Volume 11, Issue 6 (November & December 2020)
BCN 2020, 11(6): 737-752 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Dehghani H, Oghabian M A, Batouli S A H, Arab Kheradmand J, Khatibi A. Effect of Physiological Noise on Thoracolumbar Spinal Cord Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging in 3T Magnetic Field. BCN 2020; 11 (6) :737-752
URL: http://bcn.iums.ac.ir/article-1-1236-en.html
URL: http://bcn.iums.ac.ir/article-1-1236-en.html
Hamed Dehghani1 

 , Mohammad Ali Oghabian *1
, Mohammad Ali Oghabian *1 

 , Seyed Amir Hosein Batouli2
, Seyed Amir Hosein Batouli2 

 , Jalil Arab Kheradmand3
, Jalil Arab Kheradmand3 
 , Ali Khatibi4
, Ali Khatibi4 




 , Mohammad Ali Oghabian *1
, Mohammad Ali Oghabian *1 

 , Seyed Amir Hosein Batouli2
, Seyed Amir Hosein Batouli2 

 , Jalil Arab Kheradmand3
, Jalil Arab Kheradmand3 
 , Ali Khatibi4
, Ali Khatibi4 


1- Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Medicine, Tehran University of Medical Science, Tehran, Iran.
2- Neuro Imaging and Analysis Group (NIAG), Research Center for Molecular and Cellular Imaging (RCMCI), Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
3- Shefa Neuroscience Research Center, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
4- Centre of Precision Rehabilitation for Spinal Pain (CPR Spine), School of Sport, Exercise and Rehabilitation Sciences, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, United Kingdom.
2- Neuro Imaging and Analysis Group (NIAG), Research Center for Molecular and Cellular Imaging (RCMCI), Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
3- Shefa Neuroscience Research Center, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
4- Centre of Precision Rehabilitation for Spinal Pain (CPR Spine), School of Sport, Exercise and Rehabilitation Sciences, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, United Kingdom.
Keywords: Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), Spinal cord, Physiological noise, Imaging, General linear model
Full-Text [PDF 2657 kb]
| Abstract (HTML)
Previous research suggested that the lumbar spinal cord is motionless and the noise fitting can be ignored (Figley, Yau, & Stroman, 2008). Others only considered the cardiac motion-related effects on the spinal cord and CSF (Alexander et al., 2017; Alexander et al., 2016; R. Bosma & Stroman, 2015; Figley & Stroman, 2009; Kozyrev et al., 2012), and both these approaches may lead to biased information due to ignoring the respiration noise as one of the main sources of noise production. In this study, we investigated the effect of each source of physiological noise and their contributions to the outcome of the analysis of the Blood-Oxygen-Level-Dependent (BOLD) signal by recording the changes in the heart-beat and respiration during fMRI experiments. We determined the quota of respiration and heartbeat physiological noise in thoracolumbar spinal cord neural activity detected by fMRI and evaluated the impact of this physiological noise on false-positive rates.
2. Methods
2.1. Study participants
The participants included 15 right-handed healthy adults (14 males, Mean±SD age=25.88±4.44 years). None of the participants had any history or evidence of spinal cord/vertebral injury or dysmorphology. The participants provided informed consent before enrollment in the study, and the Ethics Review Board at Tehran University of Medical Sciences approved this study [Code: IR.TUMS.REC.1395.2616].
2.2. Data acquisition procedure
All subjects were scanned while lying supine in a 3T whole-body MRI system (Siemens Magnetom Prisma; Siemens, Erlangen, Germany). Uniform radiofrequency (RF) pulses were transmitted with a body coil, while a matrix coil and the elements of a spine phased-array coil were used as receivers. Initial localizer images were acquired in three planes to provide a reference position for subsequent imaging.
Subjects were carefully positioned in the scanner and a pain paradigm was performed. The pain stimulation intensity was regulated to 120% of the calculated pressure pain threshold (Mean±SD: 4.691±0.577 kg) in the form of 60 monotonic pressure pain stimuli delivered on the L5 dermatome between the two malleoli in 6 blocks of 60 seconds during one run of 540 seconds.
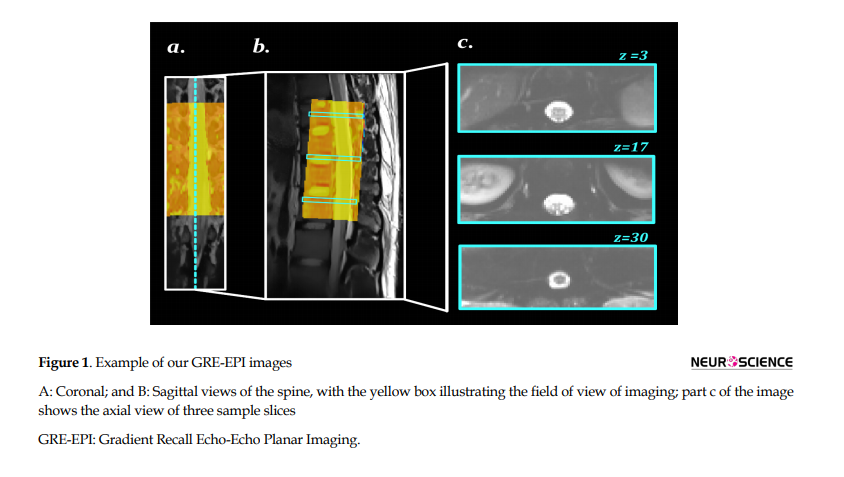
MRI images were acquired in an axial orientation and were sampled in an ascending, interleaved order between the ninth thoracic and the second lumbar vertebras with high-order shimming, optimized over the vertebral canal. We performed fMRI which was optimized to minimize the unwanted artifacts, as well as the susceptibility-induced signal drop-out. High-resolution functional images of the thoracic and lumbar spinal cord were acquired with a T2*-weighted GRE-EPI sequence using ZOOMit selective field-of-view imaging EPI (TR = 3000 ms; TE = 30 ms; FA = 80°; FOV = 160 × 160 mm; matrix size = 64 × 64; slice thickness = 4 mm; in-plane resolution = 2.5×2.5 mm; spectral attenuated inversion recovery [SPAIR]). Figure 1 shows some GRE-EPI images for the thoracolumbar spinal cord are shown in.
Cardiovascular and respiratory procedures were monitored utilizing the scanner’s photoplethysmograph, located on a finger of the left hand, and a pneumatic belt tied around and under the chest region, respectively. Heart and respiratory data were both inspected at 400 Hz on the Magnetom Prisma physiological monitoring unit. A record containing heartbeat trigger times and respiratory waveforms were produced for each scanning session. Quantities in the respiratory waveform were transformed to a level of the full scale (the distinction between the most extreme and least belt positions measured during imaging).
2.3. fMRI data preprocessing
Preprocessing steps were performed using the Oxford Center for fMRI of the Brain’s FMRIB software library (FSL) (Jenkinson, Beckmann, Behrens, Woolrich, & Smith, 2012; Smith et al., 2004), and Spinal Cord Toolbox (SCT) (De Leener et al., 2017). In the motion correction step, the effect of non-rigid motion of tissues outer on the vertebral column was decreased. This step was performed in two steps; I) 3D-realignment was performed using FMRIB’s linear image registration tool (Jenkinson, Bannister, Brady, & Smith, 2002) and II) the output of the previous step was entered into the 2D slice-wise realignment procedure by SliceReg, which estimates the slice-by-slice translations and regularization qualifications in the Z-axis direction (Cohen-Adad, Levy, & Avants, 2015; De Leener et al., 2017). In the motion correction level, we utilized a drawn binary cylindrical mask to cover the spinal cord and exclude other organs in the axial slices. The output of each motion correction level was visually and quantitatively (by calculating temporal SNR) inspected over the spinal cord and CSF, for quality control.
Then slice-timing correction and image intensity normalization procedures were applied. Advanced spatial smoothing was performed next with a Gaussian kernel of 2 mm full width half maximum (FWHM) in the straight spinal cord, and a high pass temporal filtering (sigma = 90 s). It is clear that the motion correction step does not remove all motion-related impacts and therefore, to complete this step, motion outlier volumes were identified with FSL’s motion outlier detection tool, and using the intensity-based DVARS (root mean square variance of intensity difference of volume N to volume N+1) metric and the default threshold calculated as follows: boxplot cutoff = 75th percentile + 1.5 × interquartile range (IQR) (Afyouni & Nichols, 2018; Power et al., 2014).
Spatial ICA categorizes signal components into either neural activity, unwanted impacts of artifacts, or physiological changes outside of the vertebral column. This step was performed in two levels, visual and quantitative characterization of the independent components. In the first step, activated clusters outside of the vertebral column were considered as a structure of non-physiological patterns such as the activated voxels in kidneys that are usually correlated to physiological noise (respiration, pulsation) (Griffanti et al., 2017). In the second step, components were obtained for each data set, and specified criteria were determined as noise: (a) the power of the spatial component’s time series at high frequencies were larger than 0.08 Hz (b) more than 50% of significantly activated voxels [Z > 2.3] was seen out of the manually drawn spinal cord and CSF mask in the component’s spatial map (Kelly Jr et al., 2010; Vahdat et al., 2015).
2.4. Physiological noise modelling
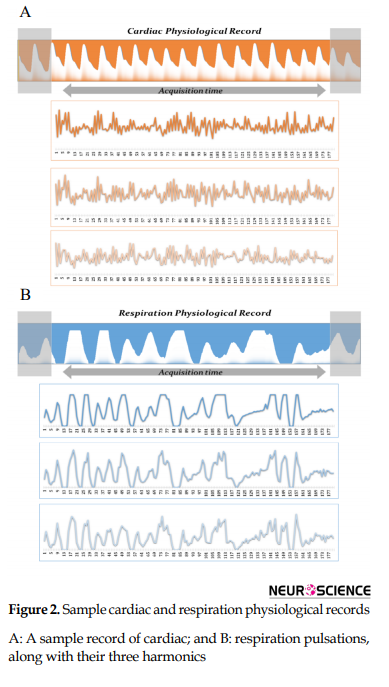
To remove the respiratory and cardiovascular effects, and to evaluate each source of physiological noise, slice-specific regressors were generated by MATLAB and using a custom-made algorithm, based on a model similar to the retrospective image correction (RETROICOR) and FSL’s physiological noise modeling tool (PNM) (Brooks et al., 2008; Glover, Li, & Ress; Glover, Li, & Ress, 2000). After distinction of the recorded physiological signal, a cardiac and respiratory phase was defined for each slice, and next the respiratory and cardiac signals were modeled using a Fourier series (sine and cosine terms), using the principal frequency and the next three harmonics (Glover et al., 2000). Figure 2 illustrates the example of respiration and cardiac noise regressors for GLM analysis.
Full-Text:
1. Introduction
unctional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) methods have been used to study sensorimotor processing in the brain and the spinal cord. Nowadays, spinal cord fMRI studies have investigated spinal cord in several pathologic conditions such as spinal cord injury (Alexander, Kozyrev, Figley & Richards, 2017; Cadotte et al., 2012; Chen, Mishra, Yang, Wang, & Gore, 2015; Chen, Kong, Wang, Xie, & Wu, 2007; Choe, 2017; Stroman et al., 2004; Stroman et al., 2016; Zhong et al., 2017), multiple sclerosis (Agosta et al., 2009; Agosta, Valsasina, Caputo, Stroman, & Filippi, 2008; Agosta et al., 2008; Kearney, Miller, & Ciccarelli, 2015; Rocca et al., 2012; Valsasina et al., 2010; Valsasina et al., 2012), chronic and neuropathic pain (Bosma et al., 2016; Leitch, Cahill, Ghazni, Figley, & Stroman, 2009), all of which need consistent and sensitive clinical results. However, there are numerous challenges for spinal cord fMRI which arises from the nature of spinal cord: bony structure of the vertebral canal; movement of the cord and adjacent tissues due to physiological processes such as swallowing, breathing, and so on; the CSF flux in the subarachnoid space circumambient the spinal cord; small cross-sectional dimensions of the spinal cord and; changing in the susceptibility of tissues due to breathing and bulk motion (Brooks et al., 2008; Fratini, Moraschi, Maraviglia, & Giove, 2014; Stroman et al., 2014; Verma & Cohen‐Adad, 2014). Some of these challenges can be addressed by improving the pulse sequence (Bosma & Stroman, 2014; Bouwman, Wilmink, Mess, & Backes, 2008; Cohen-Adad, 2017; Nash et al., 2013; Weber, Chen, Wang, Kahnt, & Parrish, 2016; Xie et al., 2009), utilizing relevant MR imaging equipment (Bodurka, Ledden, & Bandettini, 2008; Cohen‐Adad, Mareyam, Keil, Polimeni, & Wald, 2011; Topfer, Foias, Stikov, & Cohen-Adad, 2017; Topfer et al., 2016; Zhang, Seifert, Kim, Borrello, & Xu, 2017), correction of B0-related distortions (Finsterbusch, Eippert, & Büchel, 2012; Finsterbusch, Sprenger, & Büchel, 2013; Ryan et al., 2016; Topfer et al., 2016; Van Gelderen, De Zwart, Starewicz, Hinks, & Duyn, 2007), k-space sampling and Fourier image reconstruction (Agosta et al., 2008; Fruehwald-Pallamar et al., 2012; Glover, 2012; Griswold et al., 2002; Li, Yu, Griffin, Levine, & Ji, 2015; Moeller et al., 2010; Nash et al., 2013), acquisition-based k- and image-space corrections (Bollmann et al., 2017; Brooks, 2014; Xie et al., 2012), and raw-data processing in the form of signal and image (Brooks et al., 2008; Brooks, 2014; Cohen-Adad, Rossignol, & Hoge, 2009; Kong, Jenkinson, Andersson, Tracey, & Brooks, 2012; Piché et al., 2009; Stroman, 2006; Xie et al., 2012). Although these solutions help improve the signal quality, ultimately the effect of physiological fluctuations’ contribution to the measured signal is still controversial (Caballero-Gaudes & Reynolds, 2017; Kong et al., 2012). Several sources of physiological noises have been described in the fMRI literature, including those associated with cardiac and respiratory processes which were recognized as the most significant ones (Brooks, 2014; Fratini et al., 2014; Kong et al., 2014). Spinal cord in thoracolumbar is close to the lungs and the diaphragm, that influence cerebrospinal fluid-filled spaces and cause changes in the susceptibility due to the changes in the amount of air in the lung (Tillieux et al., 2018; Verma & Cohen‐Adad, 2014). Cardiac physiological noise is produced as a result of changes in Cerebral Blood Flow (CBF), Cerebral Blood Volume (CBV), arterial pulsatility, and effect of those on the CSF flow (Fratini et al., 2014; Parrish, Gitelman, LaBar, & Mesulam, 2000). On the other hand, spinal cord in thoracolumbar is close to the lungs and the diaphragm, that influences cerebrospinal fluid-filled spaces and causes changes in the susceptibility due to the changes in the amount of air in the lung (Verma & Cohen‐Adad, 2014).
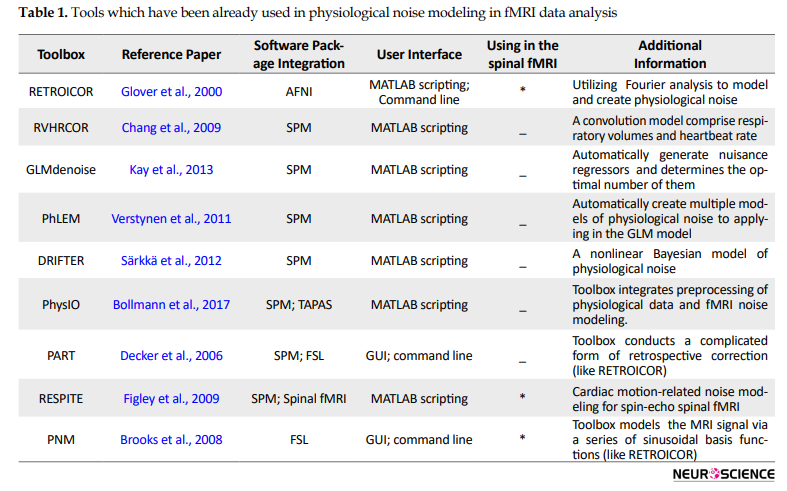
Solutions for the effect of physiological noise in the spinal cord fMRI data series are categorized into three: strategies of image acquisition, preprocessing strategies, and physiological noise modeling in the general linear model (GLM) analysis for the first level data processing (Brooks, 2014). There are two main strategies for the acquisition of spinal cord fMRI data. First, imaging in axial orientation with Gradient Recall Echo-Echo Planar Imaging (GRE-EPI) sequence that has a high in-plane resolution to make difference between white matter and gray matter. GRE-EPI sequence combining double-shot spiral in/out trajectories can reduce physiological noise in spinal cord fMRI by diminishing susceptibility-induced B0 field variations. Second, imaging in sagittal orientation to cover the considerable part of the spinal cord for the mapping based on the segments which remove susceptibility artifact which is necessary to suppress the effect of respiration using Fast Spin-Echo pulse (FSE) sequence and has a high contrast to noise ratio (Cohen-Adad, 2017; Leitch, Figley, & Stroman, 2010). In some previous studies, researchers used cardiac and respiratory gating to suppress the effect of respiration and heartbeat in the image acquisition strategies (Backes, Mess, & Wilmink, 2001; Mainero, Zhang, Kumar, Rosen, & Sorensen, 2007; Stroman & Ryner, 2000; Stroman & Ryner, 2001), but the cardiac and respiration gating alone is suggested not being sufficient in eliminating the noise. Alternative solutions for detecting and mitigating physiological noise are based on recommendations for pre-processing spinal cord fMRI data. These recommendations include combining pre-whitening with high-pass filtering (Eippert, Kong, Jenkinson, Tracey, & Brooks, 2017; Xie et al., 2012) and identifying and scrubbing noise components which are obtained from spatiotemporal decomposing fMRI signal by Independent Component Analysis (ICA)- and principal component analysis (PCA)-based methods (Hu, Jin, Li, Luk, & Wu, 2018; Xie et al., 2012). Furthermore, the main solution for spinal cord fMRI analysis is the methods based on GLM fitting of noise regressors. These methods are generated from the principal components of spinal cord physiological motion-related signal fluctuation, along with functionally-relevant signal changes. These regressors will be given from subject-specific cardiac and respiration recorded data during the imaging session (Brooks, 2014; Figley & Stroman, 2009; Kong et al., 2014). The toolboxes which can be used in fMRI data analysis are summarized in Table 1.
unctional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) methods have been used to study sensorimotor processing in the brain and the spinal cord. Nowadays, spinal cord fMRI studies have investigated spinal cord in several pathologic conditions such as spinal cord injury (Alexander, Kozyrev, Figley & Richards, 2017; Cadotte et al., 2012; Chen, Mishra, Yang, Wang, & Gore, 2015; Chen, Kong, Wang, Xie, & Wu, 2007; Choe, 2017; Stroman et al., 2004; Stroman et al., 2016; Zhong et al., 2017), multiple sclerosis (Agosta et al., 2009; Agosta, Valsasina, Caputo, Stroman, & Filippi, 2008; Agosta et al., 2008; Kearney, Miller, & Ciccarelli, 2015; Rocca et al., 2012; Valsasina et al., 2010; Valsasina et al., 2012), chronic and neuropathic pain (Bosma et al., 2016; Leitch, Cahill, Ghazni, Figley, & Stroman, 2009), all of which need consistent and sensitive clinical results. However, there are numerous challenges for spinal cord fMRI which arises from the nature of spinal cord: bony structure of the vertebral canal; movement of the cord and adjacent tissues due to physiological processes such as swallowing, breathing, and so on; the CSF flux in the subarachnoid space circumambient the spinal cord; small cross-sectional dimensions of the spinal cord and; changing in the susceptibility of tissues due to breathing and bulk motion (Brooks et al., 2008; Fratini, Moraschi, Maraviglia, & Giove, 2014; Stroman et al., 2014; Verma & Cohen‐Adad, 2014). Some of these challenges can be addressed by improving the pulse sequence (Bosma & Stroman, 2014; Bouwman, Wilmink, Mess, & Backes, 2008; Cohen-Adad, 2017; Nash et al., 2013; Weber, Chen, Wang, Kahnt, & Parrish, 2016; Xie et al., 2009), utilizing relevant MR imaging equipment (Bodurka, Ledden, & Bandettini, 2008; Cohen‐Adad, Mareyam, Keil, Polimeni, & Wald, 2011; Topfer, Foias, Stikov, & Cohen-Adad, 2017; Topfer et al., 2016; Zhang, Seifert, Kim, Borrello, & Xu, 2017), correction of B0-related distortions (Finsterbusch, Eippert, & Büchel, 2012; Finsterbusch, Sprenger, & Büchel, 2013; Ryan et al., 2016; Topfer et al., 2016; Van Gelderen, De Zwart, Starewicz, Hinks, & Duyn, 2007), k-space sampling and Fourier image reconstruction (Agosta et al., 2008; Fruehwald-Pallamar et al., 2012; Glover, 2012; Griswold et al., 2002; Li, Yu, Griffin, Levine, & Ji, 2015; Moeller et al., 2010; Nash et al., 2013), acquisition-based k- and image-space corrections (Bollmann et al., 2017; Brooks, 2014; Xie et al., 2012), and raw-data processing in the form of signal and image (Brooks et al., 2008; Brooks, 2014; Cohen-Adad, Rossignol, & Hoge, 2009; Kong, Jenkinson, Andersson, Tracey, & Brooks, 2012; Piché et al., 2009; Stroman, 2006; Xie et al., 2012). Although these solutions help improve the signal quality, ultimately the effect of physiological fluctuations’ contribution to the measured signal is still controversial (Caballero-Gaudes & Reynolds, 2017; Kong et al., 2012). Several sources of physiological noises have been described in the fMRI literature, including those associated with cardiac and respiratory processes which were recognized as the most significant ones (Brooks, 2014; Fratini et al., 2014; Kong et al., 2014). Spinal cord in thoracolumbar is close to the lungs and the diaphragm, that influence cerebrospinal fluid-filled spaces and cause changes in the susceptibility due to the changes in the amount of air in the lung (Tillieux et al., 2018; Verma & Cohen‐Adad, 2014). Cardiac physiological noise is produced as a result of changes in Cerebral Blood Flow (CBF), Cerebral Blood Volume (CBV), arterial pulsatility, and effect of those on the CSF flow (Fratini et al., 2014; Parrish, Gitelman, LaBar, & Mesulam, 2000). On the other hand, spinal cord in thoracolumbar is close to the lungs and the diaphragm, that influences cerebrospinal fluid-filled spaces and causes changes in the susceptibility due to the changes in the amount of air in the lung (Verma & Cohen‐Adad, 2014).
Solutions for the effect of physiological noise in the spinal cord fMRI data series are categorized into three: strategies of image acquisition, preprocessing strategies, and physiological noise modeling in the general linear model (GLM) analysis for the first level data processing (Brooks, 2014). There are two main strategies for the acquisition of spinal cord fMRI data. First, imaging in axial orientation with Gradient Recall Echo-Echo Planar Imaging (GRE-EPI) sequence that has a high in-plane resolution to make difference between white matter and gray matter. GRE-EPI sequence combining double-shot spiral in/out trajectories can reduce physiological noise in spinal cord fMRI by diminishing susceptibility-induced B0 field variations. Second, imaging in sagittal orientation to cover the considerable part of the spinal cord for the mapping based on the segments which remove susceptibility artifact which is necessary to suppress the effect of respiration using Fast Spin-Echo pulse (FSE) sequence and has a high contrast to noise ratio (Cohen-Adad, 2017; Leitch, Figley, & Stroman, 2010). In some previous studies, researchers used cardiac and respiratory gating to suppress the effect of respiration and heartbeat in the image acquisition strategies (Backes, Mess, & Wilmink, 2001; Mainero, Zhang, Kumar, Rosen, & Sorensen, 2007; Stroman & Ryner, 2000; Stroman & Ryner, 2001), but the cardiac and respiration gating alone is suggested not being sufficient in eliminating the noise. Alternative solutions for detecting and mitigating physiological noise are based on recommendations for pre-processing spinal cord fMRI data. These recommendations include combining pre-whitening with high-pass filtering (Eippert, Kong, Jenkinson, Tracey, & Brooks, 2017; Xie et al., 2012) and identifying and scrubbing noise components which are obtained from spatiotemporal decomposing fMRI signal by Independent Component Analysis (ICA)- and principal component analysis (PCA)-based methods (Hu, Jin, Li, Luk, & Wu, 2018; Xie et al., 2012). Furthermore, the main solution for spinal cord fMRI analysis is the methods based on GLM fitting of noise regressors. These methods are generated from the principal components of spinal cord physiological motion-related signal fluctuation, along with functionally-relevant signal changes. These regressors will be given from subject-specific cardiac and respiration recorded data during the imaging session (Brooks, 2014; Figley & Stroman, 2009; Kong et al., 2014). The toolboxes which can be used in fMRI data analysis are summarized in Table 1.
Previous research suggested that the lumbar spinal cord is motionless and the noise fitting can be ignored (Figley, Yau, & Stroman, 2008). Others only considered the cardiac motion-related effects on the spinal cord and CSF (Alexander et al., 2017; Alexander et al., 2016; R. Bosma & Stroman, 2015; Figley & Stroman, 2009; Kozyrev et al., 2012), and both these approaches may lead to biased information due to ignoring the respiration noise as one of the main sources of noise production. In this study, we investigated the effect of each source of physiological noise and their contributions to the outcome of the analysis of the Blood-Oxygen-Level-Dependent (BOLD) signal by recording the changes in the heart-beat and respiration during fMRI experiments. We determined the quota of respiration and heartbeat physiological noise in thoracolumbar spinal cord neural activity detected by fMRI and evaluated the impact of this physiological noise on false-positive rates.
2. Methods
2.1. Study participants
The participants included 15 right-handed healthy adults (14 males, Mean±SD age=25.88±4.44 years). None of the participants had any history or evidence of spinal cord/vertebral injury or dysmorphology. The participants provided informed consent before enrollment in the study, and the Ethics Review Board at Tehran University of Medical Sciences approved this study [Code: IR.TUMS.REC.1395.2616].
2.2. Data acquisition procedure
All subjects were scanned while lying supine in a 3T whole-body MRI system (Siemens Magnetom Prisma; Siemens, Erlangen, Germany). Uniform radiofrequency (RF) pulses were transmitted with a body coil, while a matrix coil and the elements of a spine phased-array coil were used as receivers. Initial localizer images were acquired in three planes to provide a reference position for subsequent imaging.
Subjects were carefully positioned in the scanner and a pain paradigm was performed. The pain stimulation intensity was regulated to 120% of the calculated pressure pain threshold (Mean±SD: 4.691±0.577 kg) in the form of 60 monotonic pressure pain stimuli delivered on the L5 dermatome between the two malleoli in 6 blocks of 60 seconds during one run of 540 seconds.
MRI images were acquired in an axial orientation and were sampled in an ascending, interleaved order between the ninth thoracic and the second lumbar vertebras with high-order shimming, optimized over the vertebral canal. We performed fMRI which was optimized to minimize the unwanted artifacts, as well as the susceptibility-induced signal drop-out. High-resolution functional images of the thoracic and lumbar spinal cord were acquired with a T2*-weighted GRE-EPI sequence using ZOOMit selective field-of-view imaging EPI (TR = 3000 ms; TE = 30 ms; FA = 80°; FOV = 160 × 160 mm; matrix size = 64 × 64; slice thickness = 4 mm; in-plane resolution = 2.5×2.5 mm; spectral attenuated inversion recovery [SPAIR]). Figure 1 shows some GRE-EPI images for the thoracolumbar spinal cord are shown in.

Cardiovascular and respiratory procedures were monitored utilizing the scanner’s photoplethysmograph, located on a finger of the left hand, and a pneumatic belt tied around and under the chest region, respectively. Heart and respiratory data were both inspected at 400 Hz on the Magnetom Prisma physiological monitoring unit. A record containing heartbeat trigger times and respiratory waveforms were produced for each scanning session. Quantities in the respiratory waveform were transformed to a level of the full scale (the distinction between the most extreme and least belt positions measured during imaging).
2.3. fMRI data preprocessing
Preprocessing steps were performed using the Oxford Center for fMRI of the Brain’s FMRIB software library (FSL) (Jenkinson, Beckmann, Behrens, Woolrich, & Smith, 2012; Smith et al., 2004), and Spinal Cord Toolbox (SCT) (De Leener et al., 2017). In the motion correction step, the effect of non-rigid motion of tissues outer on the vertebral column was decreased. This step was performed in two steps; I) 3D-realignment was performed using FMRIB’s linear image registration tool (Jenkinson, Bannister, Brady, & Smith, 2002) and II) the output of the previous step was entered into the 2D slice-wise realignment procedure by SliceReg, which estimates the slice-by-slice translations and regularization qualifications in the Z-axis direction (Cohen-Adad, Levy, & Avants, 2015; De Leener et al., 2017). In the motion correction level, we utilized a drawn binary cylindrical mask to cover the spinal cord and exclude other organs in the axial slices. The output of each motion correction level was visually and quantitatively (by calculating temporal SNR) inspected over the spinal cord and CSF, for quality control.
Then slice-timing correction and image intensity normalization procedures were applied. Advanced spatial smoothing was performed next with a Gaussian kernel of 2 mm full width half maximum (FWHM) in the straight spinal cord, and a high pass temporal filtering (sigma = 90 s). It is clear that the motion correction step does not remove all motion-related impacts and therefore, to complete this step, motion outlier volumes were identified with FSL’s motion outlier detection tool, and using the intensity-based DVARS (root mean square variance of intensity difference of volume N to volume N+1) metric and the default threshold calculated as follows: boxplot cutoff = 75th percentile + 1.5 × interquartile range (IQR) (Afyouni & Nichols, 2018; Power et al., 2014).
Spatial ICA categorizes signal components into either neural activity, unwanted impacts of artifacts, or physiological changes outside of the vertebral column. This step was performed in two levels, visual and quantitative characterization of the independent components. In the first step, activated clusters outside of the vertebral column were considered as a structure of non-physiological patterns such as the activated voxels in kidneys that are usually correlated to physiological noise (respiration, pulsation) (Griffanti et al., 2017). In the second step, components were obtained for each data set, and specified criteria were determined as noise: (a) the power of the spatial component’s time series at high frequencies were larger than 0.08 Hz (b) more than 50% of significantly activated voxels [Z > 2.3] was seen out of the manually drawn spinal cord and CSF mask in the component’s spatial map (Kelly Jr et al., 2010; Vahdat et al., 2015).
2.4. Physiological noise modelling
To remove the respiratory and cardiovascular effects, and to evaluate each source of physiological noise, slice-specific regressors were generated by MATLAB and using a custom-made algorithm, based on a model similar to the retrospective image correction (RETROICOR) and FSL’s physiological noise modeling tool (PNM) (Brooks et al., 2008; Glover, Li, & Ress; Glover, Li, & Ress, 2000). After distinction of the recorded physiological signal, a cardiac and respiratory phase was defined for each slice, and next the respiratory and cardiac signals were modeled using a Fourier series (sine and cosine terms), using the principal frequency and the next three harmonics (Glover et al., 2000). Figure 2 illustrates the example of respiration and cardiac noise regressors for GLM analysis.
2.4.1. General Linear Model analysis
FMRIB’s Improved Linear Model (FILM) with prewhitening was used to create statistical maps of the filtered data-sets (Woolrich, Ripley, Brady, & Smith, 2001; Worsley et al., 2002). The generated design matrix was included as the hemodynamic response function (gamma, phase 0 s, standard deviation 3 s, average lag 6 s) convolved pain paradigm vectors. In this design matrix, the voxel-wise cardiac and respiration effects vectors, and the temporal masks of outlier time points were also included. Voxels with a P<0.05 (uncorrected) were considered as active, separately in the spinal cord and the CSF.
2.5. Statistical evaluation
The activated voxels of the clusters were obtained from each data set in four levels: 1) without any physiological noise correction, 2) with respiration noise correction, 3) with cardiac noise correction, and 4) with cardiac along with respiration physiological effects correction. The mean value of each parameter was computed and the analysis was performed using SPSS (Version 16.0, The SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and MATLAB (Version R2016a, The MathWorks, Inc., Natick, MA, USA). Normal distribution of the active voxels in different correction levels was assessed with the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. The average value of the active voxels in the spinal cord and CSF were processed with 1-way ANOVA with repeated measures in a within-subject comparison.
For each Z-score map, sensitivity and specificity were determined by comparing the spatial locations of activated voxels. Sensitivity was estimated as the percentage of active voxels in the physiological corrected data-sets via respiration + cardiac effect modeling that was correctly detected as activated, and specificity was described as the percentage of voxels correctly detected as non-activated.
Comparisons between different source noise effects and noise modeling methods were assessed by using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves (Constable, Skudlarski, & Gore, 1995; Skudlarski, Constable, & Gore, 1999; Sorenson & Wang, 1996). ROC curves have been utilized extensively as a tool for objective comparisons of various methods in fMRI studies (Bowring, Maumet, & Nichols, 2018; Wang, Wang, Aguirre, & Detre, 2005; Zhong, Zheng, Liu, & Lu, 2014). The attributes of the distribution of the probability of the signals and noise, and the degree to which they overlap, affect the accurate state of the ROC curve but do not make a hypothesis about these distributions (Sorenson & Wang, 1996).
3. Results
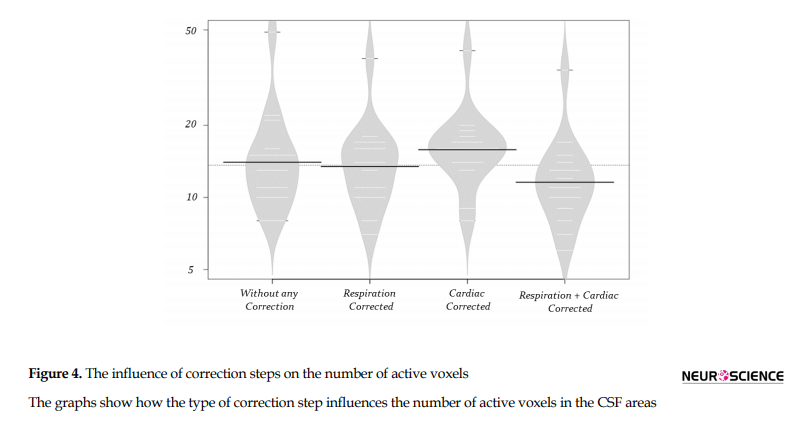
Comparison of the sum of active voxels in the spinal cord and share of each in the activated clusters are illustrated in Figures 3 and 4 and explained in Table 2.

Also, in Table 2, the results of descriptive statistical data analysis are presented. One-way within-subjects or repeated-measures ANOVA was utilized to evaluate the effect of physiological functions on spinal cord fMRI datasets, in the 4 correction levels. There was a statistically significant effect of physiological noise correction on the number of active voxels in the spinal cord (F3,42 = 21.314, P <0.001, 0.21), and in CSF (F3,42= 63.2, P <0.05, ,0.28) . The Bonferroni post hoc test results indicate that cardiac noise correction had an effective role in the increased number of active voxels in both the spinal cord (Mean±SD = 23.46±9.46) and CSF (Mean±SD = 16.99±7.43) compared to other noise correction methods.
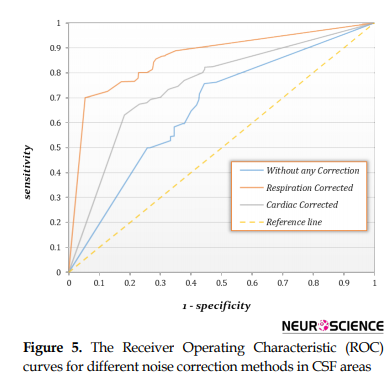
The results of ROC analysis of spinal cord and CSF GLM results in the different physiological noise correction levels are illustrated in Figures 5 and 6, and summarized in Table 3 and 4.
FMRIB’s Improved Linear Model (FILM) with prewhitening was used to create statistical maps of the filtered data-sets (Woolrich, Ripley, Brady, & Smith, 2001; Worsley et al., 2002). The generated design matrix was included as the hemodynamic response function (gamma, phase 0 s, standard deviation 3 s, average lag 6 s) convolved pain paradigm vectors. In this design matrix, the voxel-wise cardiac and respiration effects vectors, and the temporal masks of outlier time points were also included. Voxels with a P<0.05 (uncorrected) were considered as active, separately in the spinal cord and the CSF.
2.5. Statistical evaluation
The activated voxels of the clusters were obtained from each data set in four levels: 1) without any physiological noise correction, 2) with respiration noise correction, 3) with cardiac noise correction, and 4) with cardiac along with respiration physiological effects correction. The mean value of each parameter was computed and the analysis was performed using SPSS (Version 16.0, The SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and MATLAB (Version R2016a, The MathWorks, Inc., Natick, MA, USA). Normal distribution of the active voxels in different correction levels was assessed with the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. The average value of the active voxels in the spinal cord and CSF were processed with 1-way ANOVA with repeated measures in a within-subject comparison.
For each Z-score map, sensitivity and specificity were determined by comparing the spatial locations of activated voxels. Sensitivity was estimated as the percentage of active voxels in the physiological corrected data-sets via respiration + cardiac effect modeling that was correctly detected as activated, and specificity was described as the percentage of voxels correctly detected as non-activated.
Comparisons between different source noise effects and noise modeling methods were assessed by using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves (Constable, Skudlarski, & Gore, 1995; Skudlarski, Constable, & Gore, 1999; Sorenson & Wang, 1996). ROC curves have been utilized extensively as a tool for objective comparisons of various methods in fMRI studies (Bowring, Maumet, & Nichols, 2018; Wang, Wang, Aguirre, & Detre, 2005; Zhong, Zheng, Liu, & Lu, 2014). The attributes of the distribution of the probability of the signals and noise, and the degree to which they overlap, affect the accurate state of the ROC curve but do not make a hypothesis about these distributions (Sorenson & Wang, 1996).
3. Results
Comparison of the sum of active voxels in the spinal cord and share of each in the activated clusters are illustrated in Figures 3 and 4 and explained in Table 2.

Also, in Table 2, the results of descriptive statistical data analysis are presented. One-way within-subjects or repeated-measures ANOVA was utilized to evaluate the effect of physiological functions on spinal cord fMRI datasets, in the 4 correction levels. There was a statistically significant effect of physiological noise correction on the number of active voxels in the spinal cord (F3,42 = 21.314, P <0.001, 0.21), and in CSF (F3,42= 63.2, P <0.05, ,0.28) . The Bonferroni post hoc test results indicate that cardiac noise correction had an effective role in the increased number of active voxels in both the spinal cord (Mean±SD = 23.46±9.46) and CSF (Mean±SD = 16.99±7.43) compared to other noise correction methods.
The results of ROC analysis of spinal cord and CSF GLM results in the different physiological noise correction levels are illustrated in Figures 5 and 6, and summarized in Table 3 and 4.

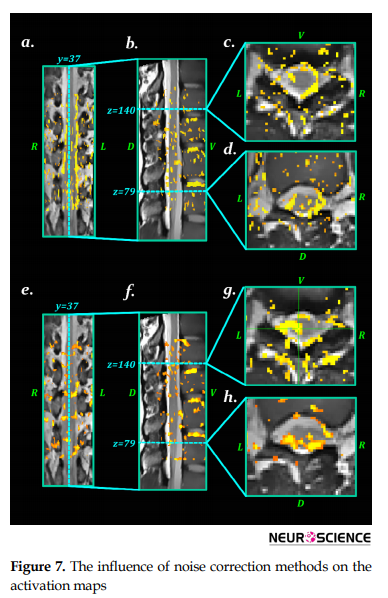
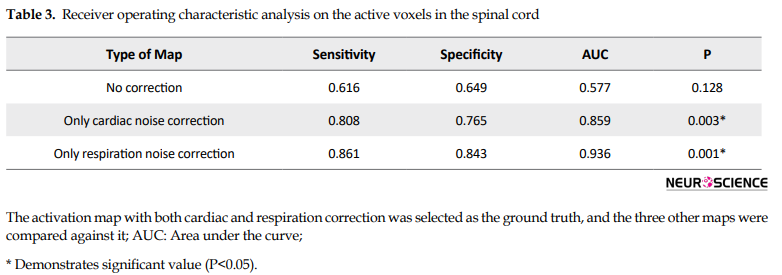
Overall performance of the correction method was rated as the area under the ROC curve (AUC), considering both uncorrected fMRI analysis results and alternative physiological effects. In the evaluation of physiological noise of both corrected and uncorrected spinal cord fMRI results, the AUC corresponding to the cardiac effect correction was 0.856 (P<0.05), and it was 0.936 (P<0.05) for the respiration effect correction. In the CSF, the AUC corresponding to the cardiac effect correction was 0.751 (P<0.05), and 0.864 (P<0.05) for the respiration effect (Figure 7). Table 4 summarizes the results of the ROC analysis.
4. Discussion
The heartbeat- and respiration-related movements are the main sources of physiological noise in the spine. Because of the concurrency between movements and tasks, correction of this movement can influence the observed effects of stimulations. Respiration effect is suggested to be the most important source, and its effects on the results are higher than the other sources of noise in the thoracolumbar and lumbar GRE-EPI fMRI. In this study, the effect of respiration physiological noise was strongly observed in the cardiac noise-corrected datasets, and ROC analysis demonstrated that the sensitivity and specificity of the respiration effect correction were increased. This result can be explained by considering the bulk magnetic susceptibility changes and the associated B0 shifts in the spinal cord by respiration and the changes in the volume of lungs (Tillieux et al., 2018; Verma, 2014). B0 field shifting is reported to affect the pre-processing and GLM analysis of the spinal cord fMRI data (Durand, van de Moortele, Pachot‐Clouard, & Le Bihan, 2001; Parkes, Fulcher, Yu, & Fornitod, 2018; Raj, Anderson, & Gore, 2001; Yeo, Fessler, & Kim, 2008).
The other source of noise is the physiological motion of the spinal cord by the respiration effects. The differences between the respiration and heartbeat noises were assessed in this study, and the results showed that the effects of respiration on lumbar and thoracolumbar spinal cord physiological movements, as well as on the CSF flow, are significantly greater than the effects of the heartbeat. The impact of cardiac and respiration effects on spinal cord movements has been illustrated in previous studies as well (Figley et al., 2008; Winklhofer et al., 2014; Yildiz et al., 2017). The effect of respiration is more frequently studied than the heartbeat (Winklhofer et al., 2014; Yildiz et al., 2017), and these effects were reported to be reduced in the lower parts of the vertebral column (Yildiz et al., 2017).
For spinal fMRI acquisition, researchers mostly use two MR imaging pulse sequences: HASTE/SS-FSE and GRE-EPI MR (Bouwman et al., 2008; Stroman et al., 2014). The effects of respiration on B0 bulk susceptibility are greater than the heartbeat in the GRE-EPI sequence. The HASTE/SS-FSE is not sensitive to the susceptibilities in the vertebral column, the intervertebral disks, and the air‐filled lung (Poser & Norris, 2007; Stroman et al., 2014; Ye, Zhuo, Xue, & Zhou, 2010).
As mentioned previously, the lumbar and sacral spinal cord are motionless in the three directions, suggesting that the spinal cord physiological motion can be ignored as a confounding factor for fMRI (Figley et al., 2008). This was observed in the HASTE/SS-FSE lumbar and thoracolumbar spinal cord fMRI as well (Alexander et al., 2017; Alexander et al., 2016; Kornelsen, Smith, & McIver, 2014; Kornelsen et al., 2013; Kozyrev et al., 2012), by using RESPITE to remove residual cardiac noise effects (Figley & Stroman, 2009). Previous studies have shown the lumbar spinal cord (L1, L2) movements to be greater than lower thoracic spinal cord (T7, T8, T9, T10) movements due to breathing (Winklhofer et al., 2014; Yildiz et al., 2017), and therefore our study suggests that the effect of respiration on physiological noise should be considered in the spinal cord fMRI analysis.
In older spinal fMRI studies, the physiological noise correction was rarely performed, and therefore in some of those studies, the activation voxels in the spinal cord were correlated with the motion caused by physiological functions (Chen et al., 2007; Komisaruk et al., 2002; Madi, Flanders, Vinitski, Herbison, & Nissanov, 2001; Maieron et al., 2007; Ng et al., 2008; Yoshizawa, Nose, Moore, & Sillerud, 1996). As an example, Kashkouli Nejad et al. investigated the impacts of interoceptive attention/awareness training on spinal cord neural activity (Kashkouli Nejad et al., 2014), which is an interesting finding; however, this study was limited by not recording the physiological measurements to correct the fMRI signal, which shows the need for replication of the results of this study.
4.1. Study limitations
Despite the interesting findings of this study, some limitations should be considered. The interaction between respiration and heartbeat is important, which is ignored here. Also, the ICA-based motion and artifact corrections are better to be applied only to the tissue of interest, which was not considered here. And finally, this study only used a GRE-EPI optimized pulse sequence, and for more reliable results, this procedure should be replicated for a HASTE/SS-FSE protocol in the sagittal orientation.
This study is novel research on physiological noise sources and their impacts on the spinal cord fMRI in the lumbar and thoracolumbar regions and illustrated that the respiration effects along with the heartbeat have much influence on the individual fMRI data and the outcomes of the analysis. These results show that correcting the fMRI data of the lower parts of the spinal cord for such effects is very essential. These physiological noise corrections can help obtain pure physiological reactions related to neural activities. For future studies, the k-space motion correction and detecting motions during the MRI acquisition can be suggested to decrease the effect of physiological noise sources, especially the respiration.
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
All procedures were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, revised in 2008. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects to be included in the study.
Funding
This project was supported by Tehran University of Medical Sciences, (Grant No. 94-03-30-29965).
Authors' contributions
All authors equally contributed to preparing this article.
Conflict of interest
All authors confirm that they have no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the use of the services and facilities of the National Brain Mapping Laboratory (NBML) and also thank Elaheh Sadri, Soodeh Moallemian, and Elaheh Saleh for their helpful discussions, as well as the feedback given by the anonymous reviewers.
4. Discussion
The heartbeat- and respiration-related movements are the main sources of physiological noise in the spine. Because of the concurrency between movements and tasks, correction of this movement can influence the observed effects of stimulations. Respiration effect is suggested to be the most important source, and its effects on the results are higher than the other sources of noise in the thoracolumbar and lumbar GRE-EPI fMRI. In this study, the effect of respiration physiological noise was strongly observed in the cardiac noise-corrected datasets, and ROC analysis demonstrated that the sensitivity and specificity of the respiration effect correction were increased. This result can be explained by considering the bulk magnetic susceptibility changes and the associated B0 shifts in the spinal cord by respiration and the changes in the volume of lungs (Tillieux et al., 2018; Verma, 2014). B0 field shifting is reported to affect the pre-processing and GLM analysis of the spinal cord fMRI data (Durand, van de Moortele, Pachot‐Clouard, & Le Bihan, 2001; Parkes, Fulcher, Yu, & Fornitod, 2018; Raj, Anderson, & Gore, 2001; Yeo, Fessler, & Kim, 2008).
The other source of noise is the physiological motion of the spinal cord by the respiration effects. The differences between the respiration and heartbeat noises were assessed in this study, and the results showed that the effects of respiration on lumbar and thoracolumbar spinal cord physiological movements, as well as on the CSF flow, are significantly greater than the effects of the heartbeat. The impact of cardiac and respiration effects on spinal cord movements has been illustrated in previous studies as well (Figley et al., 2008; Winklhofer et al., 2014; Yildiz et al., 2017). The effect of respiration is more frequently studied than the heartbeat (Winklhofer et al., 2014; Yildiz et al., 2017), and these effects were reported to be reduced in the lower parts of the vertebral column (Yildiz et al., 2017).
For spinal fMRI acquisition, researchers mostly use two MR imaging pulse sequences: HASTE/SS-FSE and GRE-EPI MR (Bouwman et al., 2008; Stroman et al., 2014). The effects of respiration on B0 bulk susceptibility are greater than the heartbeat in the GRE-EPI sequence. The HASTE/SS-FSE is not sensitive to the susceptibilities in the vertebral column, the intervertebral disks, and the air‐filled lung (Poser & Norris, 2007; Stroman et al., 2014; Ye, Zhuo, Xue, & Zhou, 2010).
As mentioned previously, the lumbar and sacral spinal cord are motionless in the three directions, suggesting that the spinal cord physiological motion can be ignored as a confounding factor for fMRI (Figley et al., 2008). This was observed in the HASTE/SS-FSE lumbar and thoracolumbar spinal cord fMRI as well (Alexander et al., 2017; Alexander et al., 2016; Kornelsen, Smith, & McIver, 2014; Kornelsen et al., 2013; Kozyrev et al., 2012), by using RESPITE to remove residual cardiac noise effects (Figley & Stroman, 2009). Previous studies have shown the lumbar spinal cord (L1, L2) movements to be greater than lower thoracic spinal cord (T7, T8, T9, T10) movements due to breathing (Winklhofer et al., 2014; Yildiz et al., 2017), and therefore our study suggests that the effect of respiration on physiological noise should be considered in the spinal cord fMRI analysis.
In older spinal fMRI studies, the physiological noise correction was rarely performed, and therefore in some of those studies, the activation voxels in the spinal cord were correlated with the motion caused by physiological functions (Chen et al., 2007; Komisaruk et al., 2002; Madi, Flanders, Vinitski, Herbison, & Nissanov, 2001; Maieron et al., 2007; Ng et al., 2008; Yoshizawa, Nose, Moore, & Sillerud, 1996). As an example, Kashkouli Nejad et al. investigated the impacts of interoceptive attention/awareness training on spinal cord neural activity (Kashkouli Nejad et al., 2014), which is an interesting finding; however, this study was limited by not recording the physiological measurements to correct the fMRI signal, which shows the need for replication of the results of this study.
4.1. Study limitations
Despite the interesting findings of this study, some limitations should be considered. The interaction between respiration and heartbeat is important, which is ignored here. Also, the ICA-based motion and artifact corrections are better to be applied only to the tissue of interest, which was not considered here. And finally, this study only used a GRE-EPI optimized pulse sequence, and for more reliable results, this procedure should be replicated for a HASTE/SS-FSE protocol in the sagittal orientation.
This study is novel research on physiological noise sources and their impacts on the spinal cord fMRI in the lumbar and thoracolumbar regions and illustrated that the respiration effects along with the heartbeat have much influence on the individual fMRI data and the outcomes of the analysis. These results show that correcting the fMRI data of the lower parts of the spinal cord for such effects is very essential. These physiological noise corrections can help obtain pure physiological reactions related to neural activities. For future studies, the k-space motion correction and detecting motions during the MRI acquisition can be suggested to decrease the effect of physiological noise sources, especially the respiration.
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
All procedures were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, revised in 2008. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects to be included in the study.
Funding
This project was supported by Tehran University of Medical Sciences, (Grant No. 94-03-30-29965).
Authors' contributions
All authors equally contributed to preparing this article.
Conflict of interest
All authors confirm that they have no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the use of the services and facilities of the National Brain Mapping Laboratory (NBML) and also thank Elaheh Sadri, Soodeh Moallemian, and Elaheh Saleh for their helpful discussions, as well as the feedback given by the anonymous reviewers.
References
Afyouni, S., & Nichols, T. E. (2018). Insight and Inference for DVARS. NeuroImage, 172, 291-312. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.12.098]
Agosta, F., Valsasina, P., Absinta, M., Sala, S., Caputo, D., & Filippi, M. (2009). Primary progressive multiple sclerosis: Tactile-associated functional MR activity in the cervical spinal cord. Radiology, 253(1), 209-15. [DOI:10.1148/radiol.2532090187] [PMID]
Agosta, F., Valsasina, P., Caputo, D., Stroman, P. W., & Filippi, M. (2008). Tactile-associated recruitment of the cervical cord is altered in patients with multiple sclerosis. NeuroImage, 39(4), 1542-8. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.10.048] [PMID]
Agosta, F., Valsasina, P., Rocca, M., Caputo, D., Sala, S., & Judica, E., et al. (2008). Evidence for enhanced functional activity of cervical cord in relapsing multiple sclerosis. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 59(5), 1035-42. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.21595] [PMID]
Alexander, M. S., Kozyrev, N., Bosma, R. L., Figley, C. R., Richards, J. S., & Stroman, P. W. (2016). fMRI localization of spinal cord processing underlying female sexual arousal. Journal of Sex & Marital Therapy, 42(1), 36-47. [DOI:10.1080/0092623X.2015.1010674] [PMID]
Alexander, M., Kozyrev, N., Figley, C. R., & Richards, J. S. (2017). Altered spinal cord activity during sexual stimulation in women with SCI: A pilot fMRI study. Spinal Cord Series and Cases, 3, 16041. [DOI:10.1038/scsandc.2016.41] [PMID] [PMCID]
Backes, W. H., Mess, W. H., & Wilmink, J. T. (2001). Functional MR imaging of the cervical spinal cord by use of median nerve stimulation and fist clenching. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 22(10), 1854-9. [PMID]
Bodurka, J., Ledden, P., & Bandettini, P. (2008). SENSE optimized sixteen element receive array for cervical spinal cord imaging at 3T. Paper presented at the ISMRM 16th Scientific Meeting & Exhibition- SMRT 17th Annual Meeting, Toronto, Canada, 3-9 May 2008. https://cds.ismrm.org/ismrm-2008/files/01078.pdf
Bollmann, S., Kasper, L., Vannesjo, S. J., Diaconescu, A. O., Dietrich, B. E., & Gross, S., et al. (2017). Analysis and correction of field fluctuations in fMRI data using field monitoring. NeuroImage, 154, 92-105. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.01.014] [PMID]
Bosma, R. L., & Stroman, P. W. (2015). Spinal cord response to stepwise and block presentation of thermal stimuli: A functional MRI study. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 41(5), 1318-25. [DOI:10.1002/jmri.24656] [PMID]
Bosma, R. L., Mojarad, E. A., Leung, L., Pukall, C., Staud, R., & Stroman, P. W. (2016). FMRI of spinal and supra‐spinal correlates of temporal pain summation in fibromyalgia patients. Human Brain Mapping, 37(4), 1349-60. [DOI:10.1002/hbm.23106] [PMID] [PMCID]
Bosma, R., & Stroman, P. (2014). Assessment of data acquisition parameters, and analysis techniques for noise reduction in spinal cord fMRI data. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 32(5), 473-81. [DOI:10.1016/j.mri.2014.01.007] [PMID]
Bouwman, C. J. C., Wilmink, J. T., Mess, W. H., & Backes, W. H. (2008). Spinal cord functional MRI at 3 T: Gradient echo echo-planar imaging versus turbo spin echo. NeuroImage, 43(2), 288-96. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.07.024] [PMID]
Bowring, A., Maumet, C., & Nichols, T. T. (2018). Exploring the impact of analysis software on task fMRI results. bioRxiv. [DOI:10.1101/285585]
Brooks, J. C. W. (2014). Physiological noise modeling and analysis for spinal cord fMRI. In J. Cohen-Adad & C. A. M. Wheeler-Kingshott (Eds.), Quantitative MRI of the spinal cord (pp. 240-257). Cambridge, MA: Academic Press. [DOI:10.1016/B978-0-12-396973-6.00016-2]
Brooks, J. C., Beckmann, C. F., Miller, K. L., Wise, R. G., Porro, C. A., & Tracey, I., et al. (2008). Physiological noise modelling for spinal functional magnetic resonance imaging studies. NeuroImage, 39(2), 680-92. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.09.018] [PMID]
Caballero-Gaudes, C., & Reynolds, R. C. (2017). Methods for cleaning the BOLD fMRI signal. NeuroImage, 154, 128-49. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.12.018] [PMID] [PMCID]
Cadotte, D. W., Bosma, R., Mikulis, D., Nugaeva, N., Smith, K., & Pokrupa, R., et al. (2012). Plasticity of the injured human spinal cord: Insights revealed by spinal cord functional MRI. PLoS One, 7(9), e45560. [DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0045560] [PMID] [PMCID]
Chang, C., Metzger, C. D., Glover, G. H., Duyn, J. H., Heinze, H. J., & Walter, M. (2013). Association between heart rate variability and fluctuations in resting-state functional connectivity. Neuroimage, 68, 93-104. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1053811912011500
Chen, L. M., Mishra, A., Yang, P. F., Wang, F., & Gore, J. C. (2015). Injury alters intrinsic functional connectivity within the primate spinal cord. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(19), 5991-6. [DOI:10.1073/pnas.1424106112] [PMID] [PMCID]
Chen, Y., Kong, K. M., Wang, W. D., Xie, C. H., & Wu, R. H. (2007). Functional MR imaging of the spinal cord in cervical spinal cord injury patients by acupuncture at LI 4 (Hegu) and LI 11 (Quchi). Paper presented at 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 22-26 August 2007. [DOI:10.1109/IEMBS.2007.4353058] [PMID]
Choe, A. S. (2017). Advances in spinal functional magnetic resonance imaging in the healthy and injured spinal cords. Current Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Reports, 5(3), 143-50. [DOI:10.1007/s40141-017-0161-x] [PMID] [PMCID]
Cohen-Adad, J. (2017). Functional magnetic resonance imaging of the spinal cord: Current status and future developments. Seminars in Ultrasound, CT and MRI, 38(2), 176-86. [DOI:10.1053/j.sult.2016.07.007] [PMID]
Cohen-Adad, J., Lvy, S., & Avants, B. (2015). Slice-by-slice regularized registration for spinal cord MRI: SliceReg. Paper presented at 23rd Annual Meeting & Exhibition, 30 May-5 June 2015, SMRT 24th Annual Meeting, 30-31 May 2015, Toronto, Ontario, Canada. http://archive.ismrm.org/2015/4428.html
Cohen‐Adad, J., Mareyam, A., Keil, B., Polimeni, J. R., & Wald, L. L. (2011). 32‐channel RF coil optimized for brain and cervical spinal cord at 3 T. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 66(4), 1198-208. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.22906] [PMID] [PMCID]
Cohen-Adad, J., Rossignol, S., & Hoge, R. D. (2009). Slice-by-slice motion correction in spinal cord fMRI: SliceCorr. Paper presented at 17th Scientific Meeting & Exhibition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 18-24 April 2009. https://cds.ismrm.org/protected/09MProceedings/files/03181.pdf
Deckers, R. H., van Gelderen, P., Ries, M., Barret, O., Duyn, J. H., &Ikonomidou, V. N., et al. (2006). An adaptive filter for suppression of cardiac and respiratory noise in MRI time series data. Neuroimage, 33(4), 1072-1081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.08.006
Constable, R. T., Skudlarski, P., & Gore, J. C. (1995). An ROC approach for evaluating functional brain MR imaging and postprocessing protocols. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 34(1), 57-64. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.1910340110] [PMID]
De Leener, B., Lévy, S., Dupont, S. M., Fonov, V. S., Stikov, N., & Collins, D. L., et al. (2017). SCT: Spinal cord toolbox, an open-source software for processing spinal cord MRI data. NeuroImage, 145(Pt A), 24-43. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.10.009] [PMID]
De Tillieux, P., Topfer, R., Foias, A., Leroux, I., El Maâchi, I., & Leblond, H., et al. (2018). A pneumatic phantom for mimicking respiration‐induced artifacts in spinal MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 79(1), 600-5. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.26679] [PMID]
Durand, E., van de Moortele, P. F., Pachot‐Clouard, M., & Le Bihan, D. (2001). Artifact due to B0 fluctuations in fMRI: Correction using the k-space central line. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 46(1), 198-201. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.1177] [PMID]
Eippert, F., Kong, Y., Jenkinson, M., Tracey, I., & Brooks, J. C. (2017). Denoising spinal cord fMRI data: Approaches to acquisition and analysis. NeuroImage, 154, 255-66. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.09.065] [PMID]
Figley, C. R., & Stroman, P. W. (2009). Development and validation of retrospective spinal cord motion time-course estimates (RESPITE) for spin-echo spinal fMRI: Improved sensitivity and specificity by means of a motion-compensating general linear model analysis. NeuroImage, 44(2), 421-7. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.08.040] [PMID]
Figley, C., Yau, D., & Stroman, P. (2008). Attenuation of lower-thoracic, lumbar, and sacral spinal cord motion: Implications for imaging human spinal cord structure and function. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 29(8), 1450-4. [DOI:10.3174/ajnr.A1154] [PMID]
Finsterbusch, J., Eippert, F., & Büchel, C. (2012). Single, slice-specific z-shim gradient pulses improve T2*-weighted imaging of the spinal cord. NeuroImage, 59(3), 2307-15. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.09.038] [PMID]
Finsterbusch, J., Sprenger, C., & Büchel, C. (2013). Combined T2*-weighted measurements of the human brain and cervical spinal cord with a dynamic shim update. NeuroImage, 79, 153-61. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.021] [PMID]
Fratini, M., Moraschi, M., Maraviglia, B., & Giove, F. (2014). On the impact of physiological noise in spinal cord functional MRI. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 40(4), 770-7. [DOI:10.1002/jmri.24467] [PMID]
Fruehwald-Pallamar, J., Szomolanyi, P., Fakhrai, N., Lunzer, A., Weber, M., & Thurnher, M., et al. (2012). Parallel imaging of the cervical spine at 3T: Optimized trade-off between speed and image quality. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 33(10), 1867-74. [DOI:10.3174/ajnr.A3101] [PMID]
Glover, G. H. (2012). Spiral imaging in fMRI. NeuroImage, 62(2), 706-12. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.10.039] [PMID] [PMCID]
Glover, G. H., Li, T. Q., & Ress, D. (2000). Image‐based method for retrospective correction of physiological motion effects in fMRI: RETROICOR. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 44(1), 162-7. [DOI:10.1002/1522-2594(200007)44:1<162::aid-mrm23>3.0.co;2-e] [PMID]
Griffanti, L., Douaud, G., Bijsterbosch, J., Evangelisti, S., Alfaro-Almagro, F., & Glasser, M. F., et al. (2017). Hand classification of fMRI ICA noise components. NeuroImage, 154, 188-205. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.12.036] [PMID] [PMCID]
Griswold, M. A., Jakob, P. M., Heidemann, R. M., Nittka, M., Jellus, V., & Wang, J., et al. (2002). Generalized Autocalibrating Partially Parallel Acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 47(6), 1202-10. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.10171] [PMID]
Hu, Y., Jin, R., Li, G., Luk, K. D., & Wu, E. X. (2018). Robust spinal cord resting-state fMRI using independent component analysis-based nuisance regression noise reduction. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 48(5), 1421-31. [DOI:10.1002/jmri.26048] [PMID]
Jenkinson, M., Bannister, P., Brady, M., & Smith, S. (2002). Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. NeuroImage, 17(2), 825-41. [DOI:10.1006/nimg.2002.1132] [PMID]
Jenkinson, M., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E. J., Woolrich, M. W., & Smith, S. M. (2012). FSL. NeuroImage, 62(2), 782-90. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.09.015] [PMID]
Kay, K., Rokem, A., Winawer, J., Dougherty, R., & Wandell, B. (2013). GLMdenoise: a fast, automated technique for denoising task-based fMRI data. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 7, 247. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnins.2013.00247/full
Kashkouli Nejad, K., Sugiura, M., Thyreau, B., Nozawa, T., Kotozaki, Y., & Furusawa, Y., et al. (2014). Spinal fMRI of interoceptive attention/awareness in experts and novices. Neural Plasticity, 2014, 2014, 679509. [DOI:10.1155/2014/679509] [PMID] [PMCID]
Kearney, H., Miller, D. H., & Ciccarelli, O. (2015). Spinal cord MRI in multiple sclerosis-diagnostic, prognostic and clinical value. Nature Reviews Neurology, 11(6), 327-38. [DOI:10.1038/nrneurol.2015.80] [PMID]
Kelly Jr, R. E., Alexopoulos, G. S., Wang, Z., Gunning, F. M., Murphy, C. F., & Morimoto, S. S., et al. (2010). Visual inspection of independent components: Defining a procedure for artifact removal from fMRI data. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 189(2), 233-45. [DOI:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2010.03.028] [PMID] [PMCID]
Komisaruk, B. R., Mosier, K. M., Liu, W. C., Criminale, C., Zaborszky, L., & Whipple, B., et al. (2002). Functional localization of brainstem and cervical spinal cord nuclei in humans with fMRI. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 23(4), 609-17. [PMID]
Kong, Y., Eippert, F., Beckmann, C. F., Andersson, J., Finsterbusch, J., & Büchel, C., et al. (2014). Intrinsically organized resting state networks in the human spinal cord. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(50), 18067-72. [DOI:10.1073/pnas.1414293111] [PMID] [PMCID]
Kong, Y., Jenkinson, M., Andersson, J., Tracey, I., & Brooks, J. C. (2012). Assessment of physiological noise modelling methods for functional imaging of the spinal cord. NeuroImage, 60(2), 1538-49. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.11.077] [PMID]
Kornelsen, J., Smith, S. D., & McIver, T. A. (2014). A neural correlate of visceral emotional responses: evidence from fMRI of the thoracic spinal cord. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 10(4), 584-8. [DOI:10.1093/scan/nsu092] [PMID] [PMCID]
Kornelsen, J., Smith, S. D., McIver, T. A., Sboto‐Frankenstein, U., Latta, P., & Tomanek, B. (2013). Functional MRI of the thoracic spinal cord during vibration sensation. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 37(4), 981-5. [DOI:10.1002/jmri.23819] [PMID]
Kozyrev, N., Figley, C. R., Alexander, M. S., Richards, J. S., Bosma, R. L., & Stroman, P. W. (2012). Neural correlates of sexual arousal in the spinal cords of able-bodied men: A spinal fMRI investigation. Journal of Sex & Marital Therapy, 38(5), 418-35. [DOI:10.1080/0092623X.2011.606887] [PMID]
Leitch, J. K., Cahill, C. M., Ghazni, N. F., Figley, C. R., & Stroman, P. W. (2009). Spinal cord and brainstem activation in carpal tunnel syndrome patients in response to noxious stimuli: A spinal fMRI study. Paper presented at 17th Scientific Meeting & Exhibition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 18-24 April 2009. https://cds.ismrm.org/protected/09MProceedings/files/01314.pdf
Leitch, J. K., Figley, C. R., & Stroman, P. W. (2010). Applying functional MRI to the spinal cord and brainstem. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 28(8), 1225-33. [DOI:10.1016/j.mri.2010.03.032] [PMID]
Li, P., Yu, X., Griffin, J., Levine, J. M., & Ji, J. (2015). High-resolution MRI of spinal cords by compressive sensing parallel imaging. Paper presented at 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25-29 August 2015. [DOI:10.1109/EMBC.2015.7319337] [PMID]
Madi, S., Flanders, A. E., Vinitski, S., Herbison, G. J., & Nissanov, J. (2001). Functional MR imaging of the human cervical spinal cord. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 22(9), 1768-74. [PMID]
Maieron, M., Iannetti, G. D., Bodurka, J., Tracey, I., Bandettini, P. A., & Porro, C. A. (2007). Functional responses in the human spinal cord during willed motor actions: Evidence for side-and rate-dependent activity. Journal of Neuroscience, 27(15), 4182-90. [DOI:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3910-06.2007] [PMID] [PMCID]
Mainero, C., Zhang, W. T., Kumar, A., Rosen, B. R., & Sorensen, A. G. (2007). Mapping the spinal and supraspinal pathways of dynamic mechanical allodynia in the human trigeminal system using cardiac-gated fMRI. NeuroImage, 35(3), 1201-10. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.01.024] [PMID] [PMCID]
Moeller, S., Yacoub, E., Olman, C. A., Auerbach, E., Strupp, J., & Harel, N., et al. (2010). Multiband multislice GE‐EPI at 7 tesla, with 16‐fold acceleration using partial parallel imaging with application to high spatial and temporal whole‐brain fMRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 63(5), 1144-53. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.22361] [PMID] [PMCID]
Nash, P., Wiley, K., Brown, J., Shinaman, R., Ludlow, D., & Sawyer, A. M., et al. (2013). Functional magnetic resonance imaging identifies somatotopic organization of nociception in the human spinal cord. Pain, 154(6), 776-81. [DOI:10.1016/j.pain.2012.11.008] [PMID]
Ng, M. C., Wu, E. X., Lau, H. F., Hu, Y., Lam, E. Y., & Luk, K. D. (2008). Cervical spinal cord BOLD fMRI study: Modulation of functional activation by dexterity of dominant and non-dominant hands. NeuroImage, 39(2), 825-31. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.09.026] [PMID]
Parkes, L., Fulcher, B., Yücel, M., & Fornito, A. (2018). An evaluation of the efficacy, reliability, and sensitivity of motion correction strategies for resting-state functional MRI. Neuroimage, 171, 415-36. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.12.073] [PMID]
Parrish, T. B., Gitelman, D. R., LaBar, K. S., & Mesulam, M. M. (2000). Impact of signal‐to‐noise on functional MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 44(6), 925-32. [DOI:10.1002/1522-2594(200012)44:6<925::aid-mrm14>3.0.co;2-m] [PMID]
Piché, M., Cohen-Adad, J., Nejad, M. K., Perlbarg, V., Xie, G., & Beaudoin, G., et al. (2009). Characterization of cardiac-related noise in fMRI of the cervical spinal cord. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 27(3), 300-10. [DOI:10.1016/j.mri.2008.07.019] [PMID]
Poser, B. A., & Norris, D. G. (2007). Fast spin echo sequences for BOLD functional MRI. Magnetic Resonance Materials in Physics, Biology and Medicine, 20(1), 11. [DOI:10.1007/s10334-006-0063-x] [PMID] [PMCID]
Power, J. D., Mitra, A., Laumann, T. O., Snyder, A. Z., Schlaggar, B. L., & Petersen, S. E. (2014). Methods to detect, characterize, and remove motion artifact in resting state fMRI. NeuroImage, 84, 320-41. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.08.048] [PMID] [PMCID]
Raj, D., Anderson, A. W., & Gore, J. C. (2001). Respiratory effects in human functional magnetic resonance imaging due to bulk susceptibility changes. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 46(12), 3331-40. [DOI:10.1088/0031-9155/46/12/318] [PMID]
Rocca, M., Absinta, M., Valsasina, P., Copetti, M., Caputo, D., & Comi, G., et al. (2012). Abnormal cervical cord function contributes to fatigue in multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis Journal, 18(11), 1552-9. [DOI:10.1177/1352458512440516] [PMID]
Särkkä, S., Solin, A., Nummenmaa, A., Vehtari, A., Auranen, T., & Vanni, S., et al. (2012). Dynamic retrospective filtering of physiological noise in BOLD fMRI: DRIFTER. NeuroImage, 60(2), 1517-27. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3303954/
Skudlarski, P., Constable, R. T., & Gore, J. C. (1999). ROC analysis of statistical methods used in functional MRI: Individual subjects. NeuroImage, 9(3), 311-29. [DOI:10.1006/nimg.1999.0402] [PMID]
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Woolrich, M. W., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E., & Johansen-Berg, H., et al. (2004). Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. NeuroImage, 23(Suppl 1), S208-19. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.051] [PMID]
Sorenson, J. A., & Wang, X. (1996). ROC methods for evaluation of fMRI techniques. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 36(5), 737-44. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.1910360512] [PMID]
Stroman, P. (2006). Discrimination of errors from neuronal activity in functional MRI of the human spinal cord by means of general linear model analysis. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 56(2), 452-6. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.20966] [PMID]
Stroman, P. W., & Ryner, L. N. (2000). Investigating BOLD signal intensity changes in fMRI of the human spinal cord. Paper presented at 8th Scientific Meeting and Exhibition, Denver, Colorado, USA, 1-7 April 2000. https://cds.ismrm.org/ismrm-2000/PDF4/0941.pdf
Stroman, P. W., & Ryner, L. N. (2001). Functional MRI of motor and sensory activation in the human spinal cord. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 19(1), 27-32. [DOI:10.1016/S0730-725X(01)00226-0]
Stroman, P. W., Khan, H. S., Bosma, R. L., Cotoi, A. I., Leung, R., & Cadotte, D. W., et al. (2016). Changes in pain processing in the spinal cord and brainstem after spinal cord injury characterized by functional magnetic resonance imaging. Journal of Neurotrauma, 33(15), 1450-60. [DOI:10.1089/neu.2015.4257] [PMID]
Stroman, P. W., Kornelsen, J., Bergman, A., Krause, V., Ethans, K., & Malisza, K. L., et al. (2004). Noninvasive assessment of the injured human spinal cord by means of functional magnetic resonance imaging. Spinal Cord, 42(2), 59-66. [DOI:10.1038/sj.sc.3101559] [PMID]
Stroman, P. W., Wheeler-Kingshott, C., Bacon, M., Schwab, J., Bosma, R., & Brooks, J., et al. (2014). The current state-of-the-art of spinal cord imaging: Methods. NeuroImage, 84, 1070-81. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.124] [PMID] [PMCID]
Topfer, R., Foias, A., Stikov, N., & Cohen-Adad, J. (2017). Real-time shimming of the human spinal cord using a 24-channel shim array coil. Paper presented at ISMRM 25th Annual Meeting & Exhibition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 22-27 April 2017.
Topfer, R., Germain, G., Stockmann, J. P., Metzemaekers, K., Hetherington, H., & Paquin, R., et al. (2016). Very-high order shimming in the human spinal cord using a dedicated 24-channel array coil. Paper presented at ISMRM 24th Annual Meeting & Exhibition, Singapore, 7-13 May 2016. http://archive.ismrm.org/2016/3628.html
Topfer, R., Starewicz, P., Lo, K. M., Metzemaekers, K., Jette, D., & Hetherington, H. P., et al. (2016). A 24‐channel shim array for the human spinal cord: Design, evaluation, and application. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 76(5), 1604-11. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.26354] [PMID]
Vahdat, S., Lungu, O., Cohen-Adad, J., Marchand-Pauvert, V., Benali, H., & Doyon, J. (2015). Simultaneous brain-cervical cord fMRI reveals intrinsic spinal cord plasticity during motor sequence learning. PLoS Biology, 13(6), e1002186. [DOI:10.1371/journal.pbio.1002186] [PMID] [PMCID]
Valsasina, P., Agosta, F., Absinta, M., Sala, S., Caputo, D., & Filippi, M. (2010). Cervical cord functional MRI changes in relapse-onset MS patients. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(4), 405-8. [DOI:10.1136/jnnp.2009.187526] [PMID]
Valsasina, P., Rocca, M. A., Absinta, M., Agosta, F., Caputo, D., & Comi, G., et al. (2012). Cervical cord FMRI abnormalities differ between the progressive forms of multiple sclerosis. Human Brain Mapping, 33(9), 2072-80. [DOI:10.1002/hbm.21346] [PMID] [PMCID]
van Gelderen, P., de Zwart, J. A., Starewicz, P., Hinks, R. S., & Duyn, J. H. (2007). Real‐time shimming to compensate for respiration‐induced B0 fluctuations. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 57(2), 362-8. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.21136] [PMID]
Verma, T., & Cohen‐Adad, J. (2014). Effect of respiration on the B0 field in the human spinal cord at 3T. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 72(6), 1629-36. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.25075] [PMID]
Verstynen, T. D., & Deshpande, V. (2011). Using pulse oximetry to account for high and low frequency physiological artifacts in the BOLD signal. NeuroImage, 55(4), 1633-44. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1053811911000218
Wang, J., Wang, Z., Aguirre, G. K., & Detre, J. A. (2005). To smooth or not to smooth? ROC analysis of perfusion fMRI data. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 23(1), 75-81. [DOI:10.1016/j.mri.2004.11.009] [PMID]
Weber II, K. A., Chen, Y., Wang, X., Kahnt, T., & Parrish, T. B. (2016). Lateralization of cervical spinal cord activity during an isometric upper extremity motor task with functional magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage, 125, 233-43. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.10.014] [PMID] [PMCID]
Winklhofer, S., Schoth, F., Stolzmann, P., Krings, T., Mull, M., & Wiesmann, M., et al. (2014). Spinal cord motion: Influence of respiration and cardiac cycle. Rofo, 186(11), 1016-21. [DOI:10.1055/s-0034-1366429] [PMID]
Woolrich, M. W., Ripley, B. D., Brady, M., & Smith, S. M. (2001). Temporal autocorrelation in univariate linear modeling of FMRI data. NeuroImage, 14(6), 1370-86. [DOI:10.1006/nimg.2001.0931] [PMID]
Worsley, K. J., Liao, C., Aston, J., Petre, V., Duncan, G., & Morales, F., et al. (2002). A general statistical analysis for fMRI data. NeuroImage, 15(1), 1-15. [DOI:10.1006/nimg.2001.0933] [PMID]
Xie, C. H., Kong, K. M., Guan, J. T., Chen, Y. X., He, J. K., & Qi, W. L., et al. (2009). SSFSE sequence functional MRI of the human cervical spinal cord with complex finger tapping. European Journal of Radiology, 70(1), 1-6. [DOI:10.1016/j.ejrad.2008.01.003] [PMID]
Xie, G., Piché, M., Khoshnejad, M., Perlbarg, V., Chen, J. I., & Hoge, R. D., et al. (2012). Reduction of physiological noise with independent component analysis improves the detection of nociceptive responses with fMRI of the human spinal cord. NeuroImage, 63(1), 245-52. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.06.057] [PMID]
Ye, Y., Zhuo, Y., Xue, R., & Zhou, X. J. (2010). BOLD fMRI using a modified HASTE sequence. NeuroImage, 49(1), 457-66. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.07.044] [PMID] [PMCID]
Yeo, D. T., Fessler, J. A., & Kim, B. (2008). Concurrent correction of geometric distortion and motion using the map-slice-to-volume method in echo-planar imaging. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 26(5), 703-14. [DOI:10.1016/j.mri.2007.11.001] [PMID] [PMCID]
Yildiz, S., Thyagaraj, S., Jin, N., Zhong, X., Heidari Pahlavian, S., & Martin, B. A., et al. (2017). Quantifying the influence of respiration and cardiac pulsations on cerebrospinal fluid dynamics using real‐time phase‐contrast MRI. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 46(2), 431-9. [DOI:10.1002/jmri.25591] [PMID]
Yoshizawa, T., Nose, T., Moore, G. J., & Sillerud, L. O. (1996). Functional magnetic resonance imaging of motor activation in the human cervical spinal cord. NeuroImage, 4(3), 174-82. [DOI:10.1006/nimg.1996.0068] [PMID]
Zhang, B., Seifert, A. C., Kim, J. W., Borrello, J., & Xu, J. (2017). 7 Tesla 22‐channel wrap‐around coil array for cervical spinal cord and brainstem imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 78(4), 1623-34. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.26538] [PMID]
Zhong, X. P., Chen, Y. X., Li, Z. Y., Shen, Z. W., & Kong, K. M., et al. (2017). Cervical spinal functional magnetic resonance imaging of the spinal cord injured patient during electrical stimulation. European Spine Journal, 26(1), 71-7. [DOI:10.1007/s00586-016-4646-6] [PMID]
Zhong, Y., Zheng, G., Liu, Y., & Lu, G. (2014). Independent component analysis of instantaneous power-based fMRI. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2014, 2014, 579652. [DOI:10.1155/2014/579652] [PMID] [PMCID]
Afyouni, S., & Nichols, T. E. (2018). Insight and Inference for DVARS. NeuroImage, 172, 291-312. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.12.098]
Agosta, F., Valsasina, P., Absinta, M., Sala, S., Caputo, D., & Filippi, M. (2009). Primary progressive multiple sclerosis: Tactile-associated functional MR activity in the cervical spinal cord. Radiology, 253(1), 209-15. [DOI:10.1148/radiol.2532090187] [PMID]
Agosta, F., Valsasina, P., Caputo, D., Stroman, P. W., & Filippi, M. (2008). Tactile-associated recruitment of the cervical cord is altered in patients with multiple sclerosis. NeuroImage, 39(4), 1542-8. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.10.048] [PMID]
Agosta, F., Valsasina, P., Rocca, M., Caputo, D., Sala, S., & Judica, E., et al. (2008). Evidence for enhanced functional activity of cervical cord in relapsing multiple sclerosis. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 59(5), 1035-42. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.21595] [PMID]
Alexander, M. S., Kozyrev, N., Bosma, R. L., Figley, C. R., Richards, J. S., & Stroman, P. W. (2016). fMRI localization of spinal cord processing underlying female sexual arousal. Journal of Sex & Marital Therapy, 42(1), 36-47. [DOI:10.1080/0092623X.2015.1010674] [PMID]
Alexander, M., Kozyrev, N., Figley, C. R., & Richards, J. S. (2017). Altered spinal cord activity during sexual stimulation in women with SCI: A pilot fMRI study. Spinal Cord Series and Cases, 3, 16041. [DOI:10.1038/scsandc.2016.41] [PMID] [PMCID]
Backes, W. H., Mess, W. H., & Wilmink, J. T. (2001). Functional MR imaging of the cervical spinal cord by use of median nerve stimulation and fist clenching. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 22(10), 1854-9. [PMID]
Bodurka, J., Ledden, P., & Bandettini, P. (2008). SENSE optimized sixteen element receive array for cervical spinal cord imaging at 3T. Paper presented at the ISMRM 16th Scientific Meeting & Exhibition- SMRT 17th Annual Meeting, Toronto, Canada, 3-9 May 2008. https://cds.ismrm.org/ismrm-2008/files/01078.pdf
Bollmann, S., Kasper, L., Vannesjo, S. J., Diaconescu, A. O., Dietrich, B. E., & Gross, S., et al. (2017). Analysis and correction of field fluctuations in fMRI data using field monitoring. NeuroImage, 154, 92-105. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.01.014] [PMID]
Bosma, R. L., & Stroman, P. W. (2015). Spinal cord response to stepwise and block presentation of thermal stimuli: A functional MRI study. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 41(5), 1318-25. [DOI:10.1002/jmri.24656] [PMID]
Bosma, R. L., Mojarad, E. A., Leung, L., Pukall, C., Staud, R., & Stroman, P. W. (2016). FMRI of spinal and supra‐spinal correlates of temporal pain summation in fibromyalgia patients. Human Brain Mapping, 37(4), 1349-60. [DOI:10.1002/hbm.23106] [PMID] [PMCID]
Bosma, R., & Stroman, P. (2014). Assessment of data acquisition parameters, and analysis techniques for noise reduction in spinal cord fMRI data. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 32(5), 473-81. [DOI:10.1016/j.mri.2014.01.007] [PMID]
Bouwman, C. J. C., Wilmink, J. T., Mess, W. H., & Backes, W. H. (2008). Spinal cord functional MRI at 3 T: Gradient echo echo-planar imaging versus turbo spin echo. NeuroImage, 43(2), 288-96. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.07.024] [PMID]
Bowring, A., Maumet, C., & Nichols, T. T. (2018). Exploring the impact of analysis software on task fMRI results. bioRxiv. [DOI:10.1101/285585]
Brooks, J. C. W. (2014). Physiological noise modeling and analysis for spinal cord fMRI. In J. Cohen-Adad & C. A. M. Wheeler-Kingshott (Eds.), Quantitative MRI of the spinal cord (pp. 240-257). Cambridge, MA: Academic Press. [DOI:10.1016/B978-0-12-396973-6.00016-2]
Brooks, J. C., Beckmann, C. F., Miller, K. L., Wise, R. G., Porro, C. A., & Tracey, I., et al. (2008). Physiological noise modelling for spinal functional magnetic resonance imaging studies. NeuroImage, 39(2), 680-92. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.09.018] [PMID]
Caballero-Gaudes, C., & Reynolds, R. C. (2017). Methods for cleaning the BOLD fMRI signal. NeuroImage, 154, 128-49. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.12.018] [PMID] [PMCID]
Cadotte, D. W., Bosma, R., Mikulis, D., Nugaeva, N., Smith, K., & Pokrupa, R., et al. (2012). Plasticity of the injured human spinal cord: Insights revealed by spinal cord functional MRI. PLoS One, 7(9), e45560. [DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0045560] [PMID] [PMCID]
Chang, C., Metzger, C. D., Glover, G. H., Duyn, J. H., Heinze, H. J., & Walter, M. (2013). Association between heart rate variability and fluctuations in resting-state functional connectivity. Neuroimage, 68, 93-104. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1053811912011500
Chen, L. M., Mishra, A., Yang, P. F., Wang, F., & Gore, J. C. (2015). Injury alters intrinsic functional connectivity within the primate spinal cord. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(19), 5991-6. [DOI:10.1073/pnas.1424106112] [PMID] [PMCID]
Chen, Y., Kong, K. M., Wang, W. D., Xie, C. H., & Wu, R. H. (2007). Functional MR imaging of the spinal cord in cervical spinal cord injury patients by acupuncture at LI 4 (Hegu) and LI 11 (Quchi). Paper presented at 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 22-26 August 2007. [DOI:10.1109/IEMBS.2007.4353058] [PMID]
Choe, A. S. (2017). Advances in spinal functional magnetic resonance imaging in the healthy and injured spinal cords. Current Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Reports, 5(3), 143-50. [DOI:10.1007/s40141-017-0161-x] [PMID] [PMCID]
Cohen-Adad, J. (2017). Functional magnetic resonance imaging of the spinal cord: Current status and future developments. Seminars in Ultrasound, CT and MRI, 38(2), 176-86. [DOI:10.1053/j.sult.2016.07.007] [PMID]
Cohen-Adad, J., Lvy, S., & Avants, B. (2015). Slice-by-slice regularized registration for spinal cord MRI: SliceReg. Paper presented at 23rd Annual Meeting & Exhibition, 30 May-5 June 2015, SMRT 24th Annual Meeting, 30-31 May 2015, Toronto, Ontario, Canada. http://archive.ismrm.org/2015/4428.html
Cohen‐Adad, J., Mareyam, A., Keil, B., Polimeni, J. R., & Wald, L. L. (2011). 32‐channel RF coil optimized for brain and cervical spinal cord at 3 T. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 66(4), 1198-208. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.22906] [PMID] [PMCID]
Cohen-Adad, J., Rossignol, S., & Hoge, R. D. (2009). Slice-by-slice motion correction in spinal cord fMRI: SliceCorr. Paper presented at 17th Scientific Meeting & Exhibition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 18-24 April 2009. https://cds.ismrm.org/protected/09MProceedings/files/03181.pdf
Deckers, R. H., van Gelderen, P., Ries, M., Barret, O., Duyn, J. H., &Ikonomidou, V. N., et al. (2006). An adaptive filter for suppression of cardiac and respiratory noise in MRI time series data. Neuroimage, 33(4), 1072-1081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.08.006
Constable, R. T., Skudlarski, P., & Gore, J. C. (1995). An ROC approach for evaluating functional brain MR imaging and postprocessing protocols. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 34(1), 57-64. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.1910340110] [PMID]
De Leener, B., Lévy, S., Dupont, S. M., Fonov, V. S., Stikov, N., & Collins, D. L., et al. (2017). SCT: Spinal cord toolbox, an open-source software for processing spinal cord MRI data. NeuroImage, 145(Pt A), 24-43. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.10.009] [PMID]
De Tillieux, P., Topfer, R., Foias, A., Leroux, I., El Maâchi, I., & Leblond, H., et al. (2018). A pneumatic phantom for mimicking respiration‐induced artifacts in spinal MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 79(1), 600-5. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.26679] [PMID]
Durand, E., van de Moortele, P. F., Pachot‐Clouard, M., & Le Bihan, D. (2001). Artifact due to B0 fluctuations in fMRI: Correction using the k-space central line. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 46(1), 198-201. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.1177] [PMID]
Eippert, F., Kong, Y., Jenkinson, M., Tracey, I., & Brooks, J. C. (2017). Denoising spinal cord fMRI data: Approaches to acquisition and analysis. NeuroImage, 154, 255-66. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.09.065] [PMID]
Figley, C. R., & Stroman, P. W. (2009). Development and validation of retrospective spinal cord motion time-course estimates (RESPITE) for spin-echo spinal fMRI: Improved sensitivity and specificity by means of a motion-compensating general linear model analysis. NeuroImage, 44(2), 421-7. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.08.040] [PMID]
Figley, C., Yau, D., & Stroman, P. (2008). Attenuation of lower-thoracic, lumbar, and sacral spinal cord motion: Implications for imaging human spinal cord structure and function. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 29(8), 1450-4. [DOI:10.3174/ajnr.A1154] [PMID]
Finsterbusch, J., Eippert, F., & Büchel, C. (2012). Single, slice-specific z-shim gradient pulses improve T2*-weighted imaging of the spinal cord. NeuroImage, 59(3), 2307-15. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.09.038] [PMID]
Finsterbusch, J., Sprenger, C., & Büchel, C. (2013). Combined T2*-weighted measurements of the human brain and cervical spinal cord with a dynamic shim update. NeuroImage, 79, 153-61. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.021] [PMID]
Fratini, M., Moraschi, M., Maraviglia, B., & Giove, F. (2014). On the impact of physiological noise in spinal cord functional MRI. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 40(4), 770-7. [DOI:10.1002/jmri.24467] [PMID]
Fruehwald-Pallamar, J., Szomolanyi, P., Fakhrai, N., Lunzer, A., Weber, M., & Thurnher, M., et al. (2012). Parallel imaging of the cervical spine at 3T: Optimized trade-off between speed and image quality. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 33(10), 1867-74. [DOI:10.3174/ajnr.A3101] [PMID]
Glover, G. H. (2012). Spiral imaging in fMRI. NeuroImage, 62(2), 706-12. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.10.039] [PMID] [PMCID]
Glover, G. H., Li, T. Q., & Ress, D. (2000). Image‐based method for retrospective correction of physiological motion effects in fMRI: RETROICOR. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 44(1), 162-7. [DOI:10.1002/1522-2594(200007)44:1<162::aid-mrm23>3.0.co;2-e] [PMID]
Griffanti, L., Douaud, G., Bijsterbosch, J., Evangelisti, S., Alfaro-Almagro, F., & Glasser, M. F., et al. (2017). Hand classification of fMRI ICA noise components. NeuroImage, 154, 188-205. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.12.036] [PMID] [PMCID]
Griswold, M. A., Jakob, P. M., Heidemann, R. M., Nittka, M., Jellus, V., & Wang, J., et al. (2002). Generalized Autocalibrating Partially Parallel Acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 47(6), 1202-10. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.10171] [PMID]
Hu, Y., Jin, R., Li, G., Luk, K. D., & Wu, E. X. (2018). Robust spinal cord resting-state fMRI using independent component analysis-based nuisance regression noise reduction. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 48(5), 1421-31. [DOI:10.1002/jmri.26048] [PMID]
Jenkinson, M., Bannister, P., Brady, M., & Smith, S. (2002). Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. NeuroImage, 17(2), 825-41. [DOI:10.1006/nimg.2002.1132] [PMID]
Jenkinson, M., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E. J., Woolrich, M. W., & Smith, S. M. (2012). FSL. NeuroImage, 62(2), 782-90. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.09.015] [PMID]
Kay, K., Rokem, A., Winawer, J., Dougherty, R., & Wandell, B. (2013). GLMdenoise: a fast, automated technique for denoising task-based fMRI data. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 7, 247. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnins.2013.00247/full
Kashkouli Nejad, K., Sugiura, M., Thyreau, B., Nozawa, T., Kotozaki, Y., & Furusawa, Y., et al. (2014). Spinal fMRI of interoceptive attention/awareness in experts and novices. Neural Plasticity, 2014, 2014, 679509. [DOI:10.1155/2014/679509] [PMID] [PMCID]
Kearney, H., Miller, D. H., & Ciccarelli, O. (2015). Spinal cord MRI in multiple sclerosis-diagnostic, prognostic and clinical value. Nature Reviews Neurology, 11(6), 327-38. [DOI:10.1038/nrneurol.2015.80] [PMID]
Kelly Jr, R. E., Alexopoulos, G. S., Wang, Z., Gunning, F. M., Murphy, C. F., & Morimoto, S. S., et al. (2010). Visual inspection of independent components: Defining a procedure for artifact removal from fMRI data. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 189(2), 233-45. [DOI:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2010.03.028] [PMID] [PMCID]
Komisaruk, B. R., Mosier, K. M., Liu, W. C., Criminale, C., Zaborszky, L., & Whipple, B., et al. (2002). Functional localization of brainstem and cervical spinal cord nuclei in humans with fMRI. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 23(4), 609-17. [PMID]
Kong, Y., Eippert, F., Beckmann, C. F., Andersson, J., Finsterbusch, J., & Büchel, C., et al. (2014). Intrinsically organized resting state networks in the human spinal cord. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(50), 18067-72. [DOI:10.1073/pnas.1414293111] [PMID] [PMCID]
Kong, Y., Jenkinson, M., Andersson, J., Tracey, I., & Brooks, J. C. (2012). Assessment of physiological noise modelling methods for functional imaging of the spinal cord. NeuroImage, 60(2), 1538-49. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.11.077] [PMID]
Kornelsen, J., Smith, S. D., & McIver, T. A. (2014). A neural correlate of visceral emotional responses: evidence from fMRI of the thoracic spinal cord. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 10(4), 584-8. [DOI:10.1093/scan/nsu092] [PMID] [PMCID]
Kornelsen, J., Smith, S. D., McIver, T. A., Sboto‐Frankenstein, U., Latta, P., & Tomanek, B. (2013). Functional MRI of the thoracic spinal cord during vibration sensation. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 37(4), 981-5. [DOI:10.1002/jmri.23819] [PMID]
Kozyrev, N., Figley, C. R., Alexander, M. S., Richards, J. S., Bosma, R. L., & Stroman, P. W. (2012). Neural correlates of sexual arousal in the spinal cords of able-bodied men: A spinal fMRI investigation. Journal of Sex & Marital Therapy, 38(5), 418-35. [DOI:10.1080/0092623X.2011.606887] [PMID]
Leitch, J. K., Cahill, C. M., Ghazni, N. F., Figley, C. R., & Stroman, P. W. (2009). Spinal cord and brainstem activation in carpal tunnel syndrome patients in response to noxious stimuli: A spinal fMRI study. Paper presented at 17th Scientific Meeting & Exhibition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 18-24 April 2009. https://cds.ismrm.org/protected/09MProceedings/files/01314.pdf
Leitch, J. K., Figley, C. R., & Stroman, P. W. (2010). Applying functional MRI to the spinal cord and brainstem. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 28(8), 1225-33. [DOI:10.1016/j.mri.2010.03.032] [PMID]
Li, P., Yu, X., Griffin, J., Levine, J. M., & Ji, J. (2015). High-resolution MRI of spinal cords by compressive sensing parallel imaging. Paper presented at 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25-29 August 2015. [DOI:10.1109/EMBC.2015.7319337] [PMID]
Madi, S., Flanders, A. E., Vinitski, S., Herbison, G. J., & Nissanov, J. (2001). Functional MR imaging of the human cervical spinal cord. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 22(9), 1768-74. [PMID]
Maieron, M., Iannetti, G. D., Bodurka, J., Tracey, I., Bandettini, P. A., & Porro, C. A. (2007). Functional responses in the human spinal cord during willed motor actions: Evidence for side-and rate-dependent activity. Journal of Neuroscience, 27(15), 4182-90. [DOI:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3910-06.2007] [PMID] [PMCID]
Mainero, C., Zhang, W. T., Kumar, A., Rosen, B. R., & Sorensen, A. G. (2007). Mapping the spinal and supraspinal pathways of dynamic mechanical allodynia in the human trigeminal system using cardiac-gated fMRI. NeuroImage, 35(3), 1201-10. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.01.024] [PMID] [PMCID]
Moeller, S., Yacoub, E., Olman, C. A., Auerbach, E., Strupp, J., & Harel, N., et al. (2010). Multiband multislice GE‐EPI at 7 tesla, with 16‐fold acceleration using partial parallel imaging with application to high spatial and temporal whole‐brain fMRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 63(5), 1144-53. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.22361] [PMID] [PMCID]
Nash, P., Wiley, K., Brown, J., Shinaman, R., Ludlow, D., & Sawyer, A. M., et al. (2013). Functional magnetic resonance imaging identifies somatotopic organization of nociception in the human spinal cord. Pain, 154(6), 776-81. [DOI:10.1016/j.pain.2012.11.008] [PMID]
Ng, M. C., Wu, E. X., Lau, H. F., Hu, Y., Lam, E. Y., & Luk, K. D. (2008). Cervical spinal cord BOLD fMRI study: Modulation of functional activation by dexterity of dominant and non-dominant hands. NeuroImage, 39(2), 825-31. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.09.026] [PMID]
Parkes, L., Fulcher, B., Yücel, M., & Fornito, A. (2018). An evaluation of the efficacy, reliability, and sensitivity of motion correction strategies for resting-state functional MRI. Neuroimage, 171, 415-36. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.12.073] [PMID]
Parrish, T. B., Gitelman, D. R., LaBar, K. S., & Mesulam, M. M. (2000). Impact of signal‐to‐noise on functional MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 44(6), 925-32. [DOI:10.1002/1522-2594(200012)44:6<925::aid-mrm14>3.0.co;2-m] [PMID]
Piché, M., Cohen-Adad, J., Nejad, M. K., Perlbarg, V., Xie, G., & Beaudoin, G., et al. (2009). Characterization of cardiac-related noise in fMRI of the cervical spinal cord. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 27(3), 300-10. [DOI:10.1016/j.mri.2008.07.019] [PMID]
Poser, B. A., & Norris, D. G. (2007). Fast spin echo sequences for BOLD functional MRI. Magnetic Resonance Materials in Physics, Biology and Medicine, 20(1), 11. [DOI:10.1007/s10334-006-0063-x] [PMID] [PMCID]
Power, J. D., Mitra, A., Laumann, T. O., Snyder, A. Z., Schlaggar, B. L., & Petersen, S. E. (2014). Methods to detect, characterize, and remove motion artifact in resting state fMRI. NeuroImage, 84, 320-41. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.08.048] [PMID] [PMCID]
Raj, D., Anderson, A. W., & Gore, J. C. (2001). Respiratory effects in human functional magnetic resonance imaging due to bulk susceptibility changes. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 46(12), 3331-40. [DOI:10.1088/0031-9155/46/12/318] [PMID]
Rocca, M., Absinta, M., Valsasina, P., Copetti, M., Caputo, D., & Comi, G., et al. (2012). Abnormal cervical cord function contributes to fatigue in multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis Journal, 18(11), 1552-9. [DOI:10.1177/1352458512440516] [PMID]
Särkkä, S., Solin, A., Nummenmaa, A., Vehtari, A., Auranen, T., & Vanni, S., et al. (2012). Dynamic retrospective filtering of physiological noise in BOLD fMRI: DRIFTER. NeuroImage, 60(2), 1517-27. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3303954/
Skudlarski, P., Constable, R. T., & Gore, J. C. (1999). ROC analysis of statistical methods used in functional MRI: Individual subjects. NeuroImage, 9(3), 311-29. [DOI:10.1006/nimg.1999.0402] [PMID]
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Woolrich, M. W., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E., & Johansen-Berg, H., et al. (2004). Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. NeuroImage, 23(Suppl 1), S208-19. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.051] [PMID]
Sorenson, J. A., & Wang, X. (1996). ROC methods for evaluation of fMRI techniques. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 36(5), 737-44. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.1910360512] [PMID]
Stroman, P. (2006). Discrimination of errors from neuronal activity in functional MRI of the human spinal cord by means of general linear model analysis. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 56(2), 452-6. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.20966] [PMID]
Stroman, P. W., & Ryner, L. N. (2000). Investigating BOLD signal intensity changes in fMRI of the human spinal cord. Paper presented at 8th Scientific Meeting and Exhibition, Denver, Colorado, USA, 1-7 April 2000. https://cds.ismrm.org/ismrm-2000/PDF4/0941.pdf
Stroman, P. W., & Ryner, L. N. (2001). Functional MRI of motor and sensory activation in the human spinal cord. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 19(1), 27-32. [DOI:10.1016/S0730-725X(01)00226-0]
Stroman, P. W., Khan, H. S., Bosma, R. L., Cotoi, A. I., Leung, R., & Cadotte, D. W., et al. (2016). Changes in pain processing in the spinal cord and brainstem after spinal cord injury characterized by functional magnetic resonance imaging. Journal of Neurotrauma, 33(15), 1450-60. [DOI:10.1089/neu.2015.4257] [PMID]
Stroman, P. W., Kornelsen, J., Bergman, A., Krause, V., Ethans, K., & Malisza, K. L., et al. (2004). Noninvasive assessment of the injured human spinal cord by means of functional magnetic resonance imaging. Spinal Cord, 42(2), 59-66. [DOI:10.1038/sj.sc.3101559] [PMID]
Stroman, P. W., Wheeler-Kingshott, C., Bacon, M., Schwab, J., Bosma, R., & Brooks, J., et al. (2014). The current state-of-the-art of spinal cord imaging: Methods. NeuroImage, 84, 1070-81. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.124] [PMID] [PMCID]
Topfer, R., Foias, A., Stikov, N., & Cohen-Adad, J. (2017). Real-time shimming of the human spinal cord using a 24-channel shim array coil. Paper presented at ISMRM 25th Annual Meeting & Exhibition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 22-27 April 2017.
Topfer, R., Germain, G., Stockmann, J. P., Metzemaekers, K., Hetherington, H., & Paquin, R., et al. (2016). Very-high order shimming in the human spinal cord using a dedicated 24-channel array coil. Paper presented at ISMRM 24th Annual Meeting & Exhibition, Singapore, 7-13 May 2016. http://archive.ismrm.org/2016/3628.html
Topfer, R., Starewicz, P., Lo, K. M., Metzemaekers, K., Jette, D., & Hetherington, H. P., et al. (2016). A 24‐channel shim array for the human spinal cord: Design, evaluation, and application. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 76(5), 1604-11. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.26354] [PMID]
Vahdat, S., Lungu, O., Cohen-Adad, J., Marchand-Pauvert, V., Benali, H., & Doyon, J. (2015). Simultaneous brain-cervical cord fMRI reveals intrinsic spinal cord plasticity during motor sequence learning. PLoS Biology, 13(6), e1002186. [DOI:10.1371/journal.pbio.1002186] [PMID] [PMCID]
Valsasina, P., Agosta, F., Absinta, M., Sala, S., Caputo, D., & Filippi, M. (2010). Cervical cord functional MRI changes in relapse-onset MS patients. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(4), 405-8. [DOI:10.1136/jnnp.2009.187526] [PMID]
Valsasina, P., Rocca, M. A., Absinta, M., Agosta, F., Caputo, D., & Comi, G., et al. (2012). Cervical cord FMRI abnormalities differ between the progressive forms of multiple sclerosis. Human Brain Mapping, 33(9), 2072-80. [DOI:10.1002/hbm.21346] [PMID] [PMCID]
van Gelderen, P., de Zwart, J. A., Starewicz, P., Hinks, R. S., & Duyn, J. H. (2007). Real‐time shimming to compensate for respiration‐induced B0 fluctuations. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 57(2), 362-8. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.21136] [PMID]
Verma, T., & Cohen‐Adad, J. (2014). Effect of respiration on the B0 field in the human spinal cord at 3T. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 72(6), 1629-36. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.25075] [PMID]
Verstynen, T. D., & Deshpande, V. (2011). Using pulse oximetry to account for high and low frequency physiological artifacts in the BOLD signal. NeuroImage, 55(4), 1633-44. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1053811911000218
Wang, J., Wang, Z., Aguirre, G. K., & Detre, J. A. (2005). To smooth or not to smooth? ROC analysis of perfusion fMRI data. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 23(1), 75-81. [DOI:10.1016/j.mri.2004.11.009] [PMID]
Weber II, K. A., Chen, Y., Wang, X., Kahnt, T., & Parrish, T. B. (2016). Lateralization of cervical spinal cord activity during an isometric upper extremity motor task with functional magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage, 125, 233-43. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.10.014] [PMID] [PMCID]
Winklhofer, S., Schoth, F., Stolzmann, P., Krings, T., Mull, M., & Wiesmann, M., et al. (2014). Spinal cord motion: Influence of respiration and cardiac cycle. Rofo, 186(11), 1016-21. [DOI:10.1055/s-0034-1366429] [PMID]
Woolrich, M. W., Ripley, B. D., Brady, M., & Smith, S. M. (2001). Temporal autocorrelation in univariate linear modeling of FMRI data. NeuroImage, 14(6), 1370-86. [DOI:10.1006/nimg.2001.0931] [PMID]
Worsley, K. J., Liao, C., Aston, J., Petre, V., Duncan, G., & Morales, F., et al. (2002). A general statistical analysis for fMRI data. NeuroImage, 15(1), 1-15. [DOI:10.1006/nimg.2001.0933] [PMID]
Xie, C. H., Kong, K. M., Guan, J. T., Chen, Y. X., He, J. K., & Qi, W. L., et al. (2009). SSFSE sequence functional MRI of the human cervical spinal cord with complex finger tapping. European Journal of Radiology, 70(1), 1-6. [DOI:10.1016/j.ejrad.2008.01.003] [PMID]
Xie, G., Piché, M., Khoshnejad, M., Perlbarg, V., Chen, J. I., & Hoge, R. D., et al. (2012). Reduction of physiological noise with independent component analysis improves the detection of nociceptive responses with fMRI of the human spinal cord. NeuroImage, 63(1), 245-52. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.06.057] [PMID]
Ye, Y., Zhuo, Y., Xue, R., & Zhou, X. J. (2010). BOLD fMRI using a modified HASTE sequence. NeuroImage, 49(1), 457-66. [DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.07.044] [PMID] [PMCID]
Yeo, D. T., Fessler, J. A., & Kim, B. (2008). Concurrent correction of geometric distortion and motion using the map-slice-to-volume method in echo-planar imaging. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 26(5), 703-14. [DOI:10.1016/j.mri.2007.11.001] [PMID] [PMCID]
Yildiz, S., Thyagaraj, S., Jin, N., Zhong, X., Heidari Pahlavian, S., & Martin, B. A., et al. (2017). Quantifying the influence of respiration and cardiac pulsations on cerebrospinal fluid dynamics using real‐time phase‐contrast MRI. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 46(2), 431-9. [DOI:10.1002/jmri.25591] [PMID]
Yoshizawa, T., Nose, T., Moore, G. J., & Sillerud, L. O. (1996). Functional magnetic resonance imaging of motor activation in the human cervical spinal cord. NeuroImage, 4(3), 174-82. [DOI:10.1006/nimg.1996.0068] [PMID]
Zhang, B., Seifert, A. C., Kim, J. W., Borrello, J., & Xu, J. (2017). 7 Tesla 22‐channel wrap‐around coil array for cervical spinal cord and brainstem imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 78(4), 1623-34. [DOI:10.1002/mrm.26538] [PMID]
Zhong, X. P., Chen, Y. X., Li, Z. Y., Shen, Z. W., & Kong, K. M., et al. (2017). Cervical spinal functional magnetic resonance imaging of the spinal cord injured patient during electrical stimulation. European Spine Journal, 26(1), 71-7. [DOI:10.1007/s00586-016-4646-6] [PMID]
Zhong, Y., Zheng, G., Liu, Y., & Lu, G. (2014). Independent component analysis of instantaneous power-based fMRI. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2014, 2014, 579652. [DOI:10.1155/2014/579652] [PMID] [PMCID]
Type of Study: Original |
Subject:
Behavioral Neuroscience
Received: 2018/06/11 | Accepted: 2019/02/19 | Published: 2020/11/1
Received: 2018/06/11 | Accepted: 2019/02/19 | Published: 2020/11/1
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |