. This approach, characterized by visualizing and mapping knowledge and information, ultimately constructs a scientific map encompassing a specific specialty, subject area, discipline, or group of disciplines.
The methods for visually representing scientometrics information can serve as a foundation for generating initial working hypotheses while analyzing scientometrics data and presenting the final results.
This research used statistical analyses to identify the most influential authors, publications, institutes, universities, and articles on craving and addictive behaviors. Furthermore, patterns of co-authorship, co-citation, co-word analysis, and coincidences in the realm of drug addiction and addictive behaviors were examined.
To this end, a comprehensive search was conducted in the Scopus reference database. Ultimately, our analysis encompassed 1720 research and review articles published within the last decade related to craving in the context of drug use or addictive behaviors. As demonstrated by the outcomes of our analyses, Boswell’s study (2016) received the most citations, totaling 355. However, Li X, which has produced 40 scientific documents, ranks among the top contributors in the field of craving over the past decade. This finding underscores the principle that the quantity of scientific publications by an author does not necessarily equate to the quality of those publications.
The journal of addictive behaviors, boasting a site score of 6.7 and an impact factor of 4.591, as part of Elsevier Publications, and the Department of Psychiatry at Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA, have emerged as the most prolific sources of articles in this field. Notably, the United States maintains a significantly higher scientific production and references to these scientific documents than other countries. Collaboration among researchers is particularly prevalent in the United States, China, Germany, the Netherlands, England, Canada, and Iran.
Among these studies, the term “craving” has been the most frequently used keyword, while words such as “men,” “adult,” and “women” have been highly prevalent. Notably, the evolution of keywords over the past decade demonstrates a shift from terms like “response to cues” to keywords such as “naloxone.” In conclusion, it can be inferred that research on drug addiction and addictive behaviors remains at the forefront of worldwide studies on etiology and therapeutic interventions for addictive disorders. The prominence of authors and publications in this field continues to be remarkable.
Study limitations
The present study may have potential limitations:
The search for bibliometric analysis did not allow for the reading and in-depth analysis of the selected articles due to their large number.
Only one database was utilized, which could potentially result in the omission of relevant information.
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
This study was conducted in compliance with all ethical principles and was approved by Zanjan University of Medical Sciences, Zanjan, Iran (Code: IR.ZUMS.REC.1399.449).
Funding
This study was funded by Zanjan University of Medical Sciences, Zanjan, Iran
Authors' contributions
Implementation, data collection, and writing the original draft: Roghayeh Najafi-Dehjalali; Supervison and project coordination: Mohsen Dadashi, and Peyman Hassani Abharian; Consultation, review and editing: Hojjatullah Farahani, and Ali Reza Faridi.
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mohsen Moradi and Aida Miralmas for their technical guidance throughout this project.
References
Albarracín, M. L. G., Castro, C. M., & Chaparro, P. E. (2020). Importance, definition and conflicts of authorship in scientific publications. Revista Bioética, 28(1), 10-16. [DOI:10.1590/1983-80422020281361]
Ashrafioun, L., & Rosenberg, H. (2012). Methods of assessing craving to gamble: A narrative review. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors: Journal of the Society of Psychologists in Addictive Behaviors, 26(3), 536–549. [DOI:10.1037/a0026367] [PMID]
Babaii, E., & Taase, Y. (2013). Author-assigned keywords in research articles: Where do they come from. Iranian Journal of Applied Linguistics, 16(2), 1-19. [Link]
Boswell, R. G., & Kober, H. (2016). Food cue reactivity and craving predict eating and weight gain: A meta-analytic review. Obesity Reviews, 17(2), 159-177. [DOI:10.1111/obr.12354] [PMID]
Candel, G., & Naccache, D. (2021). Generating local maps of science using deep bibliographic coupling [Preprint]. arXiv. [DOI:10.48550/arXiv.2109.10007]
Cornil, A., Rothen, S., De Timary, P., & Billieux, J. (2021). Interference-based methods to mitigate gambling craving: A proof-of-principle pilot study. International Gambling Studies, 21(3), 426-449. [DOI:10.1080/14459795.2021.1903063]
Cyr, L., Bernard, L., Pedinielli, J. L., Cutarella, C., & Bréjard, V. (2023). Association between negative affectivity and craving in substance-related disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of direct and indirect relationships. Psychological Reports, 126(3), 1143–1180. [DOI:10.1177/00332941211061079] [PMID]
De La Cruz Vargas, J. A. (2019). La investigación: más allá del ranking de las universidades. Revista de La Facultad de Medicina Humana, 19(1), 1-5. [DOI:10.25176/rfmh.v19.n1.1786]
de Lara, C. M. R., & Perales, J. C. (2020). Psychobiology of gambling-related cognitions in gambling disorder. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 31, 60-68. [DOI:10.1016/j.cobeha.2019.11.012]
No Author. Drug and alcohol dependence. (1976). Medical Journal of Australia, 1(16), 558. [DOI:10.5694/j.1326-5377.1976.tb140860.x]
Drummond, D. C. (2000). What does cue‐reactivity have to offer clinical research? Addiction (Abingdon, England), 95 (Suppl 2), S129–S144.[DOI:10.1080/09652140050111708] [PMID]
Ekendahl, M., & Karlsson, P. (2022). A matter of craving-An archeology of relapse prevention in Swedish addiction treatment. The International Journal on Drug Policy, 101, 103575.[DOI:10.1016/j.drugpo.2021.103575] [PMID]
Gay, A., Cabe, J., De Chazeron, I., Lambert, C., Defour, M., & Bhoowabul, V., et al. (2022). Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) as a promising treatment for craving in stimulant drugs and behavioral addiction: A meta-analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(3), 624. [DOI:10.3390/jcm11030624] [PMID]
Gomez, R., Stavropoulos, V., Brown, T., & Griffiths, M. D. (2022). Factor structure of ten psychoactive substance addictions and behavioural addictions. Psychiatry Research, 313, 114605. [DOI:10.1016/j.psychres.2022.114605] [PMID]
Harzing, A. W. (2010). The publish or perish book. Melbourne: Tarma Software Research Pty Limited. [Link]
Kamal, S. (2019). Research paradigm and the philosophical foundations of a qualitative study. PEOPLE: International Journal of Social Sciences, 4(3), 1386-1394. [DOI:10.20319/pijss.2019.43.13861394]
Lambert, L., Serre, F., Thirioux, B., Jaafari, N., Roux, P., & Jauffret-Roustide, M., et al. (2022). Link between perception of treatment need and craving reports in addiction. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 12, 790203. [DOI:10.3389/fpsyt.2021.790203] [PMID]
Li, X., Hartwell, K. J., Borckardt, J., Prisciandaro, J. J., Saladin, M. E., & Morgan, P. S., et al. (2013). Volitional reduction of anterior cingulate cortex activity produces decreased cue craving in smoking cessation: A preliminary real-time fMRI study. Addiction Biology, 18(4), 739-748. [DOI:10.1111/j.1369-1600.2012.00449.x] [PMID]
Limbrick-Oldfield, E. H., Mick, I., Cocks, R. E., McGonigle, J., Sharman, S. P., & Goldstone, A. P., et al. (2017). Neural substrates of cue reactivity and craving in gambling disorder. Translational Psychiatry, 7(1), e992. [DOI:10.1038/tp.2016.256] [PMID]
Martín-Martín, A., Thelwall, M., Orduna-Malea, E., & Delgado López-Cózar, E. (2021). Google Scholar, Microsoft Academic, Scopus, Dimensions, Web of Science, and OpenCitations’ COCI: A multidisciplinary comparison of coverage via citations. Scientometrics, 126(1), 871-906. [DOI:10.1007/s11192-020-03690-4] [PMID]
Millones-Gómez, P. A., Yangali-Vicente, J. S., Arispe-Alburqueque, C. M., Rivera-Lozada, O., Calla-Vásquez, K. M., & Calla-Poma, R. D., et al. (2021). Research policies and scientific production: A study of 94 Peruvian universities. Plos One, 16(5), e0252410. [DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0252410] [PMID]
Moradi, M., & Miralmasi, A. (2020). Pragmatic research method. In F. Seydi (Ed.), School of quantitative and qualitative research. New York: MPT Academy. [Link]
Moral-Muñoz, J. A., Herrera-Viedma, E., Santisteban-Espejo, A., & Cobo, M. J. (2020). Software tools for conducting bibliometric analysis in science: An up-to-date review. Profesional de la Informacion, 29(1). [DOI:10.3145/epi.2020.ene.03]
Nathan, P. E., Conrad, M., & Skinstad, A. H. (2016). History of the concept of addiction. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 12, 29-51. [DOI:10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-021815-093546] [PMID]
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., & Mulrow, C. D., et al. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ (Clinical research ed.), 372, n71. [DOI:10.1136/BMJ.N71] [PMID]
Park, Y. S., Konge, L., & Artino, A. R. (2020). The positivism paradigm of research. Academic Medicine, 95(5), 690-694. [DOI:10.1097/ACM.0000000000003093] [PMID]
Perrotta, D., & Perri, R. L. (2022). Mini-review: When neurostimulation joins cognitive-behavioral therapy: On the need of combining evidence-based treatments for addiction disorders. Neuroscience Letters, 777, 136588. [DOI:10.1016/j.neulet.2022.136588] [PMID]
Perry, C. J., & Cornish, J. L. (2022). Addiction neuroscience. Addiction Neuroscience, 2, 100018. [DOI:10.1016/j.addicn.2022.100018]
Perry, C. J., & Cornish, J. L. (2022). Four hypothalamic peptides and their impact on drug-seeking behaviour: A prefrontal cortex view. Addiction Neuroscience, 2, 100018. [DOI:10.1016/j.addicn.2022.100018]
Pranckutė, R. (2021). Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus: The titans of bibliographic information in today’s academic world. Publications, 9(1), 12. [DOI:10.3390/publications9010012]
Rezvanian, S., Saraei, M., Mohajeri, H., & Hassani-Abharian, P. (2022). The effect of different transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) protocols on drug craving and cognitive functions in methamphetamine addicts. Basic and Clinical Neuroscience, 13(3), 349–355. [DOI:10.32598/bcn.2021.1929.1] [PMID]
Sayette, M. A., Shiffman, S., Tiffany, S. T., Niaura, R. S., Martin, C. S., & Schadel, W. G. (2000). The measurement of drug craving. Addiction, 95(Suppl 2), S189–S210.[DOI:10.1080/09652140050111762] [PMID]
Scandura, T. A., & Williams, E. A. (2000). Research methodology in management: Current practices, trends, and implications for future research. Academy of Management Journal, 43(6), 1248-1264. [Link]
Serenko, A. (2021). A structured literature review of scientometric research of the knowledge management discipline: A 2021 update. Journal of Knowledge Management, 25(8), 1889-1925. [DOI:10.1108/JKM-09-2020-0730]
Shahsavari, A., & Alamolhoda, J. (2019). Methodology of research reviews and its role in knowledge production: Developing a typology. Methodology of Social Sciences and Humanities, 25(98), 79-105. [Link]
Smyrnova-Trybulska, E., Morze, N., Kuzminska, O., & Kommers, P. (2017). Bibliometric science mapping as a popular trend: Chosen examples of visualisation of international research network results. Paper presented at: International Conference Educational Technologies. [Link]
Song, S., Zilverstand, A., Gui, W., Li, H. J., & Zhou, X. (2019). Effects of single-session versus multi-session non-invasive brain stimulation on craving and consumption in individuals with drug addiction, eating disorders or obesity: A meta-analysis. Brain Stimulation, 12(3), 606-618. [DOI:10.1016/j.brs.2018.12.975] [PMID]
Snyder, H. (2019). Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. Journal of business research, 104, 333-339. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.07.039]
Thelwall, M., & Sud, P. (2022). Scopus 1900-2020: Growth in articles, abstracts, countries, fields, and journals. Quantitative Science Studies, 3(1), 37-50. [DOI:10.1162/qss_a_00177]
Fortunato, S., Bergstrom, C. T., Börner, K., Evans, J. A., Helbing, D., Milojević, S., Petersen, A. M., Radicchi, F., Sinatra, R., Uzzi, B., Vespignani, A., Waltman, L., Wang, D., & Barabási, A. L. (2018). Science of science. Science (New York, N.Y.), 359(6379), eaao0185. [DOI: 10.1126/science.aao0185]
Van Eck, N. J., & Waltman, L. (2010). VOSviewer: Visualizing scientific landscapes [Software]. Leiden University.
Venniro, M., Reverte, I., Ramsey, L. A., Papastrat, K. M., D’Ottavio, G., & Milella, M. S., et al. (2021). Factors modulating the incubation of drug and non-drug craving and their clinical implications. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 131, 847-864. [DOI:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.09.050] [PMID]
Wegmann, E., & Brand, M. (2018). Cue reactivity and craving in behavioral addictions with a focus on internet use disorder. Verhaltenstherapie, 28(4), 238-246. [Link]
Wolf, M. E. (2016). Synaptic mechanisms underlying persistent cocaine craving. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 17(6), 351-365. [DOI:10.1038/nrn.2016.39] [PMID]
Yaminfirooz, M., & Ardali, F. (2018). Identifying the factors affecting papers’ citability in the field of medicine: An evidence-based approach using 200 highly and lowly-cited papers. Acta Informatica Medica: AIM: Journal of the Society for Medical Informatics of Bosnia & Herzegovina: Casopis Drustva za medicinsku informatiku BiH, 26(1), 10–14. [DOI:10.5455/aim.2018.26.10-14] [PMID]
Zheng, R., Hao, L., Li, Y., Zhang, T., Bai, D., & Zhang, L., et al. (2021). Commentary: Craving in opioid use disorder: From neurobiology to clinical practice. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 12, 615921. [DOI:10.3389/fpsyt.2021.615921] [PMID]
Valderrama Zurián, J. C., Bueno Cañigral, F. J., Castelló Cogollos, L., & Aleixandre-Benavent, R. (2021). The most 100 cited papers in addiction research on cannabis, heroin, cocaine and psychostimulants: A bibliometric cross-sectional analysis. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 221, 108616. [DOI:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2021.108616] [PMID]
Type of Study: Review |
Subject:
Cognitive Neuroscience
Received: 2023/07/31 | Accepted: 2023/09/26 | Published: 2025/03/18
Received: 2023/07/31 | Accepted: 2023/09/26 | Published: 2025/03/18
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |





